91st Minnesota Legislature
The Ninety-first Minnesota Legislature is the legislature of the U.S. state of Minnesota from January 8, 2019 to January 4, 2021. It is composed of the Senate and House of Representatives, based on the results of the 2016 Senate election and 2018 House election. It first convened and held its regular session in Saint Paul from January 8 to May 20, 2019, and from February 11 to May 18, 2020. A special session was held from May 24 to 25, 2019, to pass bills enacting the state budget following an agreement between the governor and legislative leaders during the final weekend of the regular session in 2019.[1]
| 91st Minnesota Legislature | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||
| Overview | |||||||||||||||
| Term | January 8, 2019 – January 4, 2021 | ||||||||||||||
| Senate | |||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||
| Members | 67 senators | ||||||||||||||
| President | Jeremy Miller (R) until November 12, 2020 David Tomassoni (Independent) from November 12, 2020 | ||||||||||||||
| Majority Leader | Paul Gazelka (R) | ||||||||||||||
| Minority Leader | Tom Bakk (DFL) until February 1, 2020 Susan Kent (DFL) from February 1, 2020 | ||||||||||||||
| House of Representatives | |||||||||||||||
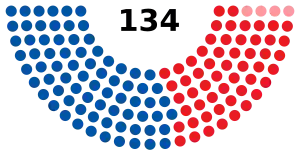 | |||||||||||||||
| Members | 134 representatives | ||||||||||||||
| Speaker | Melissa Hortman (DFL) | ||||||||||||||
| Majority Leader | Ryan Winkler (DFL) | ||||||||||||||
| Minority Leader | Kurt Daudt (R) | ||||||||||||||
| Sessions | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Special sessions | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Another special session was held from June 12 to 20, 2020, which was required by state law as Governor Tim Walz extended Minnesota's peacetime emergency in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. It also the followed the killing of George Floyd in Minneapolis and the subsequent protests. Walz and several legislators said they intended to use the special session to address concerns raised by Floyd's death related to racial inequities in policing,[2] on which the House and Senate were unable to reach an agreement.[3][4][5] They were also unable to reach agreements on a public works borrowing bill, appropriating money from the CARES Act to local governments, and assistance for Minneapolis and Saint Paul for damage caused by riots in those cities.[5][6] Senate Majority Leader Paul Gazelka had said at the beginning of the special session Republicans would adjourn the Senate by June 19 regardless of whatever legislation had or had not been passed by the Legislature, which House Speaker Melissa Hortman said was an arbitrary deadline.[7] Gazelka said at the end of the special session a deadline was needed to force discussions and was willing to return for another special session when there were agreements on these issues.[5]
On July 10, 2020, Walz called another special session that was held from July 13 to 21, 2020, as he again extended the peacetime emergency.[8] The Legislature passed a bill on police reform, but was unable to reach an agreement on a public works borrowing bill.[9][10]
On August 7, 2020, Walz called another special session that was held on August 12, 2020, as he again extended the peacetime emergency.[11][12]
On September 9, 2020, Walz called another special session that was held on September 11, 2020, as he again extended the peacetime emergency.[13]
On October 7, 2020, Walz called another special session that was held from October 12 to 15, 2020, as he again extended the peacetime emergency.[14]
On November 9, 2020, Walz called another special session that was held on November 12, 2020, as he again extended the peacetime emergency.[15]
