Whale vocalization
Whale sounds are used by whales for different kinds of communication.[1]
The mechanisms used to produce sound vary from one family of cetaceans to another. Marine mammals, such as whales, dolphins, and porpoises, are much more dependent on sound for communication and sensation than are land mammals, because other senses are of limited effectiveness in water. Sight is less effective for marine mammals because of the particulate way in which the ocean scatters light. Smell is also limited, as molecules diffuse more slowly in water than in air, which makes smelling less effective. However, the speed of sound is roughly four times greater in water than in the atmosphere at sea level. As sea mammals are so dependent on hearing to communicate and feed, environmentalists and cetologists are concerned that they are being harmed by the increased ambient noise in the world's oceans caused by ships, sonar and marine seismic surveys.[2]
The word "song" is used to describe the pattern of regular and predictable sounds made by some species of whales, notably the humpback whale. This is included with or in comparison with music, and male humpback whales have been described as "inveterate composers" of songs that are "'strikingly similar' to human musical traditions".[3] It has been suggested that humpback songs communicate male fitness to female whales.[4] The click sounds made by sperm whales and dolphins are not strictly song, but the clicking sequences have been suggested to be individualized rhythmic sequences that communicate the identity of a single whale to other whales in its group. This clicking sequences reportedly allow the groups to coordinate foraging activities.[5]
Production of sound
Humans produce voiced sounds by passing air through the larynx. Within the larynx, when the vocal cords are brought close together, the passing air will force them to alternately close and open, separating the continuous airstream into discrete pulses of air that are heard as a vibration.[6] This vibration is further modified by speech organs in the oral and nasal cavities, creating sounds which are used in human speech.
Cetacean sound production differs markedly from this mechanism. The precise mechanism differs in the two major suborders of cetaceans: the Odontoceti (toothed whales—including dolphins) and the Mysticeti (baleen whales—including the largest whales, such as the blue whale).
Odontocete whales

Odontocetes produce rapid bursts of high-frequency clicks that are thought to be primarily for echolocation. Specialized organs in an odontocete produce collections of clicks and buzzes at frequencies from 0.2 to 150 kHz to obtain sonic information about its environment. Lower frequencies are used for distance echolocation, due to the fact that shorter wavelengths do not travel as far as longer wavelengths underwater. Higher frequencies are more effective at shorter distances, and can reveal more detailed information about a target. Echoes from clicks convey not only the distance to the target, but also the size, shape, speed, and vector of its movement. Additionally, echolocation allows the odontocete to easily discern the difference between objects that are different in material composition, even if visually identical, by their different densities. Individuals also appear to be able to isolate their own echoes during pod feeding activity without interference from other pod members' echolocations.[7]
Whistles are used for communication, and four- to six-month-old calves develop unique sounds that they use most frequently throughout their lives. Such "signature whistles" are distinctive to the individual and may serve as a form of identification among other odontocetes.[7] Though a large pod of dolphins will produce a wide range of different noises, very little is known about the meaning of the sound. Frankel quotes one researcher who says listening to a school of odontocetes is like listening to a group of children at a school playground.[8]
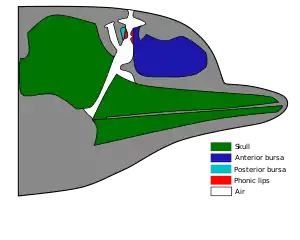
The multiple sounds odontocetes make are produced by passing air through a structure in the head called the phonic lips.[9] The structure is analogous to the human nasal cavity, but the phonic lips act similarly to human vocal cords, which in humans are located in the larynx. As the air passes through this narrow passage, the phonic lip membranes are sucked together, causing the surrounding tissue to vibrate. These vibrations can, as with the vibrations in the human larynx, be consciously controlled with great sensitivity.[9] The vibrations pass through the tissue of the head to the melon, which shapes and directs the sound into a beam of sound useful in echolocation. Every toothed whale except the sperm whale has two sets of phonic lips and is thus capable of making two sounds independently.[10] Once the air has passed the phonic lips it enters the vestibular sac. From there, the air may be recycled back into the lower part of the nasal complex, ready to be used for sound creation again, or passed out through the blowhole.
