Zagovory
In Eastern Slavic mythology, zagоvory (singular zagоvor) is a form of verbal folk magic. Users of zagоvory can enchant objects or people.

Etymology
The present-day Russian word zagоvor (Russian: заговор) corresponds to the English word conjuration, which once meant a 'conspiracy, plot, act of plotting'.[1] Zagоvor ('what is performed with speech') originates from Russian folklore. So does the term Nagоvory (Russian: наговор), with its prefix of initiation na- and the root -govor ('speech'), meaning 'what is launched with speech'.
Their slight difference in sense can be seen in constructions like zagovory from maleficium/from bullets (defensive, apotropaic aspect) and nagovory onto water (to make it "healing"). The latter phrase seems to reflect a more offensive action.[Note 1][Note 2]
The Ukrainian zamowliannia (Ukrainian: замовляння) and Belarusian zamowy (Belarusian: замовы) are semantically identical to the Russian zagоvory, as they both possess the root -mov ('speech'). Both of these East Slavic words are close to the Polish term zamawianie. Polish folklore retains rudiments of verbal magic as zamawianie choroby ('popular healing').
History
Zagоvory arose from pagan prayers and incantations, and so was initially based on the belief in the power of the human word. Hence followed the importance of exact pronunciation of the words (whether whispered or sung) as well as exact observing the associated rites. A greate deal of life stamina was obligatory for a rites' performer. As an example of this, a zagоvory practitioner should have either a full set of teeth, or a knife as a symbolic substitute for teeth that were missing.[3]
Originally part of the art of a volkhv (Cyrillic: Волхвы; Polish: wołchw), who disappeared during the prosecution of the Eastern Orthodox Church, the zagоvory tradition survived until the 20th century in popular folk culture, often under the guise of a noncanonical Christian prayer.
In the Russian Empire zagovory praxes were for centuries prosecuted by its church and by its secular, caesaropapist authorities[Note 3] (at least from mid-17th till mid-19th century). Russian archives yielded more than 600 cases of church and civil prosecution of witchcraft, blasphemy and rational heresies in the 18th century.[4] Even in 1832, after Digest of Laws of the Russian Empire had been first codified under the leadership of Mikhail Speransky[Note 4], witchcraft and sorcery still remained a subject of the secular Penal law.[5]
For the sake of survival zagovory tradition began to mimic Christianity. Zagovory imagery became saturated with Christian themes and motifs, used as a reference base for performing magic acts. However within Byzantine written tradition (which embraced the Southern Slavs cultural intermediation) both Christian orthodoxy and some heterodox manuscripts circulated, which might echo back local heathen concepts.
For example, one of the zagovory (apparently influenced by christianization, though representing rather a specific vision) named "how to heal wounds" said "like Jesus Christ having been crucified didn't feel any pain[Note 5], so may the same way not feel any wounds, any illnesses".[6][7]
Another layer in zagovory heritage could be of Western origin. Each of the motifs shared by East and West Slavs has West European (mostly Germanic) matches. This indicates that West Slavic charms served as a mediator between the East Slavic tradition and Western influences.
The magical formula "Stop, blood, as still in the wound, as water/Jesus in the Jordan" is an example of a treated person's bleeding wound assimilation with a Medieval apocryphal story of how the Jordan waters stopped flowing when Jesus entered them. It is attested in Belarus, Ukraine, somewhat rare in South and West Russia. As for other Slavic traditions, the formula occurs in Poland and, even more commonly, in Polish texts recorded in Lithuania; it is also found in Czech charms, though intended against disorders other than bleeding.[7]
Geographically the Eastern Slavic zagovory tradition area could be roughly divided into two subareas.
One of them is the tradition of the Russian North and adjoining Central Russian regions. This tradition was less influenced by neighboring cultures through direct contacts, though strongly influenced by the manuscript tradition. As a result it is not too diverse in the composition of plots and motifs. But the most famous plots, motifs and formulas which are considered an authentic feature of Russian (and all East Slavic) zagovory (such as the motive of the sacred center, Alatyr stone on Buyan island amid holy sea) seem to come from there.