On December 9, 2020, Walz called another special session as he again extended the peacetime emergency. The Legislature convened on December 14, 2020. [16]
Major events
- April 3, 2019: Governor Tim Walz delivered his first State of the State Address.[17]
- May 9, 2019: A joint convention of the Senate and House of Representatives was held to elect regents of the University of Minnesota.[18]
- April 5, 2020: Walz delivered his second State of the State Address. Originally scheduled to be held on March 23 in the House chamber, it was postponed and moved to the governor's residence due to the COVID-19 pandemic.[19][20]
Major legislation
Enacted
- April 12, 2019: Hands-free cell phone use while driving act[21] (Laws 2019, chapter 11)
- May 2, 2019: Voluntary relationship defense for criminal sexual conduct repeal act[22] (Laws 2019, chapter 16)
- May 22, 2019: Assisted living act[23][24] (Laws 2019, chapter 60)
- May 22, 2019: Opioid addiction prevention and treatment act[25][26] (Laws 2019, chapter 63)
- Omnibus appropriations acts:[27]
- May 22, 2019: Omnibus higher education act[28] (Laws 2019, chapter 64)
- May 30, 2019: Omnibus agriculture, housing, and rural development act (Laws 2019, First Special Session chapter 1)
- May 30, 2019: Omnibus transportation act (Laws 2019, First Special Session chapter 3)
- May 30, 2019: Omnibus environment and natural resources act (Laws 2019, First Special Session chapter 4)
- May 30, 2019: Omnibus judiciary and public safety act (Laws 2019, First Special Session chapter 5)
- May 30, 2019: Omnibus jobs, economic development, and energy act (Laws 2019, First Special Session chapter 7)
- May 30, 2019: Omnibus health and human services act (Laws 2019, First Special Session chapter 9)
- May 30, 2019: Omnibus state government act (Laws 2019, First Special Session chapter 10)
- May 30, 2019: Omnibus education act[29] (Laws 2019, First Special Session chapter 11)
- May 30, 2019: Omnibus legacy act (Laws 2019, First Special Session chapter 2)
- May 30, 2019: Omnibus tax act[30] (Laws 2019, First Special Session chapter 6)
- March 10, 2020: COVID-19 pandemic response act[31] (Laws 2020, chapter 66)
- March 17, 2020: COVID-19 pandemic response act[32][33] (Laws 2020, chapter 70)
- March 28, 2020: COVID-19 pandemic response act[34][35] (Laws 2020, chapter 71)
- April 7, 2020: COVID-19 first responders workers' compensation act[36][37] (Laws 2020, chapter 72)
- April 15, 2020: Alec Smith Insulin Affordability Act[38][39] (Laws 2020, chapter 73)
- April 15, 2020: COVID-19 pandemic response act[40][41] (Laws 2020, chapter 74)
- May 12, 2020: 2020 elections special procedures act[42] (Laws 2020, chapter 77)
- May 27, 2020: Outdoor heritage fund appropriations act (Laws 2020, chapter 104)
- July 23, 2020: Police reform act[43][44] (Laws 2020, Second Special Session chapter 1)
- October 21, 2020: Omnibus capital investment "bonding" act[45] (Laws 2020, Fifth Special Session chapter 3)
Proposed
- Boldface indicates the bill was passed by its house of origin.
- Clean Energy First Act[46] (H.F. No. 1405/S.F. No. 1456)
- Energy Conservation and Optimization Act of 2020[46] (H.F. No. 4502/S.F. No. 4409)
- Extreme risk protection order bill[47] (H.F. No. 9/S.F. No. 436)
- Family leave insurance bill[48] (H.F. No. 5/S.F. No. 1060)
- Firearm transfer background check bill[47] (H.F. No. 8/S.F. No. 3426)
- Omnibus environment and natural resources bill[49][50][51] (H.F. No. 4554/S.F. No. 4499)
- Proposed constitutional amendment establishing a fundamental right to a quality public education bill[52][53] (H.F. No. 3658/S.F. No. 3977)
- Recreational cannabis bill[54][55] (H.F. No. 420/S.F. No. 619)
- Voting rights restoration for felons bill[56][57] (H.F. No. 40/S.F. No. 856)
Political composition
- Resignations and new members are discussed in the "Changes in membership" section below.
