A2 autostrada (Poland)
The autostrada A2 in Poland, officially named Autostrada Wolności (Motorway of Freedom),[1] is a motorway which runs from the Polish-German border in Świecko/Frankfurt an der Oder (connecting to A12 autobahn), through Poznań and Łódź to Warsaw and, in the future, to the Polish-Belarusian border in Terespol/Brest (connecting to M1 highway).[2] The motorway is a part of the European route E30 connecting Berlin and Moscow.
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autostrada Wolności | ||||
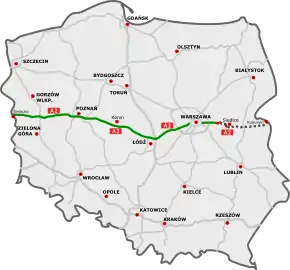 A2
Existing sections
Under construction
Planned sections | ||||
| Route information | ||||
| Part of | ||||
| Maintained by GDDKiA (Konin - Kukuryki) Autostrada Wielkopolska (Świecko – Konin) | ||||
| Length | 475.0 km (295.2 mi) 610 km (379 mi) planned | |||
| Major junctions | ||||
| From | ||||
| ||||
| To | ||||
| Location | ||||
| Major cities | Poznań, Łódź, Warszawa (Warsaw – Capital city & biggest city in Poland) | |||
| Highway system | ||||
National roads in Poland
| ||||
_Tarnawa_toll_plaza%252C_dir._%C5%9Awiecko.jpg.webp)

_3_km_east_of_Pozna%C5%84_Komorniki_interchange.jpg.webp)


_Go%C5%82uski_toll_plaza%252C_Ticket_machine.jpg.webp)
_Tarnawa_toll_plaza%252C_price_list.jpg.webp)
The motorway between German border and Warsaw (452 km (281 mi)) was constructed between 2001 and 2012, with the exception of a 48 km (30 mi) fragment built between 1977 and 1988, and is now complete. Most of the stretch from the border to Łódź is tolled, with fees being collected in toll booths across the motorway.
A2 does not formally run through Warsaw itself, instead turning into S2 Expressway (partially completed). Eastwards from Warsaw, A2 is being gradually extended. The first 21 km (13 mi) segment of this section is the bypass of Mińsk Mazowiecki, which opened in August 2012. The second, a 14.6 km (9.1 mi) segment between Mińsk Mazowiecki and Warsaw, will be completed in 2020. The longest section from Mińsk Mazowiecki to Biała Podlaska (101 km (63 mi)) is planned to be completed by 2024. The last segment to the Belarusian border (32 km (20 mi)) might be completed by 2025,[3] but the precise schedule will depend on government funding decisions.
Route
| Motorway section | Length | Construction dates | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Świecko – Nowy Tomyśl | 105.9 km (65.8 mi) | 2009–2011 | opened 1 December 2011; toll motorway |
| Nowy Tomyśl – Poznań Komorniki | 50.4 km (31.3 mi) | 2001–2004 | opened 27 October 2004; toll motorway on Nowy Tomyśl – Poznań Zachód stretch |
| Poznań Komorniki – Poznań Krzesiny | 13.3 km (8.3 mi) | 2001–2003 | opened 13 September 2003; widened to 2x3 lanes in 2019 |
| Poznań Krzesiny – Września | 37.5 km (23.3 mi) | 2001–2003 | opened 27 November 2003; toll motorway on Poznań Wschód – Września stretch |
| Września – Golina | 34.2 km (21.3 mi) | 1977–1985 | opened 9 October 1985; toll motorway since 20 December 2002 |
| Golina – Modła | 13.8 km (8.6 mi) | 1986–1988 | opened 10 November 1988 |
| Modła – Stryków | 103 km (64 mi) | 2004–2006 | opened 26 July 2006; toll motorway on Konin Wschód – Stryków stretch since 1 July 2011 |
| Stryków – Łódź Północ | 1.7 km (1.1 mi) | 2008 | opened 22 December 2008 |
| Łódź Północ – Grodzisk Mazowiecki | 73.4 km (45.6 mi) | 2010–2012 | opened to traffic June 2012, fully completed in fall of 2012;[4][5] planned widening to 2x3 lanes |
| Grodzisk Mazowiecki – Konotopa | 17.4 km (10.8 mi) | 2010–2012 | opened in May 2012;[6][7] planned widening to 2x3 lanes |
| S2 in Warsaw (Konotopa – Lubelska) | |||
| Lubelska – Choszczówka Stojecka | 14.6 km (9.1 mi) | 2018 – 2020 | Contracts signed in July, 2017. Partially opened on 14. August 2020,[8] Lubelska interchange to be opened completely in 2021. |
| Choszczówka Stojecka – Kałuszyn | 20.8 km (12.9 mi) | 2009–2012 | opened 29 August 2012 (Mińsk Mazowiecki bypass) |
| Kałuszyn – Siedlce | 37 km (23 mi) | 2021–2023 | Contracts for sections Kałuszyn - Groszki and Gręzów - Siedlce signed respectively on 5. March[9] and 7. April 2020.[10] Contract for Groszki - Gręzów section expected to be signed in 2021.[11] |
| Siedlce – Biała Podlaska | 63.5 km (39.5 mi) | 2022–2024 | Design&Build tenders announced in 2020[12][13] |
| Biała Podlaska – Kukuryki (border) | 32 km (20 mi) | Possibly to be finished by 2025 depending on funding decisions[3] | Pre-design ongoing |
History of construction
The first highway planned along part of this route was a Reichsautobahn initiated by Nazi Germany to connect Berlin with Poznań (Posen). The construction of this highway, accelerated after Poznań was incorporated into Germany following the Invasion of Poland in 1939, was interrupted by the war and never finished, but traces of its earthworks were clearly visible on satellite photographs for decades afterwards, especially between the border with Germany and Nowy Tomyśl. Most of these traces have now disappeared as the modern motorway was built largely following the same route. A short stretch of the uncompleted highway between the border and Rzepin was finished as a dual carriageway road after 1945, in effect forming an extension of the German A 12 highway (opened as a Reichsautobahn in the 1930s). Except for this stretch, the construction work was not continued in the decades after the war.
