2018 United States federal budget
The United States federal budget for fiscal year 2018, which ran from October 1, 2017, to September 30, 2018, was named America First: A Budget Blueprint to Make America Great Again. It was the first budget proposed by newly elected president Donald Trump, submitted to the 115th Congress on March 16, 2017.[4][5]
 | |
| Submitted | March 16, 2017 |
|---|---|
| Submitted by | Donald Trump |
| Submitted to | 115th Congress |
| Total revenue | $3.654 trillion (estimated) $3.330 trillion (actual)[1] 16.5% of GDP[2] |
| Total expenditures | $4.094 trillion[3] (requested) $4.109 trillion (actual)[1] 20.3% of GDP[2] |
| Deficit | $440 billion (requested) $779 billion (actual)[1] 3.8% of GDP[2] |
| GDP | $20.236 trillion[1] |
| Website | Official website containing the 2018 budget |
‹ 2017 2019 › | |
The government was initially funded through a series of five temporary continuing resolutions. The final funding package was passed as an omnibus spending bill, the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2018, enacted on March 23, 2018.
Background
Donald Trump was elected as President of the United States in the November 8, 2016 election, campaigning for the Republican Party on a platform of tax cuts and projects like the Mexican border wall. During his campaign, Trump promised to cut federal spending and taxes for individuals and corporations.
Trump administration budget proposal
The Trump administration proposed its 2018 budget on February 27, 2017, ahead of his address to Congress, outlining $54 billion in cuts to federal agencies and an increase in defense spending.[6] On March 16, 2017, President Trump sent his budget proposal to Congress, remaining largely unchanged from the initial proposal.[7] The OMB estimated FY2018 would involve outlays of $4.094 trillion and revenues of $3.654 trillion, a $440 billion deficit. The 2018–2027 period planned $48.901T in outlays and $45.751T in revenues, a $3.15T deficit.[8]
CBO scoring of the budget
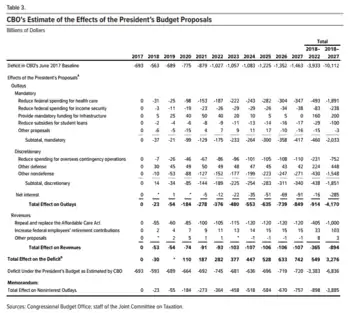
The Congressional Budget Office reported its evaluation of the budget on July 13, 2017, including its effects over the 2018–2027 period.
- Mandatory spending: The budget cuts mandatory spending by a net $2.033 trillion (T) over the 2018–2027 period. This includes reduced spending of $1.891T for healthcare, mainly due to the proposed repeal and replacement of the Affordable Care Act (ACA/Obamacare); $238 billion (B) in income security ("welfare"); and $100 billion in reduced subsidies for student loans. These savings would be partially offset by $200B in additional infrastructure investment.
- Discretionary spending: The budget cuts discretionary spending by a net $1.851 trillion over the 2018–2027 period. This includes reduced spending of $752 billion for overseas contingency operations (defense spending in Afghanistan and other foreign countries), which is partially offset by other increases in defense spending of $448B, for a net defense cut of $304B. Other discretionary spending (cabinet departments) would be reduced by $1.548T.
- Revenues would be reduced by $1 trillion, mainly by repealing the ACA, which had applied higher tax rates to the top 5% of income earners. Trump's budget proposal was not sufficiently specific to score other tax proposals; these were simply described as "deficit neutral" by the Administration.