Senate

| Party (Shading indicates majority caucus) |
Total | Vacant | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Democratic– Farmer–Labor |
Independent | |||
| End of the previous Legislature | 34 | 32 | 0 | 66 | 1 |
| Begin (January 8, 2019) | 34 | 32 | 0 | 66 | 1 |
| February 13, 2019 | 35 | 67 | 0 | ||
| November 18, 2020 | 30 | 2 | 67 | 0 | |
| Latest voting share | 52.2% | 44.8% | 3% | ||
House of Representatives

| Party (Shading indicates majority caucus) |
Total | Vacant | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic– Farmer–Labor |
Republican | ||||
| Republican Caucus |
New Republican Caucus | ||||
| End of the previous Legislature | 55 | 75 | 0 | 130 | 4 |
| Begin (January 8, 2019) | 74 | 55 | 4 | 133 | 1 |
| January 10, 2019 | 75 | 134 | 0 | ||
| February 12, 2019 | 54 | 133 | 1 | ||
| March 27, 2019 | 55 | 134 | 0 | ||
| November 16, 2019 | 74 | 133 | 1 | ||
| December 6, 2019 | 54 | 132 | 2 | ||
| February 11, 2020 | 75 | 55 | 134 | 0 | |
| Latest voting share | 56% | 41% | 3% | ||
Leadership
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Minnesota |
| Constitution |
|
Senate
- President:
- Jeremy Miller (R)[58] (until November 12, 2020)
- David Tomassoni (I) (from November 12, 2020)
- President pro tempore: Mary Kiffmeyer (R)[59]
Majority (Republican) leadership
- Majority Leader: Paul Gazelka[58]
- Deputy Majority Leader: Michelle Benson[60]
- Assistant Majority Leaders:[60]
- Majority Whips:[61]
Minority (DFL) leadership
- Minority Leader:
- Tom Bakk[58] (until February 1, 2020)[62]
- Susan Kent (from February 1, 2020)[62]
- Assistant Minority Leaders:[61]
- Nick Frentz (from February 7, 2020)[63]
- Jeff Hayden
- Susan Kent (until February 1, 2020)[62]
- Carolyn Laine
- Erik Simonson (from February 7, 2020)[63]
- Minority Whips:[61]
House of Representatives
- Speaker: Melissa Hortman (DFL)[58]
- Speakers pro tempore:[64]
- Gene Pelowski (DFL)
- Paul Marquart (DFL)
- Jeanne Poppe (DFL)
- Liz Olson (DFL)
- Laurie Halverson (DFL)
- Tony Albright (R)
Majority (DFL) leadership
- Majority Leader: Ryan Winkler[58]
- Majority Whip: Liz Olson[58]
- Assistant Majority Leaders:[65]
Minority (Republican) leadership
- Minority Leader: Kurt Daudt[66]
- Deputy Minority Leader: Anne Neu[67]
- Minority Whip: Dan Fabian[67]
- Assistant Minority Leaders:[67]
Members
- For full lists of members of the 91st Minnesota Legislature, see Minnesota Senate and Minnesota House of Representatives.
House of Representatives
On December 8, 2018, four Republican members of the House (Reps. Steve Drazkowski of Mazeppa, Cal Bahr of East Bethel, Tim Miller of Prinsburg, Jeremy Munson of Lake Crystal) announced that they would not join the Republican caucus in the 91st Legislature and instead would form a new caucus, called the "New Republican Caucus." They cited displeasure with "the attitudes and actions by [Leader Daudt] and some of his supporters" and said they still consider themselves to be members of the Republican Party.[68]
Changes in membership
Senate
| District | Vacator | Reason for change | Successor | Date successor seated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | Tony Lourey (DFL) | Resigned effective on January 3, 2019, to become commissioner of human services.[69] A special election was held on February 5, 2019. |
Jason Rarick (R) | February 13, 2019 |
| 14 | Jerry Relph (R) | Died due to complications from COVID-19.[70]
Relph, who had been defeated in the November general election, was replaced when the 92nd Minnesota Legislature convened. |
Aric Putnam (DFL) | January 5, 2021 |
House of Representatives
| District | Vacator | Reason for change | Successor | Date successor seated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 57A | Vacant | Hospitalized due to an infection.[71] | Robert Bierman (DFL) | January 10, 2019 |
| 11B | Jason Rarick (R) | Resigned effective on February 12, 2019, to assume Minnesota Senate seat.[72] A special election was held on March 19, 2019. |
Nathan Nelson (R) | March 27, 2019 |
| 60A | Diane Loeffler (DFL) | Died of cancer on November 16, 2019.[73] A special election was held on February 4, 2020. |
Sydney Jordan (DFL) | February 11, 2020 |