The French name for phonic lips, museau de singe, translates literally as "monkey's muzzle", which the phonic lip structure is supposed to resemble.[11] New cranial analysis using computed axial and single photon emission computed tomography scans in 2004 showed, at least in the case of bottlenose dolphins, that air might be supplied to the nasal complex from the lungs by the palatopharyngeal sphincter, enabling the sound creation process to continue for as long as the dolphin is able to hold its breath.[12]
Mysticete whales
Baleen whales (formally called mysticetes) do not have phonic lip structure. Instead, they have a larynx that appears to play a role in sound production, but it lacks vocal cords, and scientists remain uncertain as to the exact mechanism.[13] The process, however, cannot be completely analogous to humans, because whales do not have to exhale in order to produce sound. It is likely that they recycle air around the body for this purpose.[14] Cranial sinuses may also be used to create the sounds, but again, researchers are currently unsure how.
Vocal plasticity and acoustic behavior
There are at least nine separate blue whale acoustic populations worldwide.[15] Over the last 50 years blue whales have changed the way they are singing. Calls are progressively getting lower in frequency. For example the Australian pygmy blue whales are decreasing their mean call frequency rate at approximately 0.35 Hz/year.[16]
The migration patterns of blue whales remains unclear. Some populations appear to be resident in habitats of year-round high productivity in some years,[17] while others undertake long migrations to high-latitude feeding grounds, but the extent of migrations and the components of the populations that undertake them are poorly known.[18]
Sound levels
The frequency of baleen whale sounds ranges from 10 Hz to 31 kHz.[19] A list of typical levels is shown in the table below.
| Source | Broadband source level (dB re 1 Pa at 1m)[20] |
|---|---|
| Fin whale moans | 155–186 |
| Blue whale moans | 155–188 |
| Gray whale moans | 142–185 |
| Bowhead whale tonals, moans and song | 128–189 |
Purpose of whale-created sounds
While the complex sounds of the humpback whale (and some blue whales) are believed to be primarily used in sexual selection,[21] the simpler sounds of other whales have a year-round use. While toothed whales are capable of using echolocation to detect the size and nature of objects, this capability has never been demonstrated in baleen whales. Further, unlike some fish such as sharks, a whale's sense of smell is not highly developed.[22] Thus, given the poor visibility of aquatic environments and that sound travels so well in water, sounds audible to humans may play a role in navigation. For instance, the depth of water or the existence of a large obstruction ahead may be detected by loud noises made by baleen whales.
The question of whether whales sometimes sing purely for aesthetic enjoyment, personal satisfaction, or 'for art's sake', is considered by some to be "an untestable question".[23]
Song of the humpback whale
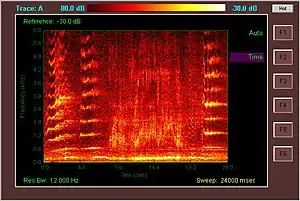
Two groups of whales, the humpback whale and the subspecies of blue whale found in the Indian Ocean, are known to produce a series of repetitious sounds at varying frequencies known as whale song. Marine biologist Philip Clapham describes the song as "probably the most complex in the animal kingdom."[24]
Male humpback whales perform these vocalizations often during the mating season, and so it is believed the purpose of songs is to aid mate selection.[8]
Interest in whale song was aroused by researchers Roger Payne and Scott McVay after the songs were brought to their attention by a Bermudian named Frank Watlington who was working for the US government at the SOFAR station listening for Russian submarines with underwater hydrophones off the coast of the island.[25] Payne released the best-selling Songs of the Humpback Whale in 1970, and the whale songs were quickly incorporated into human music by, among others, singer Judy Collins.
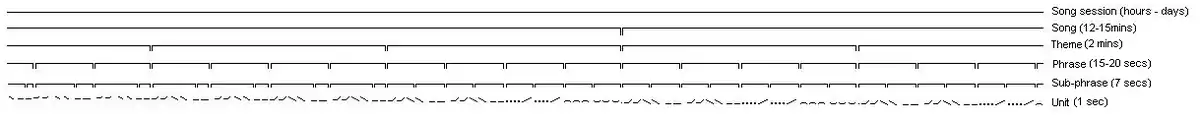
The songs follow a distinct hierarchical structure. The base units of the song (sometimes loosely called the "notes") are single uninterrupted emissions of sound that last up to a few seconds. These sounds vary in frequency from 20 Hz to upward of 24 kHz (the typical human range of hearing is 20 Hz to 20 kHz). The units may be frequency modulated (i.e., the pitch of the sound may go up, down, or stay the same during the note) or amplitude modulated (get louder or quieter). However, the adjustment of bandwidth on a spectrogram representation of the song reveals the essentially pulsed nature of the FM sounds.
