A8 (classification)
A8 is an amputee sport classification used by the International Sports Organization for the Disabled (ISOD).for people with acquired or congenital amputations. People in this class have one arm amputated below the elbow, but through or above the wrist joint. Their amputations impact their sport performance, including being more prone to overuse injuries. Sports people in this class are eligible to participate in include athletics, swimming, cycling, amputee basketball, amputee football, lawn bowls, and sitzball.
Definition
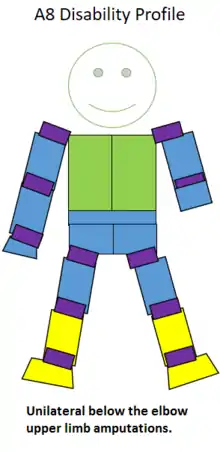
This class is for people who have one arm amputated below the elbow, but through or above the wrist joint.[1] This classification is sometimes abbreviated as B/E.[2] In competing in some sports, this class may have a different name:
| Class | Abbr | Athletics | Cycling | Skiing | Swimming | Comparable classifications in other sports | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A8 | B/E | T46, F46 | LC1 | LW 6/8.2 | S8, S9 | Amputee basketball: Open.
Amputee football: Goalkeeper. Badminton: STU5. Lawn bowls: LB3. Sitzball: Open. Ten-pin bowling: TPB10. |
[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8] |
Performance
The nature of a person's amputations in this class can effect their physiology and sports performance. Because they are missing a limb, amputees are more prone to overuse injuries in their remaining limbs. Common problems for intact upper limbs for people in this class include rotator cuffs tearing, shoulder impingement, epicondylitis and peripheral nerve entrapment.[9]
Governance
This classification was set up by ISOD, with the current version adopted in 1992 and then modified in 1993.[1][10] IWAS was created following the merger of ISOD and International Stoke Mandeville Games Federation (ISMGF) in 2005. Subsequently, IWAS became the classification governing body for some amputee sports.[2][11]
Sports
Athletics
.jpg.webp)
For athletics competitions that use the IPC athletics classification system, this class competes in T46, F46 and T47.[1][4][12] The extent of their below elbow amputation needs to be greater than a below wrist amputation or they are not eligible to compete in this class.[13] The missing arm weight changes their running form by creating differences in rotation between hip and shoulder.[12]
A study of was done comparing the performance of athletics competitors at the 1984 Summer Paralympics. It found there was no significant difference in performance in times between women in A6, A7 and A8 in the discus, women in A6, A7 and A8 in the shot put, women in the A6, A7 and A8 in the long jump, women in A6, A7 and A8 in the 100 meter race, women in A5, A6, A7 and A8 in the 100 meter race, men in the A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8 and A9 in the discus, men in A6, A7 and A8 in the discus, men in A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8 and A9 in the javelin, men in A6, A7 and A8 in the javelin, men in A8 and A9 in the shot put, men in A6, A7 and A8 in the high jump, men in A6, A7 and A8 in the long jump, men in A6, A7 and A8 in the 100 meter race, men in A7 and A8 in the 400 meter race, and men in A7 and A8 in the 1,500 meter race.[14]
In general, track athletes with amputations in this class should be considerate of the surface they are running on, and avoid asphalt and cinder tracks.[1]
Basketball
There is a basketball variant called amputee basketball. It uses the ISOD classification system as to whom is eligible to participate, but it is open in terms of all eligible classes, including this one, can play. There is no point system for who is allowed on the floor at any given time like there is in wheelchair basketball.[15]
Cycling
People in this class tend to be classified in cycling events as LC1. The class is for cyclists with upper limb disabilities including amputations.[5] Classification is handled by Union Cycliste Internationale.[16]
Football
One of the sports available to people in this class is amputee football. There are two variants of the game, one with 4 players a side and one with 7 players a side. In both variants, A2 and A4 players must be field players while A6 and A8 players must be goalkeepers. In the 4 person variant, there are two halves of 15 minutes each. In the 7 person variant, there are two halves of 25 minutes each.[5]
Swimming