| 30A | Nick Zerwas (R) | Resigned effective on December 6, 2019, to spend more time with his family and to seek employment outside of the Legislature.[74] A special election was held on February 4, 2020. |
Paul Novotny (R) | February 11, 2020 |
Committees
Senate
| Committee[75] | Chair | Vice Chair | DFL Lead | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture, Rural Development, and Housing Finance | Torrey Westrom | Mark Johnson | Kari Dziedzic | |
| Agriculture, Rural Development, and Housing Policy | Bill Weber | Mike Goggin | Foung Hawj | |
| Capital Investment | Dave Senjem | Scott Newman | Sandy Pappas | |
| Commerce and Consumer Protection Finance and Policy | Gary Dahms | Karin Housley | Dan Sparks | |
| E–12 Education Finance and Policy | Carla Nelson | Gary Dahms | Chuck Wiger | |
| Energy and Utilities Finance and Policy | David Osmek | Andrew Mathews | Erik Simonson | |
| Environment and Natural Resources Finance | Bill Ingebrigtsen | Carrie Ruud | David Tomassoni | |
| Environment and Natural Resources Policy and Legacy Finance | Carrie Ruud | Bill Weber | Chris Eaton | |
| Family Care and Aging | Karin Housley | Jerry Relph | Kent Eken | |
| Finance | Julie Rosen | Bill Ingebrigtsen | Dick Cohen | |
| Health and Human Services Finance and Policy | Michelle Benson | Scott Jensen | John Marty | |
| Higher Education Finance and Policy | Paul Anderson | Rich Draheim | Greg Clausen | |
| Human Services Reform Finance and Policy | Jim Abeler | Paul Utke | Jeff Hayden | |
| Jobs and Economic Growth Finance and Policy | Eric Pratt | Justin Eichorn | Bobby Joe Champion | |
| Judiciary and Public Safety Finance and Policy | Warren Limmer | Dan Hall | Ron Latz | |
| Local Government | Dan Hall | Bruce Anderson | Patricia Torres Ray | |
| Rules and Administration | Paul Gazelka | Michelle Benson | Tom Bakk | |
| Subcommittees[76] | Committees | Paul Gazelka | ||
| Conference Committees | Paul Gazelka | |||
| Ethical Conduct | Jeremy Miller | |||
| Litigation Expenses | Scott Newman | |||
| Permanent and Joint Rules[nb 1] | Jeremy Miller | |||
| State Government Finance and Policy and Elections | Mary Kiffmeyer | Mark Koran | Jim Carlson | |
| Taxes | Roger Chamberlain | Dave Senjem | Ann Rest | |
| Transportation Finance and Policy | Scott Newman | John Jasinski | Scott Dibble | |
| Veterans and Military Affairs Finance and Policy | Bruce Anderson | Andrew Lang | Jerry Newton | |
| Select Committees | ||||
| Home Ownership Affordability and Availability[nb 2] | Rich Draheim | |||
House of Representatives
Administrative officers
Senate
House of Representatives
Notes
- Established January 30, 2019.[77]
- Established May 14, 2019. Dissolved May 17, 2020.[78]
- Until December 6, 2019.
- From February 11, 2020.
- Until February 12, 2019.
- From February 13, 2019.[80]
- Until November 16, 2019.
- From January 10, 2020.[81]
- Until February 11, 2020.[82]
- From February 11, 2020.[82]
- Established May 12, 2020.[83]
References
- Van Oot, Torey; Van Berkel, Jessie (May 25, 2019). "Minnesota lawmakers approve $48 billion budget after all-night special session". Star Tribune. Retrieved May 25, 2019.
- Van Berkel, Jessie (June 12, 2020). "Police reform shadows Minnesota Legislature's special session". Star Tribune. Retrieved June 12, 2020.
- Van Berkel, Jessie; Bierschbach, Briana (June 21, 2020). "Police reform efforts collapse in divided Minnesota Legislature". Star Tribune. Retrieved June 21, 2020.
- Orenstein, Walker (June 20, 2020). "Minnesota Legislature ends special session without deal on policing reforms". MinnPost. Retrieved June 20, 2020.
- Bakst, Brian (June 19, 2020). "Special session ends without deal on policing, bonding". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved June 20, 2020.
- Bierschbach, Briana; Van Berkel, Jessie; Condon, Patrick (June 20, 2020). "Minnesota Legislature adjourns without agreement on key issues". Star Tribune. Retrieved June 20, 2020.
- Pugmire, Tim (June 12, 2020). "Special session begins with debate over COVID-19 emergency, police powers". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved June 20, 2020.
- Bakst, Brian (July 10, 2020). "Special session, part 2, planned for Monday". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved July 10, 2020.