A collection of four or six units is known as a sub-phrase, lasting perhaps ten seconds (see also phrase (music)).[8] A collection of two sub-phrases is a phrase. A whale will typically repeat the same phrase over and over for two to four minutes. This is known as a theme. A collection of themes is known as a song.[8] The whale song will last up to 30 or so minutes, and will be repeated over and over again over the course of hours or even days.[8] This "Russian doll" hierarchy of sounds suggests a syntactic structure[26] that is more human-like in its complexity than other forms of animal communication like bird songs, which have only linear structure.[27]
All the whales in an area sing virtually the same song at any point in time and the song is constantly and slowly evolving over time. For example, over the course of a month a particular unit that started as an upsweep (increasing in frequency) might slowly flatten to become a constant note.[8] Another unit may get steadily louder. The pace of evolution of a whale's song also changes—some years the song may change quite rapidly, whereas in other years little variation may be recorded.[8]

Whales occupying the same geographical areas (which can be as large as entire ocean basins) tend to sing similar songs, with only slight variations. Whales from non-overlapping regions sing entirely different songs.[8]
As the song evolves, it appears that old patterns are not revisited.[8] An analysis of 19 years of whale songs found that while general patterns in song could be spotted, the same combination never recurred.
Humpback whales may also make stand-alone sounds that do not form part of a song, particularly during courtship rituals.[28] Finally, humpbacks make a third class of sound called the feeding call. This is a long sound (5 to 10 s duration) of near constant frequency. Humpbacks generally feed cooperatively by gathering in groups, swimming underneath shoals of fish and all lunging up vertically through the fish and out of the water together. Prior to these lunges, whales make their feeding call. The exact purpose of the call is not known.
Some scientists have proposed that humpback whale songs may serve an echolocative purpose,[29] but this has been subject to disagreement.[30]
Other whale sounds
Humpback whales have also been found to make a range of other social sounds to communicate such as "grunts", "groans", "thwops", "snorts" and "barks".[31]
Most baleen whales make sounds at about 15–20 hertz. However, a team of marine biologists, led by Mary Ann Daher of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, reported in New Scientist in December 2004 that they had been tracking a whale in the North Pacific for 12 years that was "singing" at 52 Hz.[32] The scientists are unable to explain this dramatic difference from the norm; however, they believe the whale is baleen[33] and unlikely to be a new species,[32] suggesting that currently known species may have a wider vocal range than previously thought. There is disagreement in the scientific community regarding the uniqueness of the whale's vocalization[34] and whether it is a member of a hybrid whale[34] such as the well documented blue and fin whale hybrids.[35]
In 2009, researchers found that blue whale song has been deepening in its tonal frequency since the 1960s.[36] While noise pollution has increased ambient ocean noise by over 12 decibels since the mid-20th century, researcher Mark McDonald indicated that higher pitches would be expected if the whales were straining to be heard.[37]
Killer whales have been observed to produce long range calls that are stereotyped and high frequency travelling distances from 10–16 km (6.2–9.9 mi) as well as short range calls that can travel distances from 5–9 km (3.1–5.6 mi). Short range calls are reported during social and resting periods while long range are more commonly reported during foraging and feeding.[38]
Most other whales and dolphins produce sounds of varying degrees of complexity. Of particular interest is the Beluga (the "sea canary") which produces an immense variety of whistles, clicks and pulses.[39][40]
Human interaction


Researchers use hydrophones (often adapted from their original military use in tracking submarines) to ascertain the exact location of the origin of whale noises. Their methods also allow them to detect how far through an ocean a sound travels. Research by Dr. Christopher Clark of Cornell University conducted using military data showed that whale noises travel for thousands of kilometres.[41] As well as providing information about song production, the data allows researchers to follow the migratory path of whales throughout the "singing" (mating) season. An important finding is that whales, in a process called the Lombard effect, adjust their song to compensate for background noise pollution.[42] Moreover, there is evidence that blue whales stop producing foraging D calls once a mid-frequency sonar is activated, even though the sonar frequency range (1–8 kHz) far exceeds their sound production range (25–100 Hz).[2]
Prior to the introduction of human noise production, Clark says the noises may have travelled right from one side of an ocean to the other, agreeing with a thirty-year-old concept blaming large-scale shipping.[41] His research indicates that ambient noise from boats is doubling with each decade.[41] This has the effect of reducing the range at which whale noises can be heard. Environmentalists fear that such boat activity is putting undue stress on the animals as well as making it difficult to find a mate.[41]
In the past decade, many effective automated methods, such as signal processing, data mining, and machine learning techniques have been developed to detect and classify whale vocalizations.[43][44]
Media
Selected discography
- Songs of the Humpback Whale (SWR 118) was originally released in 1970 by CRM Records from recordings made by Roger Payne, Frank Watlington, and others. The LP was later re-released by Capitol Records, published in a flexible format in the National Geographic Society magazine, Volume 155, Number 1, in January 1979, re-released by Living Music/Windham Hill/BMG Records on CD in 1992, and remastered on CD by BGO-Beat Goes On in 2001.