- Deficits: CBO estimated that based on the policies in place as of the start of the Trump administration, the debt increase over the 2018–2027 period would be $10.112T. If all of President Trump's proposals were implemented, CBO estimated that the sum of the deficits (debt increases) for the 2018–2027 period would be reduced by $3.276T, resulting in $6.836T in total debt added over the period.[9]
- CBO estimated that the debt held by the public, the major subset of the national debt, would rise from $14.168T (77.0% GDP) in 2016 to $22.337T (79.8% GDP) in 2027 under the President's budget.[10]
Department and program changes
The proposed 2018 budget includes $54 billion in cuts to federal departments, and a corresponding increase in defense and military spending.[11][12]
| Department | Budget | Amount change | Percent change | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Department of Agriculture | $17.9 billion | $−4.7 billion | −21% | Includes the elimination of food for education and water and wastewater loan programs. Decreases funding for the United States Forest Service by $118 million.[13] |
| Department of Commerce | $7.8 billion | $−1.4 billion | −16% | Includes cuts to coastal research programs at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the elimination of the Economic Development Administration |
| Department of Defense | $574 billion | $52 billion | +9% | Includes an increase in the size of the Army and Marine Corps, as well as the Naval fleet |
| Department of Education | $68.2 billion | $−9.2 billion | −14% | Cuts programs and grants for teacher training, after-school and summer care, and aid to low-income students. Eliminates $1.2 billion from the 21st Century Community Learning Center program and cuts $732 million from the Federal Supplemental Educational Opportunity Grant. Eliminates Striving Readers/Comprehensive Literacy Development Grants as well as cuts funding for Supporting Effective Instruction State grants by $2.3 billion.[14] |
| Department of Energy | $28 billion | $−1.7 billion | −6% | Largest cuts go to the Office of Science; ARPA-E and Departmental Loan Programs eliminated. Increases spending on National Nuclear Security Administration by 11.4% while slashing high energy physics and almost all other science programs (Basic Energy Sciences, Biological and Environmental Research, Fusion Energy Sciences, High Energy Physics, Nuclear Physics, Infrastructure and Administration, Workforce Development for Teachers and Scientists) by 18%. The only science program not to receive a cut is the Advanced Scientific Computing Research program, which is to receive a small budget increase of $101 million. Money spent on the NNSA would go to the modernization and upkeep of nuclear weapons as well as $1.5 billion going to naval nuclear reactors. The budget cuts funding for energy programs by over 50% reducing the funding by $2.4 billion. Energy programs cut include: Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, Electricity Delivery and Energy Reliability, Nuclear Energy, Fossil Energy Research and Development.[15][16] |
| Department of Health and Human Services | $65.1 billion | $−15.1 billion | −18% | Cuts funding for the National Institutes of Health and training programs. Proposes phasing out many functions of the US Public Health Service. |
| Department of Homeland Security | $44.1 billion | $2.8 billion | +7% | Increases spending on border security and immigration enforcement and builds a wall on the US-Mexico border. Cuts funding for certain FEMA grant programs. |
| Department of Housing and Urban Development | $40.7 billion | $−6.2 billion | −13% | Eliminates grant programs for community development, investment partnerships, home-ownership, and Section 4 affordable housing |
| Department of the Interior | $11.7 billion | $−1.6 billion | −12% | Eliminates over 4000 jobs. Eliminates funding for 49 National Historic Sites and decreases funding for land acquisition. Decreases funding for Cooperative Endangered Species Conservation Fund. Cuts funding by $2 million for dealing with invasive species.[17][18] |
| Department of Justice | $27.7 billion | $−1.1 billion | −4% | Reduces spending on prison construction and reimbursements to state and local governments for incarceration of undocumented immigrants |
| Department of Labor | $9.6 billion | $−2.6 billion | −21% | Eliminates funding for senior-work programs, grants for non-profits and public agencies used for health training, and closes some Job Corps centers |
| State Department | $27.1 billion | $−10.9 billion | −29% | Eliminates funding for United Nations programs, including peacekeeping and climate change mitigation |
| Department of Transportation | $16.2 billion | $−2.4 billion | −13% | Eliminates funding for the Federal Transit Administration's New Starts grant program, long-distance Amtrak service, cuts the TIGER grant program and eliminates funding for the Essential Air Service. Air traffic control would be shifted to private service under the proposal. |
| Treasury Department | $11.2 billion | $−0.5 billion | −4% | Reduces funding for the Internal Revenue Service |
| Department of Veterans Affairs | $78.9 billion | $4.4 billion | +6% | Expands health services and the benefit claims system. Individual Unemployability (IU) for veterans eligible for Social Security retirement benefits would be terminated upon reaching the minimum retirement age for Social Security purposes, or upon enactment of the proposal if the Veteran is already in receipt of Social Security retirement benefits. These Veterans would continue to receive VA disability benefits based on their original disability rating, at the scheduler evaluation level. IU benefits would not be terminated for Veterans who are ineligible for Social Security retirement benefits, thus allowing them to continue to receive IU past minimum retirement age. Savings to the Compensation and Pensions account are estimated to be $3.2 billion in 2018, $17.9 billion over five years, and $40.8 billion over ten years.[19] |
| Environmental Protection Agency | $5.7 billion | $−2.5 billion | −31% | Eliminates more than 50 programs and 3,200 jobs |
| National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) | $19.1 billion | $-0.1 billion | −1% | Cuts funding for Earth science programs and missions, and eliminates the Office of Education. Cuts funding for the Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate by $166 million (−21%). Cuts funding for Space Technology research by $148.4 million (−18%). Cuts funding for Human Exploration Operations by $478.9 million (−53%). Cuts funding for the Education program by $62.7 million (−62.7%).[20][21] |
| Small Business Administration | $.8 billion | $−0.1 billion | −5% | Eliminates technical-assistance grant programs |
The $971 million budget for arts and cultural agencies, including the Corporation for Public Broadcasting, National Endowment for the Arts, and National Endowment for the Humanities, would be eliminated entirely.