- Bierschbach, Briana (July 21, 2020). "Minnesota lawmakers pass sweeping package of police accountability measures". Star Tribune. Retrieved July 21, 2020.
- Bakst, Brian (July 21, 2020). "Legislature passes policing bill, ends special session". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved July 21, 2020.
- Jackson, Zoë (August 8, 2020). "Gov. Tim Walz to convene third special session of the summer starting Wednesday". Star Tribune. Retrieved August 12, 2020.
- Callaghan, Peter (August 11, 2020). "Don't expect much to get done during the Minnesota Legislature's latest special session". MinnPost. Retrieved August 12, 2020.
- Van Oot, Torey (September 9, 2020). "Gov. Tim Walz calls Legislature back for fourth special session". Star Tribune. Retrieved September 10, 2020.
- Van Oot, Torey (October 7, 2020). "Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz extends state of emergency for coronavirus response". Star Tribune. Retrieved October 8, 2020.
- Van Oot, Torey (November 9, 2020). "Gov. Tim Walz extends pandemic state of emergency, prompting Legislature's return". Star Tribune. Retrieved November 12, 2020.
- https://www.lrl.mn.gov/history/spsess
- Van Berkel, Jessie (April 4, 2019). "Gov. Tim Walz aims to break through gridlock at State of the State by telling Minnesotans' stories". Star Tribune. Retrieved May 23, 2019.
- Phaneuf, Taryn (May 10, 2019). "Legislature chooses four new University of Minnesota regents". MinnPost. Retrieved May 23, 2019.
- Van Berkel, Jessie (April 6, 2020). "Walz calls for a 'united' state of the state amid COVID-19". Star Tribune. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Montgomery, David H. (April 5, 2020). "Walz: Staying home is the only vaccine we have right now". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Montemayor, Stephen (April 12, 2019). "'Hands-free' cellphone bill signed by Gov. Walz". Star Tribune. Retrieved May 20, 2019.
- Van Berkel, Jessie (May 2, 2019). "Gov. Tim Walz signs law repealing Minnesota's marital rape exemption". Star Tribune. Retrieved May 20, 2019.
- Serres, Chris (May 25, 2019). "A landmark new law aims to protect Minnesota's elderly, but who writes the rules?". Star Tribune. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Nelson, Tim (May 20, 2019). "Elder care reform package on way to governor's desk". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Van Oot, Torey (May 20, 2019). "Minnesota lawmakers strike deal on opioid response bill". Star Tribune. Retrieved May 22, 2019.
- Van Oot, Torey (May 22, 2019). "Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz signs opioid crisis response bill". Star Tribune. Retrieved May 22, 2019.
- Coolican, J. Patrick (May 25, 2019). "Legislature finishes $48.3 billion budget in overtime; Gov. Tim Walz expected to sign it". Star Tribune. Retrieved May 25, 2019.
- Cox, Peter (May 22, 2019). "This session, higher ed got less than requested, but also real money". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved May 25, 2019.
- Phaneuf, Taryn (May 29, 2019). "Incremental change, 'lackluster' year: Compromises all around in final Minnesota education budget". MinnPost. Retrieved May 31, 2019.
- Coolican, J. Patrick (May 31, 2019). "New Minnesota law should make filing taxes simpler, cheaper". Star Tribune. Retrieved May 31, 2019.
- Bakst, Brian (March 9, 2020). "Minnesota Legislature speeds $21M in coronavirus money". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Bierschbach, Briana (March 17, 2020). "Minnesota governor signs $200 million package for emergency COVID-19 response". Star Tribune. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- "Walz signs $200 million emergency COVID-19 funding bill". Minnesota Public Radio. March 17, 2020. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Van Berkel, Jessie; Van Oot, Torey (March 27, 2020). "Minnesota House, Senate pass $330 million in COVID-19 aid". Star Tribune. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Bakst, Brian (March 26, 2020). "Minnesota lawmakers send $330M COVID-19 bill to Walz". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Van Oot, Torey (April 6, 2020). "Minnesota poised to expand workers' comp for first responders hit by COVID-19". Star Tribune. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Pugmire, Tim (April 7, 2020). "Lawmakers pass workers' compensation bill — with cost unresolved". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Van Berkel, Jessie; Montemayor, Stephen (April 14, 2020). "Minnesota Legislature passes emergency insulin bill after 'long and arduous road'". Star Tribune. Retrieved June 14, 2020.