- Deep Voices: The Second Whale Record (Capitol/EMI Records 0777 7 11598 1 0) was released on LP in 1977 from additional recordings made by Roger Payne, and re-released on CD in 1995 by Living Music/Windham Hill/BMG Records. It includes recordings of humpbacks, blues, and rights.
- Northern Whales (MGE 19) was released by Music Gallery Editions from recordings made by Pierre Ouellet, John Ford, and others affiliated with Interspecies Music and Communication Research. It includes recordings of belugas, narwhals, orca, and bearded seals.
- Sounds of the Earth: Humpback Whales (Oreade Music) was released on CD in 1999.
- Rapture of the Deep: Humpback Whale Singing (Compass Recordings) was released on CD in 2001.
- Songlines: Songs of the East Australian Humpback whales. was released in 2009.
History
Whaling Captain Wm. H. Kelly was the first person known to recognize whale singing for what it was, while on the brig Eliza in the Sea of Japan in 1881.[45][46]
References
- Communication and behavior of whales, R Payne. 1983. Westview Press.
- Melcón, Mariana L.; Cummins, Amanda J.; Kerosky, Sara M.; Roche, Lauren K.; Wiggins, Sean M.; Hildebrand, John A. (2012). Mathevon, Nicolas (ed.). "Blue Whales Respond to Anthropogenic Noise". PLOS ONE. 7 (2): e32681. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...732681M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032681. PMC 3290562. PMID 22393434.
- Payne Roger, quoted in: Author(s): Susan Milius. "Music without Borders", p. 253. Source: Science News, Vol. 157, No. 16, (15 April 2000), pp. 252-254. Published by: Society for Science & the Public.
- Wright, A.J.; Walsh, A (2010). "Mind the gap: why neurological plasticity may explain seasonal interruption in humpback whale song". Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 90 (8): 1489–1491. doi:10.1017/s0025315410000913.
- Michel Andre and Cees Kamminga (2000) Rhythmic dimension in the echolocation click trains of sperm whales: a possible function of identification and communication Journal of Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, Vol. 80, pp. 163-169.
- "How do marine mammals produce sounds?". July 2009. Retrieved 15 October 2013.
- "Page not found - Dolphin Research Center". Dolphin Research Center. Cite uses generic title (help)
- Frankel, Adam S. "Sound production", Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals, 1998, pp. 1126–1137. ISBN 0-12-551340-2.
- Cranford, Ted W.; Elsberry, Wesley R.; Bonn, William G. Van; Jeffress, Jennifer A.; Chaplin, Monica S.; Blackwood, Diane J.; Carder, Donald A.; Kamolnick, Tricia; Todd, Mark A. (2011). "Observation and analysis of sonar signal generation in the bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus): Evidence for two sonar sources". Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology. 407 (1): 81–96. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2011.07.010.
- Fitch, W. T.; Neubauer, J.; Herzel, H. (2002). "Calls out of chaos: the adaptive significance of nonlinear phenomena in mammalian vocal production". Anim. Behav. 63 (3): 407–418. doi:10.1006/anbe.2001.1912. S2CID 16090497.
- Ted W. Cranford. "Selected Whale Sciences Images - Volume 1". Retrieved 20 October 2010.
- Houser, Dorian S.; Finneran, James; Carder, Don; Van Bonn, William; Smith, Cynthia; Hoh, Carl; Mattrey, Robert; Ridgway, Sam (2004). "Structural and functional imaging of bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) cranial anatomy". Journal of Experimental Biology. 207 (Pt 21): 3657–3665. doi:10.1242/jeb.01207. PMID 15371474.
- Dvorsky, George; Gadye, Levi. "Why Whale Songs Are Still One Of Science's Greatest Mysteries". Gizmodo. Retrieved 8 June 2016.