Within the second tradition, covering most of Ukraine and Belarus, as well as the south and west Russian regions, the West and South Slavic (as well as Byzantine) influence manifested itself to the greatest extent. The result is the coexistence and active interaction of plots, motifs and poetic formulas of different origins.[7]
Mythological center and assimilation formulas

While the idea of the mythological center is totally absent in incantations of West and South Slavs, it is known in the folklore of all East Slavs, especially in Russian tradition of zagovory.
In Eastern Slavic folk religion the concept of Navel of the World is embodied by a sacred stone Alatyr (frequently referred as white and hot), located somewhere in the East (either in a pristine ("clear") field or Buyan island amid a holy sea/ocean).
The Alatyr appears in most of the zagovory under a variety of names. Much less than usually it is replaced by a sacred tree (for instance, a willow or a white birch) or a non-specified Christian church.
Appeals to such natural phenomena as dawn with red sun (and Eastern side of the world as such), young (new) moon, stars, winds are also very often.
As to personalized phenomena in those mythopoetic texts, one can see that heathen and Christian characters are often interchangeable. For instance, in different versions of the same zagovory, the supreme power that a practitioner applies to is either Maria (Mother of God) or "Dawn the Red[Note 6] Maiden" (Zorya).[8]
In some of the zagovory a practitioner appeals to Western side of the world for help in maleficium. Nevertheless, the absolute majority of zagovory texts focused on good deeds, such as healing people and livestock, attracting luck, love affairs, wedding protection, birth support and public relations. In Western Siberia a zagovor was written down, named "for good deeds", which should have been read thrice around new moon. It said: "...I behold a young crescent with golden horns, give, my God, golden horns to new moon, so give to me, for good deeds..."[9]
Also, it might be a love wish "just like doves live in love, so would we with so-and-so do..." But sentencing that zagovor from Perm Governorate should have been well-prepared: a guy should have caught and stabbed a dove, kneaded the dough on its fat and baked a kind of a small kalach, then fed a girlfriend with it, saying the above mentioned words.[10]
A recorded in 1648 nagovor onto wax named "how to endure a torture" established that "both heaven and earth are made of bast", and then made a wish "like the dead in the earth don't feel anything, so may so-and-so the same way not feel any atrocities, any tortures".[11]
The most usual beginning of a Russian North zagovor was "I'm getting up blessed, going out through doors and gates to the East, toward Eastern side, to pristine field, to sea-ocean, on to holy God's island... on that island there lies stone Alatyr..."
In the middle of zagovory the wishful part was patterned as assimilation with natural or sacred phenomena, like in this hemostatic example: "... neither stone Alatyr yields any water, nor would I bleed... neither a hen yields any milk, a cock any egg, nor would so-and-so bleed... neither blood from a bone, nor water from a stone..."[12]
The typical ending of zagovory (accompanied by symbolism of both key and lock) often included the statement "May my words be (both) firm and plasteringly adherent".
Notes
- It also reminds difference between evocation and invocation in the Western mystery tradition
- Such descriptive terms as whispering or just words were also in popular use. As an obsolete may be mentioned a recorded in Dal's Dictionary term
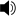 veschba Russian: вещба, made of verb veschati Russian: вещать[2] "tell/speak", "foretell/divine" stem (as in the adjective veschiy Russian: вещий "wise", "cognizant") and -ba suffix, used mainly to form verbal action nouns, like -ing in English, thus meaning "doing of the wise, cognizant". Veschba has deep linguistic roots going back to the Sanskrit word véda "knowledge, wisdom" and the Proto-Indo-European root *u̯eid-, meaning "see" or "know".
veschba Russian: вещба, made of verb veschati Russian: вещать[2] "tell/speak", "foretell/divine" stem (as in the adjective veschiy Russian: вещий "wise", "cognizant") and -ba suffix, used mainly to form verbal action nouns, like -ing in English, thus meaning "doing of the wise, cognizant". Veschba has deep linguistic roots going back to the Sanskrit word véda "knowledge, wisdom" and the Proto-Indo-European root *u̯eid-, meaning "see" or "know". - Formally speaking, Russia became caesaropapist starting from church reform of Peter the Great
- Count Speransky is often referred as 'father of Russian liberalism'
- This is rather a Monophysite idea of the purely divine nature of Christ, different from the Orthodox dogma of Dyophysitism.
