Acacia microsperma
Acacia microsperma, commonly known as bowyakka, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of eastern Australia].[1] It is rated as least concern according to the Nature Conservation Act 1992.[2]
| Bowyakka | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Clade: | Mimosoideae |
| Genus: | Acacia |
| Species: | A. microsperma |
| Binomial name | |
| Acacia microsperma | |
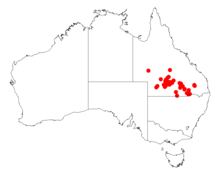 | |
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
Description
The tree can grow to a height of about 10 m (33 ft) and has sub-glabrous to moderately hair branchlets that appear quite scaly and leprous. Like most species of Acacia it has phyllodes rather than true leaves. The green to grey-green, slightly hairy and evergreen phyllodes have a linear shape and are quite straight with a length of 7 to 14 cm (2.8 to 5.5 in) and a width of 1.5 to 4 mm (0.059 to 0.157 in) and have multiple obscure, closely parallel nerves.[1] When it blooms it produces inflorescences that appear in groups of one to four with spherical flower-heads that have a diameter of 4 to 5 mm (0.16 to 0.20 in) and contain 20 to 40 golden coloured flowers. Following flowering firmly chartaceous seed pods form that resemble a string of beads. The pods are straight with a length of up to 6 cm (2.4 in) and a width of 2 to 3 mm (0.079 to 0.118 in) and are sparsely haired. The brown seeds inside have a narrowly elliptic shape with a length of 2.5 to 4 mm (0.098 to 0.157 in) and have a fleshy aril that is repeatedly folded.[1]
Taxonomy
The species was first formally described by the botanist Leslie Pedley in 1974 as a part of the work Contributions from the Queensland Herbarium. Pedley reclassified it as Racosperma microspermum in 1987 but it was transferred back to genus Acacia in 2001.[3]
Distribution
The tree has a scattered distribution across southern Queensland with a range that extends from around Adavale in the north west down to around the New South Wales border around Talwood where it is found growing in clay to shallow loamy soils over weathered rock as a part of open woodland along with Acacia cambagei or Eucalyptus thozetiana or sometimes forming dense stands of its own.[1]
See also
References
- "Acacia microsperma". World Wide Wattle. Western Australian Herbarium. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- "Species profile — Acacia microsperma (bowyakka)". Queensland Government. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- "Acacia microsperma Pedley". Atlas of Living Australia. Global Biodiversity Information Facility. Retrieved 17 December 2020.