- Reidenberg, JS; Laitman, JT (2007). "Discovery of a low frequency sound source in Mysticeti (baleen whales): anatomical establishment of a vocal fold homolog". Anatomical Record. 290 (6): 745–59. doi:10.1002/ar.20544. PMID 17516447. S2CID 24620936.
- McDonald, MA, Messnick SL, Hildebrand JA (2006). "Biogeographic characterisation of blue whale song worldwide: using song to identify populations" (PDF). Journal of Cetacean Research and Management. 8: 55–65.
- Tripovich, Joy S.; Klinck, Holger; Nieukirk, Sharon L.; Adams, Tempe; Mellinger, David K.; Balcazar, Naysa E.; Klinck, Karolin; Hall, Evelyn J. S.; Rogers, Tracey L. (22 May 2015). "Temporal segregation of the Australian and Antarctic blue whale call types (Balaenoptera musculus spp.)". Journal of Mammalogy. 96 (3): 603–610. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyv065. PMC 4668953. PMID 26937046.
- Tripovich, Joy S.; Klinck, Holger; Nieukirk, Sharon L.; Adams, Tempe; Mellinger, David K.; Balcazar, Naysa E.; Klinck, Karolin; Hall, Evelyn J. S.; Rogers, Tracey L. (2015). "Temporal segregation of the Australian and Antarctic blue whale call types (Balaenoptera musculusspp.)". Journal of Mammalogy. 96 (3): 603–610. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyv065. PMC 4668953. PMID 26937046.
- Cooke, J.G. (2018). "Balaenoptera musculus (errata version published in 2019)". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T2477A156923585. Retrieved 27 January 2020.
- Richardson, Greene, Malme, Thomson (1995). Marine Mammals and Noise. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-588440-2.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Kuperman, Roux (2007). "Underwater Acoustics". In Rossing, Thomas D. (ed.). Springer Handbook of Acoustics. Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-30446-5.
- Smith, Joshua N.; Goldizen, Anne W.; Dunlop, Rebecca A.; Noad, Michael J. (2008). "Songs of male humpback whales, Megaptera novaeangliae, are involved in intersexual interactions". Animal Behaviour. 76 (2): 467–477. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2008.02.013. S2CID 29660106.
- Kishida, Takushi; Thewissen, JGM; Hayakawa, Takashi; Imai, Hiroo; Agata, Kiyokazu (13 February 2015). "Aquatic adaptation and the evolution of smell and taste in whales". Zoological Letters. 1: 9. doi:10.1186/s40851-014-0002-z. ISSN 2056-306X. PMC 4604112. PMID 26605054.
- Entomologist and ecologist Thomas Eisner called it "an untestable question in scientific terms", quoted in: Milius (2000), p. 254
- Clapham, Philip (1996). Humpback whales. Colin Baxter Photography. ISBN 978-0-948661-87-7.
- Rothenberg, David (2008). Thousand mile song. Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-07128-9.
- Suzuki, R; Buck, JR; Tyack, PL (2006). "Information entropy of humpback whale songs". J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 119 (3): 1849–66. Bibcode:2006ASAJ..119.1849S. doi:10.1121/1.2161827. PMID 16583924.
- Berwick, R. C., Okanoya, K., Beckers, G. J. L., & Bolhuis, J. J. (2011). Songs to syntax: The linguistics of birdsong. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15(3), 113–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2011.01.002
- Mattila, David. K; Guinee, Linda N.; Mayo, Charles A. (1987). "Humpback Whale Songs on a North Atlantic Feeding Ground". Journal of Mammalogy. 68 (4): 880–883. doi:10.2307/1381574. JSTOR 1381574.
- Mercado, E. III & Frazer, L.N. (2001). "Humpback whale song or humpback whale sonar? A Reply to Au et al" (PDF). IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering. 26 (3): 406–415. Bibcode:2001IJOE...26..406M. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.330.3653. doi:10.1109/48.946514. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 June 2007.
- W. W. L. Au; A. Frankel; D. A. Helweg & D. H. Cato (2001). "Against the humpback whale sonar hypothesis". IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering. 26 (2): 295–300. Bibcode:2001IJOE...26..295A. doi:10.1109/48.922795.
- Cecilia Burke, ''A whale's varied vocabulary', Australian Geographic, AG Online. Retrieved 7 August 2010.
- "Lonely whale's song remains a mystery". New Scientist. Reed Business Information Ltd. 11 December 2004. Retrieved 12 July 2009.
- "Strange-voiced whale at large in the ocean". Daily Times. Associated Press. 13 December 2004. Retrieved 12 July 2009.