People with amputations are eligible to compete in swimming at the Paralympic Games.[17][18] A8 swimmers may be found in several classes. These include S8, and S9.[3] People with below the wrist amputations may be eligible to compete in swimming.[13] Prior to the 1990s, this class was often grouped with other amputee classes in swimming competitions, including the Paralympic Games.[14]
S8 and S9 swimmers in this class have similar start times to people with legs amputations in S8 to S10 classes.[19] Paralympic S9 swimmers in this class can get water entry distance off the block comparable to Olympic athletes. S8 swimmers in this class have much shorter points of entry into the water off the block.[19] Compared to able bodied swimmers, swimmers in this class have a shorter stroke length and increased stroke rate.[19] Because their legs are their greatest strength, they modify their entry into the water to take advantage of this.[19]
Other sports
There are a number of sports to people in this class, including lawn bowls. A8 lawn bowlers can be classified as LB3.[20] They can also play badminton, where they are classified as STU5. The class is for standing players with minimal arm impairment.[20] Another sport open to people in this class is sitzball, the precursor to sitting volleyball. It is open to A1 to A9 classified players along with anyone who might be classified as "les autres" or who have lesser amputations that would not qualify them for ISOD classification. It is not open to people with spinal cord injuries. Play is open, with no requirements as to which types of disabilities are on the court at any time.[20] Ten pin bowling is also open to people in this class, where they compete in the TPB10 class.[21] Rowing is another sport open to people with amputations. In 1991, the first internationally accepted adaptive rowing classification system was established and put into use. People from this class were initially classified as A2 for people with double amputations.[22]
Becoming classified
Classification is often based on the anatomical nature of the amputation.[2][23] The classification system takes several things into account when putting people into this class. These includes which limbs are effected, how many limbs are effected, and how much of a limb is missing.[10][24]
For this class, classification generally has four phase. The first stage of classification is a health examination. For amputees, this is often done on site at a sports training facility or competition. The second stage is observation in practice, the third stage is observation in competition and the last stage is assigning the sportsperson to a relevant class.[13] Sometimes the health examination may not be done on site because the nature of the amputation could cause not physically visible alterations to the body.[25]
Classification can be sport specific. For athletics, the training portion of the observation may include being asked to demonstrate their skills in athletics, such as running, jumping or throwing.[26]
References
- "Classification 101". Blaze Sports. Blaze Sports. June 2012. Archived from the original on August 16, 2016. Retrieved July 24, 2016.
- Pasquina, Paul F.; Cooper, Rory A. (2009-01-01). Care of the Combat Amputee. Government Printing Office. ISBN 9780160840777.
- Tim-Taek, Oh; Osborough, Conor; Burkett, Brendan; Payton, Carl (2015). "Consideration of Passive Drag in IPC Swimming Classification System" (PDF). VISTA Conference. International Paralympic Committee. Retrieved July 24, 2016.
- "CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM FOR STUDENTS WITH A DISABILITY". Queensland Sport. Queensland Sport. Archived from the original on April 4, 2015. Retrieved July 23, 2016.
- Bressan, ES (2008). "Striving for fairness in Paralympic sport-Support from applied sport science". Continuing Medical Education.
- Consejo Superior de Deportes (2011). Deportistas sin Adjectivos (PDF) (in Spanish). Spain: Consejo Superior de Deportes. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-11-04. Retrieved 2016-07-25.
- KOCCA (2011). "장애인e스포츠 활성화를 위한 스포츠 등급분류 연구" [Activate e-sports for people with disabilities: Sports Classification Study] (PDF). KOCCA (in Korean). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-08-17.
- Alpine Skiing Technical Manual. Salt Lake City, Utah: Salt Lake Organizing Committee. 2002. p. 23. Archived from the original on 2016-03-08. Retrieved 2016-07-26. This is included as an appendix in the media guide, but it is not published by the APC.