Criticism
A recipient of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, economist Joseph Stiglitz said about the 2018 budget proposal: "Trump's budget takes a sledgehammer to what remains of the American Dream".[22] Senator Bernie Sanders also criticized the proposal: "This is a budget which says that if you are a member of the Trump family, you may receive a tax break of up to $4 billion, but if you are a child of a working-class family, you could well lose the health insurance you currently have through the Children's Health Insurance Program and massive cuts to Medicaid".[23] The actual text of the budget blueprint did not seem to include any cuts to CHIP or Medicaid at the time; however, the ultimate Senate bill stipulates that extension of CHIP funding will not increase the deficit, while not mentioning Medicaid, which did not require extension for FY2018.[24]
Congressional budget resolution
On October 17, 2017, the Senate started to debate the 2018 proposed budget.[25] On October 19, 2017, Senator Heidi Heitkamp (D-N.D.) proposed an amendment to prevent tax increases on people making less than $250,000 a year. It would have also required the Senate to approve a tax-reform bill with 60 votes rather than a simple majority. Senate Budget Committee Chairman Mike Enzi (R-Wyo.) called this language a “poison pill,” and the amendment was defeated 51-47.[26] Several Republican amendments were adopted with broad support. Senator Jeff Flake (R-Ariz.) proposed language to make the “American tax system simpler and fairer for all Americans,” which passed 98-0. Senator Marco Rubio (R-Fla.) proposed an amendment in support of increasing the child tax credit, which passed by voice vote, meaning it was approved without any Senator raising an issue.[26] Senator John McCain (R-Ariz.), chairman of the Senate Armed Services Committee, offered an amendment to ensure increases in federal defense spending are prioritized over increases in spending in other areas. “Defense and nondefense are not of the same urgency,” he told reporters Thursday. ”[26]
Related fiscal legislation
Appropriations
On September 8, 2017, Trump signed the Continuing Appropriations Act, 2018 and Supplemental Appropriations for Disaster Relief Requirements Act, 2017.[27] The bill contained a continuing resolution and a suspension of the debt ceiling lasting until December 8, as well as additional disaster funding for FY2017.[28][29] Two additional continuing resolutions were passed: the Further Continuing Appropriations Act, 2018 (H.J.Res. 123) funding the government through December 22, 2017, and the Further Additional Continuing Appropriations Act, 2018 (H.R. 1370) funding it through January 19, 2018.[30]
As of January 19, 2018, the Extension of Continuing Appropriations Act, 2018[31] was under consideration to extend funding through February 16, 2018. The failure of the bill to pass the Senate led to the first federal government shutdown of 2018.