New plans to build the A2 motorway were seriously formulated in communist Poland in the 1970s, possibly with the goal of completing it in time for the Moscow Olympics in 1980. Because of the economic crisis which hit the country in the late 1970s and continued throughout the 1980s, only a 50 km (31 mi) section from Września to Konin was opened in the 1980s. Construction of another stretch (between Łódź and Warsaw) was started and then abandoned, leaving an interesting ruin informally named Olimpijka, which was in turn demolished around 2010 when building of the motorway resumed.
Intensive construction of the motorway started only in 2001 after the fall of communism in Poland in 1989. Out of the planned total length of 610 km (380 mi), 359 km (223 mi) have been completed. A section of about 150 km (93 mi) (Nowy Tomyśl – Poznań – Września – Konin) has been fully open since 2004. This section is a toll road, with the exception of a short stretch through Poznań which serves as that city's bypass (between the interchanges at Głuchowo and Kleszczewo). An additional 100 km (62 mi) section from Konin to Stryków near Łódź was opened on 26 July 2006. A short 4.8 km (3.0 mi) bypass of Stryków, consisting of a 2 km (1.2 mi) extension of the A2 and a provisional single carriageway section of the future A1 motorway, was opened in December 2008, to ease the heavy traffic in that town generated when the motorway reached it.
As of the winter of 2009/2010, the plan was to finish the whole section between the border with Germany and Warsaw by the spring of 2012, giving the Polish capital its first motorway connection to the European motorway network in time for the Euro 2012 football championships.That ambitious goal was jeopardised due to various difficulties encountered in finalising the construction contracts and the delays that resulted. The 90 km (56 mi) section from Stryków to Warsaw was to be built in a public-private partnership, but the negotiations between the government and private companies interested in participating collapsed in February 2009 due to disputes over financing terms.[14] It was then decided that this section of the motorway would be built using public funds alone. The new bidding process was started on 27 March,[15] and the contracts for design and construction of the road were signed on 28 September.[16] The section had been divided into 5 parts and so construction work began in 2010. The contractors were required to have the motorway open to traffic in time for Euro 2012. This goal was an ambitious one and ultimately proved challenging, given the possibility of unexpected delays during construction[17] and the fact that the Chinese consortium abandoned the project less than a year later,[18] so that new contractors had to be selected to replace it. The goal was to have this motorway stretch provisionally opened to traffic in time for Euro 2012, even if it is not fully completed, with various restrictions such as a lower speed limit to ensure safety. For a while it was not clear whether even this limited goal would be reached, but the motorway opened to traffic in June 2012 after very intensive construction work in the final few months.
