1st Artillery Brigade (United Kingdom)
The British Army's 1st Artillery Brigade, formerly 1st Artillery Brigade and Headquarters South West, is a formation under 3rd UK Division that has control over close support artillery units within the British Army and was the Regional Point of Command (RPoC) for British Army units in the South West Region.[2][3]
| 1st Artillery Brigade | |
|---|---|
 Insignia of 1st Artillery Brigade | |
| Active | 1961–Present |
| Allegiance | |
| Branch | |
| Type | Artillery fire support |
| Role | Combat support |
| Size | 9 Regiments and 2 Support Units |
| Part of | 3rd (UK) Division |
| Headquarters | Jellalabad Barracks, Tidworth Camp |
| Equipment | |
| Website | HQ 1st Artillery Brigade |
| Commanders | |
| Current commander | Brigadier Charles A. Hewitt[1] |
Cold War
The brigade was originally formed as the 1st Artillery Group, Royal Artillery.[4] On 1 September 1977, 1st Artillery Brigade and 7th Artillery Brigade (Anti-Aircraft) were both disbanded, and their units absorbed by the new 1st Artillery Division which had its headquarters at Dortmund (Watson and Rinaldi 77). On formation the division had a MGM-52 Lance regiment; a M107 self-propelled gun regiment; and 94 Locating Regiment RA, as well as two RA Rapier air defence regiments. It was redesignated simply as the Artillery Division in 1981, and Artillery I (BR) Corps in 1984. 1st Artillery Brigade was further reformed on 1 November 1985 to control field and missile artillery. (Watson and Rinaldi 101).
Structure in 1989
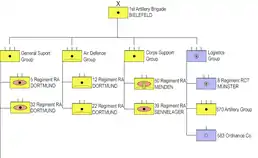
Structure of the 1st Artillery Brigade in 1989:[5]
- Headquarters 1st Artillery Brigade – Bielefeld
- General Support Group
- 5th Regiment Royal Artillery – Heavy Artillery – Dortmund, supporting 4th Armoured Division
- 32nd Regiment Royal Artillery – Heavy Artillery – Dortmund, supporting 1st Armoured Division
- Corps Support Group
- 50th Missile Regiment Royal Artillery – MGM-52 Lance surface to surface missile – Menden
- 39th Regiment Royal Artillery – Nuclear Support Artillery – Sennelager
- Air Defence Group
- 12th Regiment Royal Artillery – Dortmund
- 22nd Regiment Royal Artillery – Dortmund
- 1st Artillery Brigade Logistics Group
- 8th (Artillery Support) Regiment, Royal Corps of Transport – Münster
- 570th Artillery Group (US Army)
- 583rd Ordnance Company (US Army)
- Support (not a command group, list shows units which would be assigned to the brigade if mobilised)
- Royal Artillery Alanbrooke Band – Woolwich (Medical evacuation company if mobilised)
- Rear Link Detachment from 55 Signal Squadron, in Liverpool – assigned to HQ
- 8th (V) Battalion, Queen's Fusiliers (City of London), in Clapham, London – Infantry Defence for 50 Missile Regiment
- 94th Locating Regiment Royal Artillery, at Roberts Barracks, Larkhill – batteries detached
- 27th Regiment Royal Artillery – Light Artillery – Topcliffe, supporting 1st Armoured Division
- 45th Regiment Royal Artillery – Light Artillery – Colchester, supporting 4th Armoured Division
- 16th Regiment Royal Artillery – Air Defence – Kirton in Lindsey
- The Honourable Artillery Company (TA), Finsbury, London – Stay-behind observation posts
- 153rd (Highland) Artillery Support Regiment, Royal Corps of Transport, HQ in Dunfermline – Reserve logistics support
- General Support Group
Post Cold-War
After the Options for Change of 1992, the brigade was withdrawn from Germany and moved to Woolwich the next year where it took control of the specialist artillery regiments of the army.[6][7]
The brigade consisted of:[8][9]
- Headquarters 1st Artillery Brigade, at Royal Artillery Barracks, Woolwich
- 5th Regiment, Royal Artillery, at Marne Barracks, Catterick, Artillery Reconnaissance & Surveillance
- 32nd Regiment, Royal Artillery, at Roberts Barracks, Larkhill, equipped with Elbit Hermes 450 (UAV) and Lockheed Martin Desert Hawk (MUAS)
- 39th Regiment, Royal Artillery, at Albemarle Barracks, Stamfordham, equipped with M270B1 MLRS System and Artillery reconnaissance drones in support of 3rd (United Kingdom) Mechanised Division[10]
- Honourable Artillery Company (TA), in Finsbury, London, TA Artillery Reconnaissance & Surveillance
- 101st (Northumbrian) Regiment, Royal Artillery (TA), HQ in Newcastle upon Tyne, equipped with M270B1 MLRS System and Artillery reconnaissance drones
- 8th Artillery Support Regiment, Royal Logistic Corps, at Marne Barracks, Catterick
On 1 September 2014 under the original Army 2020 plan, the brigade merged with 43rd (Wessex) Brigade to become 1st Artillery Brigade and Headquarters South West.[11][12] The brigade's mission includes commanding, preparing and generating assigned deployable forces. The brigade comprises a large number of units including 1 Royal Horse Artillery and 19 Regiment Royal Artillery,[13] and 15 garrisons and stations across the south west.[14]