- Callaghan, Peter (April 15, 2020). "'A great day': Minnesota Legislature finally passes emergency insulin bill". MinnPost. Retrieved June 14, 2020.
- Bierschbach, Briana (April 14, 2020). "Minnesota lawmakers pass fourth COVID-19 relief package". Star Tribune. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Bakst, Brian (April 14, 2020). "As unity wanes, Minnesota lawmakers advance new COVID-19 bill". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Callaghan, Peter (May 8, 2020). "Minnesota Senate passes 2020 election bill: more money for no-excuse absentee balloting, but no all vote-by-mail". MinnPost. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Van Oot, Torey; Bierschbach, Briana (July 23, 2020). "Political antagonists united by George Floyd's death to forge deal on police reform". Star Tribune. Retrieved August 7, 2020.
- Orenstein, Walker; Callaghan, Peter (July 21, 2020). "The Legislature just passed a police reform bill. What it does — and doesn't do — to reshape law enforcement in Minnesota". MinnPost. Retrieved July 23, 2020.
- Van Berkel, Jessie (October 15, 2020). "Minnesota House passes $1.9 billion infrastructure bonding bill". Star Tribune. Retrieved October 15, 2020.
- Bakst, Brian (October 14, 2020). "House passes $1.8 billion public works borrowing bill". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved October 15, 2020.
- Van Oot, Torey (October 15, 2020). "Minnesota Senate approves $1.9 billion infrastructure package". Star Tribune. Retrieved October 15, 2020.
- Pugmire, Tim (October 15, 2020). "Senate passes massive public works bill; ends special session". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved October 15, 2020.
- Van Berkel, Jessie (October 21, 2020). "Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz signs $1.9 billion public works bill". Star Tribune. Retrieved October 26, 2020.
- Bakst, Brian (October 21, 2020). "Walz hails building plan 'done because of hard work'". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved October 26, 2020.
- Orenstein, Walker (May 15, 2020). "Minnesota lawmakers poised to pass two clean energy initiatives". MinnPost. Retrieved June 14, 2020.
- Montemayor, Stephen (February 28, 2020). "Red flag, background check gun bills clear Minnesota House". Star Tribune. Retrieved June 14, 2020.
- Van Berkel, Jessie (March 6, 2020). "Minnesota House passes bill for paid family and medical leave". Star Tribune. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Bjorhus, Jennifer (April 24, 2020). "Standoff at Capitol could block Minnesota environmental spending". Star Tribune. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Marohn, Kirsti (May 4, 2020). "Dispute over environmental fund leaves projects on wolves, weeds and mussels in limbo". Minnesota Public Radio. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- Stanley, Greg (July 12, 2020). "Partisan fight over emission standards threatens $60 million in Minnesota environmental trust fund projects". Star Tribune. Retrieved August 7, 2020.
- Bierschbach, Briana (February 25, 2020). "Minnesota legislators introduce constitutional amendment to require a 'quality public education' for all students". Star Tribune. Retrieved June 14, 2020.
- Hinrichs, Erin (February 27, 2020). "The Page-Kashkari proposal for a constitutional right to 'quality public education' finds support at the Capitol". MinnPost. Retrieved June 14, 2020.
- Van Oot, Torey (January 28, 2019). "Minnesota measure would legalize marijuana by 2022". Star Tribune. Retrieved May 20, 2019.
- Coolican, J. Patrick (March 12, 2019). "Minnesota Senate rejects legalizing recreational marijuana". Star Tribune. Retrieved May 20, 2019.
- Montemayor, Stephen (February 5, 2019). "Push to restore felon voting rights in Minnesota gains momentum, key supporters". Star Tribune. Retrieved May 20, 2019.
- Callaghan, Peter (March 12, 2019). "Around the country, restoring felons' voting rights is often a bipartisan issue. Not in Minnesota". MinnPost. Retrieved July 23, 2020.
- Van Berkel, Jessie (November 9, 2018). "Hortman, Gazelka are chosen as Minnesota legislative leaders". Star Tribune. Retrieved November 25, 2018.
- "Tuesday, January 8, 2019" (PDF). Journal of the Senate. January 8, 2019. pp. 4, 14. Retrieved January 9, 2019.