- This is a typical in Old Russian language double sense for red as both "of rising sun color" and "beautiful", just like for Red Square.
Sources
- Agapkina, Tatiana (2010). Vostochnoslavyanskie lechebnyezagovory v sravnitel'nom osveshchenii: Syuzhetika i obraz mira (in Russian). Moscow.(«Восточнославянские лечебные заговоры в сравнительном освещении: Сюжетика и образ мира»)
- Madlevskaya, Elena (2007). Russkaya Mifologia. Entsiklopedia (in Russian). Moscow.(Знахарь и знахарка // Русская мифология. Энциклопедия.)
- Viljo Johannes Mansikka Über Russische Zauberformeln mit Berucksichtigung der Blut- und Verrenkungssegen. Helsingfors, 1909. («О русских заговорных формулах. С учётом заговоров на кровь и от вывихов»)
- Viljo Johannes Mansikka Die Religion der Ostslaven. I. Quellen // FF Communications. № 43. Suomalainen Tiedeakatemia. — Helsinki, 1922. («Религия восточных славян»)
- Yudin A.V. Onomastikon russkikh zagovorov: Moskovskii obshchestvennyi nauch. fond // Language: Russian, Moscow, 1997 («Ономастикон русских заговоров»)
- Yudin A.V. Russkaya narodnaya duhovnaya kultura. Vysshaya shkola // Language: Russian ISBN 978-5060045093 («Русская народная духовная культура»)
- Aleksandrov, Aleksei (1997). 777 Zagovorov I Zaklinanii Russkogo Naroda (in Russian). Moscow: Lokid. ISBN 5320002157.
- Maykov L.N. Great Russian Spells – Saint Petersburg: Maykov's Printing House, 1869, 164 Pages; 2nd Edition, Revised and Amended – Saint Petersburg: Publishing House of the European House, 1994
References
- Online Etymology Dictionary accessed 8 January 2020
- Dal Dictionary on-line (in Russian) Accessed 09 January 2020
- Madlevskaya.
- Smilyanskaya, Elena (2003). Volshebniki. Bogohulniki. Eretiki: Narodnaya religioznost' i "dukhovniye prestupleniya" v Rossii XVIII veka (Magicians, Blaspheers, and Heretics: Popular Religiosity and 'Spiritual Crimes' in Eighteenth Century Russia) (in Russian). Moscow: INDRIK. p. 464. ISBN 5-85759-250-X.
- Digest of Laws of the Russian Empire (1832 edition, in Russian)
- Alexandrov, p. 204.
- Agapkina.
- Toporkov, Alexey (1995). "Zarya". Slavyanskaya Mifologiya: Entsiklopedicheskiy slovar (in Russian). Moscow. p. 189. ISBN 5-7195-0057-X.
- Maykov, Leonid (1869). Great Russian Spells (in Russian). Saint Petersburg: Maykov's Printing House. p. 156.
- Maykov, Leonid (1869). Great Russian Spells (in Russian). Saint Petersburg: Maykov's Printing House. p. 19.
- Maykov, Leonid (1869). Great Russian Spells (in Russian). Saint Petersburg: Maykov's Printing House. p. 154.
- Maykov, Leonid (1869). Great Russian Spells (in Russian). Saint Petersburg: Maykov's Printing House. p. 67-68.
External links
- Collection of Russian zagovorov for different occasions in the Russian language.