- Miller, Mark D.; Thompson, Stephen R. (2014-04-04). DeLee & Drez's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 9781455742219.
- Tweedy, Sean M. (2002). "Taxonomic Theory and the ICF: Foundations for a Unified Disability Athletics Classification" (PDF). Adapted Physical Activity Quarterly. 19 (2): 220–237. doi:10.1123/apaq.19.2.220. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-08-17. Retrieved July 25, 2016.
- DePauw, Karen P. and Gavron, Susan J. (2005) Disability Sport. Human Kinetics Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7360-4638-1 (Google Books)
- Subic, A.; Fuss, F. K.; Alam, F.; Pang, T. Y.; Takla, M.; Mally, Franziska; Litzenberger, Stefan; Sabo, Anton (2015-01-01). "'The Impact of Technology on Sport VI' 7th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, APCST2015Kinematics of Elite Unilateral Below-elbow Amputee Treadmill-running - A Case Study". Procedia Engineering. 112: 449–454. doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2015.07.223.
- Tweedy, Sean M.; Beckman, Emma M.; Connick, Mark J. (August 2014). "Paralympic Classification: Conceptual Basis, Current Methods, and Research Update". Paralympic Sports Medicine and Science. 6 (85). Retrieved July 25, 2016.
- van Eijsden-Besseling, M. D. F. (1985). "The (Non)sense of the Present-Day Classification System of Sports for the Disabled, Regarding Paralysed and Amputee Athletes". Paraplegia. International Medical Society of Paraplegia. 23. Retrieved July 25, 2016.
- Consejo Superior de Deportes (2011). Deportistas sin Adjectivos (PDF) (in Spanish). Spain: Consejo Superior de Deportes. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-11-04. Retrieved 2016-07-25.
- "Guide to the Paralympic Games – Appendix 1" (PDF). London Organising Committee of the Olympic and Paralympic Games. 2011. p. 42. Retrieved 9 April 2012.
- Broad, Elizabeth (2014-02-06). Sports Nutrition for Paralympic Athletes. CRC Press. ISBN 9781466507562.
- "Get Into Sports" (PDF). Paralympics GB. Paralympics GB. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 17, 2016. Retrieved July 24, 2016.
- Vanlandewijck, Yves C.; Thompson, Walter R. (2011-07-13). Handbook of Sports Medicine and Science, The Paralympic Athlete. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781444348286.
- Consejo Superior de Deportes (2011). Deportistas sin Adjectivos (PDF) (in Spanish). Spain: Consejo Superior de Deportes. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-11-04. Retrieved 2016-07-25.
- KOCCA (2011). "장애인e스포츠 활성화를 위한 스포츠 등급분류 연구" [Activate e-sports for people with disabilities: Sports Classification Study] (PDF). KOCCA (in Korean). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-08-17.
- Stichting Roeivalidatie (1991). International Symposium Adaptive Rowing Amsterdam June, 26-27 1991. Rotterdam, Netherlands: Stichting Roeivalidatie. p. 21. OCLC 221080358.
- DeLisa, Joel A.; Gans, Bruce M.; Walsh, Nicholas E. (2005-01-01). Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation: Principles and Practice. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 9780781741309.
- International Sports Organization for the Disabled. (1993). Handbook. Newmarket, ON: Author. Available Federacion Espanola de Deportes de Minusvalidos Fisicos, c/- Ferraz, 16 Bajo, 28008 Madrid, Spain.
- Gilbert, Keith; Schantz, Otto J.; Schantz, Otto (2008-01-01). The Paralympic Games: Empowerment Or Side Show?. Meyer & Meyer Verlag. ISBN 9781841262659.
- "CLASSIFICATION Information for Athletes" (PDF). Sydney Australia: Australian Paralympic Committee. 2 July 2010. Retrieved 19 November 2011.
.svg.png.webp)