On Friday, February 9, funding lapsed again at midnight after Senator Rand Paul delayed the vote on the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018, which included another continuing resolution, by objecting to measures requiring unanimous consent to expedite the parliamentary process. In addition, its passage was uncertain in the House due to opposition by both fiscal conservatives who objected to the increased deficit spending, and by liberals who opposed the omission of a DACA provision.[32][33] However, it passed the Senate 71–28 and the House 240–186 after midnight, and President Trump signed the bill early that morning, prior to when furloughs were to begin. In all, the funding gap lasted nine hours.[34]
On the evening of March 21, 2018, the text of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2018[35] was released, with Congress expecting to approve it within two days.[36] In March 2018, the House passed the legislation in a 256–167 vote and the Senate with 65–32.[37] President Trump signed it into law on 23 March 2018.[38]
Revenue
On December 20, 2017, Congress passed the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, two days after which President Trump signed it into law.[39] It made changes to personal and commercial income taxes, among other changes, taking effect in January 2018. After accounting for macroeconomic feedback effects, the Joint Committee on Taxation estimates that it will add a net of approximately $1 trillion to the federal debt over the period 2018–2027.[40]
Total revenue
Receipts
Receipts by Source – Proposed
Receipts by source: (in billions of dollars)
| Source | Requested [41] | Actual [2] |
|---|---|---|
| Individual income tax | $1,836.1 | $1,683.5 |
| Corporate income tax | $354.9 | $204.7 |
| Social Security and other payroll tax | $1,224.3 | $1,170.7 |
| Excise tax | $106.2 | $95 |
| Estate and gift taxes | $24.3 | $23 |
| Customs duties | $39.7 | $41.3 |
| Other miscellaneous receipts | $68.8 | $111.7 |
| Total | $3,654.3 | $3,329.9 |
Deficit
There was a deficit of $779 billion in the 2018 fiscal year, the highest in six years,[42] despite the fact that the Administration requested a $100 billion decrease in the deficit instead.[3]
References
- "2020 Budget Tables" (PDF). Government Publishing Office. Retrieved June 25, 2019.
- "2019 Budget Tables" (PDF). Government Publishing Office. Retrieved August 8, 2018.
- Mulvaney, Mick (March 16, 2017). "America First: A Budget Blueprint to Make America Great Again" (PDF). Office of Management and Budget. Retrieved March 16, 2017.
- Taylor, Andrew (March 16, 2017). "Trump budget would slash domestic programs to boost military". The Boston Globe. Associated Press. Retrieved March 16, 2017.
- Rampton, Roberta; Cowan, Richard (March 16, 2017). "Trump's budget seeks to boost military, slash other federal agencies". Reuters. Retrieved March 16, 2017.
- Mercia, Dan; Diamond, Jeremy; Liptak, Kevin (February 27, 2017). "Trump proposes defense spending boost, $54 billion in cuts to 'most federal agencies'". CNN. Retrieved March 16, 2017.
- Rappeport, Alan; Thursh, Glenn (March 16, 2017). "Pentagon Grows, While E.P.A. and State Dept. Shrink in Trump's Budget". The New York Times. Retrieved March 16, 2017.
- "Budget of the U.S. Government, Fiscal Year 2018" (PDF). GovInfo.
- Trump's Mathematical Error in the 2017–18 Budget: Budget Office Perspectives. Social Science Research Network. Date Accessed August 26, 2017.
- CBO (July 13, 2017). "An Analysis of the President's 2018 Budget".
- Soffen, Kim; Lu, Denise (March 16, 2017). "What Trump cut in his budget". The Washington Post. Retrieved March 16, 2017.
- Parlapiano, Alicia; Aisch, Gregor (March 16, 2017). "Who Wins and Loses in Trump's Proposed Budget". The New York Times. Retrieved March 16, 2017.
- "Land and Water Conservation Fund" (PDF). United States Government. p. 1. Retrieved August 2, 2017.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "FACT SHEET: President Trump's FY 2018 Budget A New Foundation for American Greatness Prioritizing Students, Empowering Parents 23, 2017" (PDF). United States Government. pp. 1–3. Retrieved August 2, 2017.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "BUDGET OF THE U. S. GOVERNMENT A New Foundation For American Greatness Fiscal Year 2018 Administration" (PDF). United States Government. p. 48. Retrieved August 2, 2017.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "Department of Energy FY 2018 Budget Request Fact Sheet May 23, 2017" (PDF). United States Government. pp. 2–4. Retrieved August 2, 2017.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "Staffing" (PDF). United States Government. p. 1. Retrieved August 2, 2017.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "Invasive Species" (PDF). United States Government. pp. 1–2. Retrieved August 2, 2017.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "2018 United States federal budget: Department Of Veterans Affairs Veterans Health Administration" (PDF). United States Government. p. 974. Retrieved June 8, 2017.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "NASA FY 2017 Budget Request for Science" (PDF). United States Government. pp. 1–7. Retrieved August 3, 2017.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "NASA FY 2018 BUDGET REQUEST" (PDF). United States Government. p. 1. Retrieved August 3, 2017.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "Economist Joseph Stiglitz: Trump's Budget Takes a Sledgehammer to What Remains of the American Dream". New York City: Democracy Now!. May 24, 2017. Retrieved May 24, 2017.
