Abductin
Abductin is a natural elastic protein that is found in the hinge ligament of bivalve mollusks. It is unique as it is the only protein in nature with compressible elasticity. It is similar to elastin and resilin, but amino acid analysis reveals that it has high concentrations of glycine and methionine.
| Abductin | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Organism | |||||||
| Symbol | N/A | ||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | AF026848 | ||||||
| RefSeq (Prot) | AAB94680 | ||||||
| UniProt | O44354 | ||||||
| |||||||
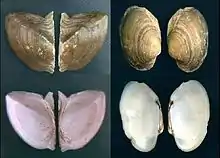
Abductin is found in the hinge ligament of bivalves such as Argopecten irradians and Placopecten magellanicus[1]
Abductin is made up of three prominent amino acids, glycine, methionine, and phenylalanine, which are arranged in a repeating pentapeptide sequence throughout the molecule.[2][1]
It has been proposed that the protein could have uses in drug delivery or tissue engineering.[3]
References
- Ehrlich H (2010). "Chapter 19: Abductin". Biological Materials Of Marine Origin, Biologically-Inspired Systems. 1. pp. 319–322.
- Kelly RE, Rice RV (January 1967). "Abductin: a rubber-like protein from the internal triangular hinge ligament of pecten". Science. 155 (3759): 208–10. PMID 6015528.
- Su RS, Renner JN, Liu JC (December 2013). "Synthesis and characterization of recombinant abductin-based proteins". Biomacromolecules. 14 (12): 4301–8. doi:10.1021/bm401162g. PMID 24147646.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.