In 2014, news articles reported that its personnel had control over the testing of the Watchkeeper Remotely Piloted Aerial System.[15][16]
The brigade used to be under Forces Troops Command but has shifted operational command to 3rd UK Division. Headquarters South West remains as a Regional Point of Command under Regional Command.[17]
Current Structure
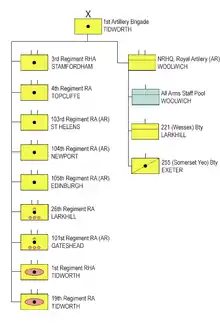
The brigade, which is based at Tidworth Camp,[18] consists of the following units:[19][20]
- Headquarters 1st Artillery Brigade, at Jellalabad Barracks, Tidworth
- National Reserve Headquarters, Royal Artillery, Royal Artillery Barracks, Woolwich – controlling the Watchkeeper pool and providing specialist batteries/troops[19] (Army Reserve)
- 1st Regiment Royal Horse Artillery, Assaye Barracks[21] (to support 12 AI Bde, equipped with AS-90)
- 3rd Regiment Royal Horse Artillery, Albemarle Barracks (to support SEG, equipped with L118 light gun)[21]
- 4th Regiment Royal Artillery, Alanbrooke Barracks (to support Stk Bde, equipped with L118 light gun)[21]
- 19th Regiment Royal Artillery, Bhurtpore Barracks[21] (to support 20 AI Bde, equipped with AS-90)
- 26th Regiment Royal Artillery, Purvis Lines, Larkhill[21] (Divisional fires, equipped with MLRS M270)
- 101st (Northumbrian) Regiment Royal Artillery, Gateshead[21] (Army Reserve – Paired with 26 Regiment RA, equipped with MLRS M270)
- 103rd (Lancashire Artillery Volunteers) Regiment Royal Artillery, St Helens[21] (Army Reserve – Paired with 3 & 4 Regiments RA, equipped with L118 light gun)
- 104th Regiment Royal Artillery, Raglan Barracks[21] (Army Reserve – Paired with 1 Regiment RHA, equipped with L118 light gun)
- 105th (Scottish and Ulster) Regiment Royal Artillery, Edinburgh[21] (Army Reserve – Paired with 19 Regiment RA, equipped with L118 light gun)
Footnotes
- Colin Mackie (1 July 2020). "Generals Jul 2020" (PDF). Colin Mackie. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- "Army 2020 Report, pages 10–12" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 April 2015. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- "Regular Army Basing Announcement, page 1" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 August 2016. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- The British Army in Germany (BAOR and After): An Organizational History 1947 – 2004. 2005. p. 28. ISBN 0 9720296 9 9.
- "BOAR 1989" (PDF).
- "Divisions and Brigades". army.mod.uk. 8 January 2007. Retrieved 8 July 2020.
- "HQ Theatre Troops Organisation". Units & Organisations. 8 January 2007. Retrieved 8 July 2020.
- Tanner, pp. 47–52.
- Staff Officer's Handbook 1999, Serial 68.
- "39th Regiment Royal Artillery". 3 December 2001. Archived from the original on 3 December 2001. Retrieved 8 July 2020.
- "Historic change of command parade in South West". Wessex Reserve Forces' & Cadets' Association. 15 December 2014. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "43 (Wessex) Brigade Lowers Flag For Last Time". Forces TV. Archived from the original on 20 December 2014. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- "Change of Command Parade in South West of England – British Army Website". Archived from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- "Garrisons and stations". Archived from the original on 13 May 2016. Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- "Army cleared to fly next-generation eye-in-the-sky". gov.uk. 5 March 2014. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- Tony Osborne (15 May 2014). "British Pilots Finally Training on Watchkeeper". Aviation Week. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- "Army Update: Commander HQ South West Colonel James Coote DSO OBE" (PDF). swlep.co.uk. Swindon & Wiltshire LEP. 25 May 2017. Retrieved 22 August 2019.
- "3rd (United Kingdom) Division". British Army. Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- "HQ 1st Artillery Brigade". www.army.mod.uk. Retrieved 9 October 2019.
- "Headquarters 1st Artillery Brigade – British Army Website". 4 January 2018. Archived from the original on 4 January 2018. Retrieved 28 October 2019.
- "Royal Artillery:Written question – 68813". parliament.uk. UK Hansard. 21 March 2017. Retrieved 13 October 2019.
References
- Ministry of Defence, Staff Officer's Handbook Number 71038, D/DGD&D/18/35/54, 1999.
- James Tanner, The British Army since 2000, 2014 Osprey Publishing, Oxford, United Kingdom. ISBN 978 178200 593 3.