- "Senate Republicans round out leadership team with Deputy Leader and two more Assistant Leaders" (Press release). Minnesota Senate Republican Caucus. November 9, 2018. Retrieved November 25, 2018.
- "Minnesota Senate Election Directory" (PDF). Minnesota Senate. p. 2. Retrieved January 9, 2019.
- Bierschbach, Briana (February 1, 2020). "Susan Kent ousts Tom Bakk as Senate DFL leader". Star Tribune. Retrieved February 1, 2020.
- "Senate DFL Leader Kent Announces New Assistant Leaders" (Press release). Minnesota Senate DFL. February 7, 2020. Retrieved February 7, 2020.
- "Tuesday, January 8, 2019" (PDF). Minnesota House of Representatives. January 8, 2019. pp. 8, 19. Retrieved January 9, 2019.
- @mnhouseDFL (December 7, 2018). "The House DFL is proud to announce our newly elected Assistant Majority Leaders for the 2019-20 sessions" (Tweet). Retrieved December 7, 2018 – via Twitter.
- Van Berkel, Jessie (November 9, 2018). "Kurt Daudt will continue to lead Minnesota House Republicans". Star Tribune. Retrieved November 25, 2018.
- "House Republicans Announce Leadership Team" (Press release). Minnesota House Republican Caucus. November 27, 2018. Retrieved November 28, 2018.
- Bakst, Brian. "Renegade House members split from GOP caucus". Capitol View. Retrieved 2018-12-08.
- Coolican, J. Patrick (January 3, 2019). "Gov.-elect Tim Walz names seven new commissioners, including state Sen. Tony Lourey". Star Tribune. Retrieved January 14, 2019.
- Bakst, Brian. "Minn. Sen. Jerry Relph dies of COVID-19 complications". MPR News. Retrieved 2021-01-15.
- Dexter, Patty (January 10, 2019). "Rep. Robert Bierman misses first day of session due to being hospitalized". Sun Thisweek. Adams Publishing Group. Retrieved January 14, 2019.
- Cook, Mike (February 12, 2019). "Rarick to officially leave House Tuesday". Session Daily. Minnesota House of Representatives Public Information Services. Retrieved February 14, 2019.
- Miller, Pamela (November 17, 2019). "Minnesota DFL Rep. Diane Loeffler dies of cancer at 66". Star Tribune. Retrieved February 4, 2020.
- Van Berkel, Jessie (November 25, 2019). "4-term Minnesota Rep. Nick Zerwas, battling heart condition, to resign". Star Tribune. Retrieved February 3, 2020.
- "2019-2020 Directory and Committee Assignments" (PDF). Minnesota Senate. Retrieved January 14, 2019.
- "Rules and Administration Committee". Minnesota Senate. Retrieved May 23, 2019.
- "Monday, February 4, 2019" (PDF). Journal of the Senate. Minnesota Senate. p. 237. Retrieved May 23, 2019.
- "Tuesday, May 14, 2019" (PDF). Journal of the Senate. Minnesota Senate. p. 4285. Retrieved July 10, 2020.
- "Committee Information" (PDF). Minnesota House of Representatives. Retrieved February 4, 2020.
- "Fifth Meeting, Committee on Labor". Minnesota House of Representatives. Retrieved May 23, 2019.
- "Speaker Hortman appoints Rep. Andrew Carlson chair of the House Property and Local Tax Division". January 10, 2020. Retrieved February 4, 2020.
- "Tuesday, February 11, 2020" (PDF). Minnesota House of Representatives. February 11, 2020. p. 6133. Retrieved February 11, 2020.
- "Minnesota House establishes Select Committee on Minnesota's Pandemic Response and Rebuilding". May 12, 2020. Retrieved July 8, 2020.
External links
- Legislature
- Senate
- List of bill summaries prepared by the Senate Counsel, Research and Fiscal Analysis Office
- List of act summaries prepared by the Senate Counsel, Research and Fiscal Analysis Office
- Fiscal tracking spreadsheets prepared by the Senate Counsel, Research and Fiscal Analysis Office
- House of Representatives
- List of bill summaries prepared by the House Research Department
- List of act summaries prepared by the House Research Department
- Fiscal tracking spreadsheets prepared by the House Fiscal Analysis Department