- "Budget of the U.S. Government: A New Foundation for American Greatness: Fiscal Year 2018". Office of Management and Budget/United States Senate. (CHIP is in Section 3004.) 2017. Retrieved February 25, 2018.
- Barrett, Ted (October 17, 2017). "Senate votes to start budget debate, key step in tax reform fight". CNN. Atlanta: Turner Broadcasting System. Retrieved October 19, 2017.
- Viebeck, Elise (October 19, 2017). "Senate approves budget in crucial step forward for Republican tax cuts". The Washington Post. Washington, D.C.: Nash Holdings LLC. Retrieved October 19, 2017.
- "H.R.601 - Continuing Appropriations Act, 2018 and Supplemental Appropriations for Disaster Relief Requirements Act, 2017". Retrieved August 10, 2018.
- Snell, Kelsey (September 7, 2017). "Senate approves bill doubling hurricane aid package, extending federal borrowing limit". Washington Post. Retrieved September 10, 2017.
- DeBonis, Mike; Snell, Kelsey. "Trump signs $15 billion Harvey aid package after Republicans booed top White House officials". The Washington Post. Washington, D.C.: Nash Holdings LLC. Retrieved September 10, 2017.
- DeBonis, Mike; Werner, Erica (December 21, 2017). "Senate passes stopgap spending bill, allowing Congress to avert partial government shutdown". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved December 22, 2017.
- "H.R. 195". Retrieved August 10, 2018.
- Werner, Erica; DeBonis, Mike (February 9, 2018). "Government shuts down as budget bill stalls in Congress". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved February 9, 2018.
- Bade, Rachael; Kim, Seung Min (February 8, 2018). "The dumbest shutdown ever". Politico. Retrieved February 9, 2018.
- DeBonis, Mike; Werner, Erica (February 9, 2018). "Brief government shutdown ends as Trump signs spending bill". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved February 9, 2018.
- "Rules Committee Print 115–66: Text of the House Amendment to the Senate Amendment to H.R. 1625 (Showing the text of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2018)" (PDF). U.S. House of Representatives. March 21, 2018. Retrieved March 21, 2018.
- Seipel, Brooke (March 21, 2018). "House poised to vote on $1.3T spending bill". The Hill. Retrieved March 22, 2018.
- Fox, Lauren; Mattingly, Phil (March 23, 2018). "Congress passes $1.3 trillion spending bill, funds government through September". CNN. Archived from the original on April 9, 2018. Retrieved July 18, 2018.
- "Trump drops $1.3tn budget veto threat but vows: 'Never again'". BBC. March 23, 2018. Archived from the original on April 20, 2018. Retrieved July 18, 2018.
- Kaplan, Thomas; Rappeport, Alan (December 19, 2017). "Republican Tax Bill Passes Senate in 51-48 Vote". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved December 22, 2017.
- Authors, Unlisted (November 30, 2017). "MACROECONOMIC ANALYSIS OF THE "TAX CUT [sic] AND JOBS ACT" AS ORDERED REPORTED BY THE SENATE COMMITTEE ON FINANCE ON NOVEMBER 16, 2017". Joint Committee on Taxation. Washington, D.C. Retrieved January 10, 2018.
- "2018 Public Budget Database" (XLS). Fiscal Year 2018 Public Budget Database. United States Office of Management and Budget. Retrieved June 25, 2019.
- Elis, Niv (October 15, 2018). "Deficit hits six-year high of $779 billion: Treasury". The Hill. Archived from the original on October 15, 2018. Retrieved October 15, 2018.