In November 2011, construction of the stretch from the German border to Nowy Tomyśl had been completed. The road was opened to public traffic on 1 December. Toll plazas on this stretch of the highway weren't opened until May 2012 so use of the western section of the A2 was free of charge until then.[19]
In May 2013, the interchange with the S3 (Jordanowo) was opened to traffic.[20] First stretch is between the interchange with the A2 motorway and the Świebodzin North interchange. In June 2013, the S3 was extended further and opened to traffic to reach from the Świebodzin South interchange to the existing stretch of the S3 expressway at Sulechów. In July 2013, the elevated bypass of Świebodzin between the interchanges of Świebodzin North and Świebodzin South fully opened to traffic thus fully extending the S3 from Szczecin to Sulechów.[21]
Guarantee scandal
After COVEC withdrew from completing its construction of the A2, Bank of China was to pay a performance guarantee to the Polish government's roads organization GDDKiA. However, with Export-Import Bank of China, they refused to pay this; only Deutsche Bank honoured its obligations under the court decision.[22]
Plans
The eastern section from Warsaw to the border crossing with Belarus at Kukuryki near Brest (connecting with M1), about 170 km (110 mi) in length, is still largely in planning stages. The decision finalizing the route of this section was announced in December 2011,[23] the exception having been a short 21 km (13 mi) section of A2 forming the bypass of Mińsk Mazowiecki which has been under construction since August 2009. It opened to traffic in August 2012.[24] The section between Warsaw and Mińsk Mazowiecki is planned to be opened in 2020.[25] The tenders for section between Mińsk Mazowiecki and Siedlce have been announced in 2019.[26] The remaining section east of Siedlce is said to be planned for completion by 2025.[3]
It is worth noting that the A2 motorway doesn't actually run through Warsaw, as the inhabitants of the districts through which it was to pass have successfully blocked its construction. This outcome was somewhat unusual, since the corridor for the motorway has been reserved by the city planners since the 1970s and kept free of construction. Instead, the traffic will be rerouted through two express roads (S2 and S8), of lower standard than the originally planned motorway. Paradoxically, one of these roads (S2) will run along the originally planned motorway corridor, so the residents who protested the construction will still end up with a busy road running through their districts, possibly even more inconvenient than the original road would have been. In the most affected area, the district of Ursynów, the express road will run in a tunnel, which will be built at considerable expense.
Exit list
| Frankfurt, Berlin | ||
| (0) | Frankfurt/Świecko border crossing | |
|
Stretch Świecko border crossing – interchange Świecko signed as | ||
| (1) | Świecko | |
| Services Glinec (dir. Świecko) | ||
| Services Sosna(dir. Warszawa) | ||
| (2) | Rzepin | |
| () | Road toll Tarnawa | |
| (3) | Torzym | |
| Services Walewice (dir. Świecko) | ||
| Services Koryta (dir. Warszawa) | ||
| (4) | Interchange Jordanowo | |
| (5) | Trzciel ( | |
| (6) | Nowy Tomyśl | |
| Wytomyśl (dir. Świecko) parking area | ||
| Kozielaski (dir. Warszawa) parking area | ||
| Services Sędzinko (dir. Świecko) | ||
| Services Zalesie (dir. Warszawa) | ||
| (7) | Buk | |
| Dopiewiec (dir. Świecko) parking area | ||
| Konarzewo (dir. Warszawa) parking area | ||
| () | Road toll Gołuski | |
| (8) | Interchange Poznań – Zachód | |
| (9) | Interchange Poznań – Komorniki | |
| Tunnel under railway line in Luboń 130 m | ||
| (10) | Poznań – Luboń | |
| Lucjan Ballenstaedt's bridge over Warta river 306 m | ||
| Bridge over railway line in Poznań | ||
| (11) | Interchange Poznań – Krzesiny | |
| Services Tulce (dir. Świecko) | ||
| Services Krzyżowniki (dir. Warszawa) | ||
| (12) | Interchange Poznań – Wschód | |
| () | Road toll Nagradowice | |
| Chwałszyce (dir. Świecko) parking area | ||
| Targowa Górka (dir. Warszawa) parking area | ||
| (13) | Września | |
| Sołeczno (dir. Świecko) parking area | ||
| Gozdowo (dir. Warszawa) parking area | ||
| Skarboszewo (dir. Świecko) parking area | ||
| (15) | Słupca | |
| Lądek (dir. Warszawa) parking area | ||
| () | Road toll Lądek | |
| (16) | Sługocin | |
| Bridge over Warta river 250 m | ||
| Services Osiecza | ||
| (17) | Interchange Modła (Konin – Zachód) | |
| (18) | Konin – Wschód | |
| () | Road toll Żdżary | |
| Kuny (dir. Świecko) parking area | ||
| Leonia (dir. Warszawa) parking area | ||
| (19) | Koło | |