- Baraniuk, Chris. "The World's Lonielist Whale May not be Alone After All". BBC. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- Berube, Martine; Aguilar, Alex (January 1998). "A New Hybrid Between a Blue Whale, Balaenoptera Musculus, and a Fin Whale, B. Physalus: Frequency and Implications of Hybridization". Marine Mammal Science. 14 (1): 82–98. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1998.tb00692.x.
- McDonald, Mark A., Hildebrand, John A., Mesnick, Sarah. Worldwide decline in tonal frequencies of blue whale songs. Endangered Species Research, Vol. 9 No. 1 23 October 2009.
- Keim, Brandon. Blue Whale Song Mystery Baffles Scientists. Wired (magazine). 2 December 2009.
- Miller, Patrick J. O. (11 January 2006). "Diversity in sound pressure levels and estimated active space of resident killer whale vocalizations". Journal of Comparative Physiology A. 192 (5): 449–459. doi:10.1007/s00359-005-0085-2. hdl:1912/532. ISSN 0340-7594. PMID 16404605. S2CID 22673399.
- ePluribus Media. "The Canaries of the Sea, granted a pardon, this time…". Retrieved 7 August 2010.
- "Beluga Whales – Communication and Echolocation". Sea World.org. Retrieved 30 July 2010.
- Bentley, Molly (28 February 2005). "Unweaving the song of whales". BBC News. Retrieved 12 July 2009.
- Scheifele, PM; Andrew, S; Cooper, RA; Darre, M; Musiek, FE; Max, L (2005). "Indication of a Lombard vocal response in the St. Lawrence River Beluga". The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 117 (3 Pt 1): 1486–92. Bibcode:2005ASAJ..117.1486S. doi:10.1121/1.1835508. PMID 15807036.
- M. Pourhomayoun, P. Dugan, M. Popescu, and C. Clark, "Bioacoustic Signal Classification Based on Continuous Region Features, Grid Masking Features and Artificial Neural Network," International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2013.
- 7. M. Popescu, P. Dugan, M. Pourhomayoun, and C. Clark, "Periodic Pulse Train Signal Detection and Classification using Spectrogram Intensity Binarization and Energy Projection," International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2013.
- Aldrich, Herbert L. (1889). "Whaling". The Outing Magazine: 113–123. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- Aldrich, Herbert Lincoln (1889). Arctic Alaska and Siberia, Or, Eight Months in Arctic Alaska and Siberia with the Arctic Whalemen. Chicago and New York: Rand, McNally & Co. pp. 32–35. Archived from the original on 20 August 2008. Retrieved 22 July 2018.
General references
- Lone whale's song remains a mystery, New Scientist, issue number 2477, 11 December 2004
- Frazer, L.N. & Mercado. E. III. (2000). "A sonar model for humpback whale song". IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering. 25 (1): 160–182. Bibcode:2000IJOE...25..160F. doi:10.1109/48.820748. S2CID 44297027.
- Helweg, D.A., Frankel, A.S., Mobley Jr, J.R. and Herman, L.M., "Humpback whale song: our current understanding," in Marine Mammal Sensory Systems, J. A. Thomas, R. A. Kastelein, and A. Y. Supin, Eds. New York: Plenum, 1992, pp. 459–483.
- In search of impulse sound sources in odontocetes by Ted Cranford in Hearing by whales and dolphins (W. Lu, A. Popper and R. Fays eds.). Springer-Verlag (2000).
- Progressive changes in the songs of humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae): a detailed analysis of two seasons in Hawaii by K.B.Payne, P. Tyack and R.S. Payne in Communication and behavior of whales. Westview Press (1983)
- "Unweaving the song of whales". BBC News. 28 February 2005.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Audio files of Balaenopteridae. |
- Voices in the Sea has whale and dolphin sounds and interpretive videos
- Cornell University's Bioacoustics Research Program
- Right Whale Listening Network, a project of the above bioacoustics program at Cornell
- Whale Songs at the Avant Garde Project has FLAC files made from high-quality LP transcriptions.
- Perspectives in Ocean Science Listening to Whales, John Hildebrand, Scripps Institution of Oceanography
- The British Library Sound Archive contains over 150,000 recordings of animal sounds and natural atmospheres from around the world.
- Songlines: Songs of the East Australian Humpback whales.
- Recording of the bearded seal's "spiralling trill," one of the most phenomenal vocalizations of the underwater kingdom
- Watkins Marine Mammal Sound Database, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and New Bedford Whaling Museum