| Police (dir. Świecko) parking area | ||
| Łęka (dir. Warszawa) parking area | ||
| Bridge over Warta river | ||
| Sobótka (dir. Świecko) parking area | ||
| Cichmiana (dir. Warszawa) parking area | ||
| (20) | Dąbie | |
| Kozanki (dir. Świecko) parking area | ||
| Zaborów (dir. Warszawa) parking area | ||
| (21) | Wartkowice | |
| Services Chrząstów Północ (dir. Świecko) | ||
| Services Chrząstów Południe (dir. Warszawa) | ||
| (22) | Emilia | |
| Ciosny parking area | ||
| (22) | Zgierz | |
| () | Road toll Stryków | |
| (23) | Stryków | |
| (24) | Interchange Łódź-Północ | |
| Services Nowostawy (dir. Świecko) | ||
| Services Niesułków (dir. Warszawa) | ||
| (25) | Łowicz | |
| Services Parma (dir. Świecko) | ||
| Services Polesie (dir. Warszawa) | ||
| (26) | Skierniewice | |
| Services Bolimów (dir. Świecko) | ||
| Services Mogiły (dir. Warszawa) | ||
| Interchange Centralny Port Komunikacyjny | ||
| (27) | Wiskitki (Żyrardów) | |
| Services Baranów Północ (dir. Świecko) | ||
| Services Baranów Południe (dir. Warszawa) | ||
| (28) | Grodzisk Mazowiecki | |
| Services Brwinów Północ (dir. Świecko) | ||
| Services Brwinów Południe (dir. Warszawa) | ||
| (29) | Pruszków | |
| (30) | Interchange Konotopa | |
|
Road will continue as | ||
| Interchange Lubelska | ||
| (32) | Interchange Halinów | |
| Rest area Kobierna (under construction) | ||
| Rest area Rysie (under construction) | ||
| Interchange | ||
| (33) | Mińsk Mazowiecki – Arynów | |
| (34) | Mińsk Mazowiecki – Airport | |
| Rest area (under construction) | ||
| Rest area (under construction) | ||
| (35) | Ryczołek | |
| Parking area (planned) | ||
| Parking area (planned) | ||
| Kotuń (planned) | ||
| Siedlce – Swoboda | ||
| Siedlce – Białki | ||
| Rest area (planned) | ||
| Rest area (planned) | ||
| Interchange Łukowisko | ||
| Rest area (planned) | ||
| Rest area (planned) | ||
| Biała Podlaska – Zachód (planned) | ||
| Biała Podlaska – Wschód (planned) | ||
| Parking area (planned) | ||
| Parking area (planned) | ||
| Kukuryki | ||
| (-) | Border crossing Kukuryki – Kazlovichy | |
| Minsk, Moscow | ||
See also
References
- "A2 – "Autostradą Wolności"". prezydent.pl (in Polish). Archived from the original on 6 June 2014.
- Official GDDKiA information page
- https://www.bankier.pl/wiadomosc/W-2025-r-autostrada-A2-mamy-doejchac-do-wschodniej-granicy-Polski-7748916.html
- Łódzkie odcinki A-2 już otwarte !
- A2 – czekały na nią pokolenia…
- "Car Travel in Poland". Poland Travel Planner. Retrieved 6 April 2019.
- "Autostrada do Pruszkowa". 22 May 2012.
- "Autostrada A2 - Autostrada Wolności. Przejezdny odcinek A2 między węzłem Lubelska a początkiem obwodnicy Mińska Mazowieckiego". www.muratorplus.pl. Retrieved 26 August 2020.
- "Autostrada A2 Mińsk Mazowiecki – Siedlce już w realizacji". www.rynekinfrastruktury.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 15 December 2020.
- "Jest druga umowa na A2 z Mińska Mazowieckiego do Siedlec". www.rynekinfrastruktury.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 15 December 2020.
- "Jednak Chińczycy. Stecol wybrany do realizacji A2". www.rynekinfrastruktury.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 15 December 2020.
- https://www.gddkia.gov.pl/pl/a/36369/Plan-przetargow-na-2020-rok-W-tym-roku-oglosimy-postepowania-na-realizacje-353-km-nowych-drog
- "Wszystkie przetargi na A2 Siedlce – Biała Podlaska ogłoszone". www.rynekinfrastruktury.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 15 December 2020.
- Budowa autostrady A2 do stolicy znów się opóźni(in Polish)
- "Budowa autostrady A2" (PDF). inżynieria.com. Retrieved 6 April 2019.
- www.newsweek.pl(in Polish)
- Rząd przejmuje budowę autostrady A2 Archived 18 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine (in Polish)
- "Autostrada Wielkopolska – News Drivers". Autostrada Wielkopolska. Archived from the original on 26 April 2012. Retrieved 25 November 2010.
- "Węzeł Jordanowo od 27 maja otwarty".
- "Obwodnica Świebodzina w ciągu S3 oddana do ruchu".
- "COVEC nie zraził się porażką na A2 i z chińskimi bankami startuje do Kozienic". 20 January 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- Official announcement from GDDKiA website
- Autostrada gotowa, więc jej nie otworzą. "Trudny grunt"
- Polish government planning decision
- https://www.rynekinfrastruktury.pl/wiadomosci/drogi/a2-minsk-mazowiecki--siedlce-jest-trzeci-przetarg-68917.html
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Freeway A2 (Poland). |
- Official page of the toll company (in Polish and English)
- Page about the planned road network through Warsaw (in Polish)
- Poland: The Chinese Motorway – news video from European Journal
