Udmurt alphabets
Since its inception in the 18th century and up to the present, it is based on the Cyrillic alphabet to write the Udmurt language. Attempts were also made to use the Latin alphabet to write the Udmurt language. In its modern form, the Udmurt alphabet was approved in 1937.
History
XVIII century
The question of dating the emergence of the Udmurt writing is controversial and related to the question of what is generally considered the beginning of writing in a particular language. Various researchers count the history of Udmurt writing from different events - the first records of the Udmurt language material (1726), the publication of the first small translated texts (1769), the publication of the first grammar (1775), the publication of the first Udmurt books with a coherent text and a certain graphics system (1847).[1]
The first known fixation of the Udmurt language material dates back to 1726. It was produced by Daniel Messerschmidt using the Latin alphabet. The dictionary of 400 Udmurt words compiled by him was not published at that time and remained unknown to science until the end of the 20th century (first published in 2001).[2] The first printed edition with the recording of Udmurt words was the book by Philip Strahlenberg "Das Nord- und Ostliche Theil von Europa und Asia ...", published in 1730. It also used the Latin alphabet.[3] Later, the Latin alphabet for fixing the Udmurt language was used in the works of Gerhard Müller and Johann Fisher (mid-18th century). To write Udmurt words, these authors used various graphic systems:[4]
| UPA | Messerschmidt | Strahlenberg | Müller | Fischer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| i̮, ә̑ | e, i, ö, u, y, yi | e, i, y | a, e, i, o, ui, ü, y | e, i, u, ui, ü, y |
| e̮ | ö, öe, y | ee, iö | e, i, ö, ü | e, i, u, ü |
| e | æ, e | e | a, ä, e, ie, ü | ä, e, i, ie |
| č | tsch | - | tsch | tsch |
| č́ | tsch | - | tsch | tsch |
| ǯ | - | - | dsch | dsch |
| ǯ́ | ds, dsh, sh, ss | - | dsch | dsch |
| š | sch | - | sch | sch |
| ž | sh | - | sch | sch |
| ŋ | hn, ng | - | n, ng | n |
| u̯ | hw, wu | - | - | w |
In the second half of the 18th century, texts written in the Udmurt language began to appear. The first of these was a poem published in a multilingual solemn collection dedicated to the arrival of Catherine II in Kazan in 1769. This is a small text (24 words) written in Cyrillic letters. Another Udmurt poem was published in a similar collection of 1782.[5] There are also other short Udmurt texts in Cyrillic printed at that time[6]..
In 1775, the first Udmurt grammar was published - “Сочинения, принадлежащие к грамматике вотского языка“ (Works belonging to the grammar of the Votyak language). This edition used the Cyrillic alphabet, which included most of the letters of the then Russian alphabet (except for ф, х, щ, ѳ, ѵ), as well as additional characters G g, ê, и̂, î, ї, ô, э̂.[7]
At the end of the 18th century, a number of Udmurt dictionaries and grammars were also compiled. Of these, only Peter Pallas's dictionary (1787-1791) and the Russian translation of Müller's dictionary (1791) were published. Z. Krotov's dictionary (1785) and M. Mogilin's grammar (1786) remained in manuscripts. In all these works, various graphic systems based on the Cyrillic basis were used:[7]
| UPA | Müller | Pallas | Poems of 1769,1782 | Grammar of 1775 | Krotov | Mogilin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| e̮ | е, у, э, ю | е, о, ы, э | е, ъе, э, | а, е, о, э | е, о, ы, э, я | е, ɛ, о, ъе, ъ̂е, ы, э |
| je̮ | е | е | - | іê, ѣ | jê, ѣ | іе, іê, ѣ |
| i̮ | а, е, и, уи, ы, ю | и, ы | и, ы | и, ы | и, ы | и, ы |
| ǯ | дж | ж | - | дж | дж | дж |
| ǯ́ | дж, дз, з, ч | дж, дз, з | дз, дч, з | дз, з | дз | дз, з |
| č́ | ч | ц, ч | ц | ц, ч | ц, ч | ц, ч |
| č | ч | ч | ч | ч | ч | ч |
| ŋ | н, нг | нг | - | н, нg | н, нg | - |
| u̯ | - | у, ув | у | у, ув | у, ув | у, ув |
First half of the XIX century
In the first half of the 19th century, various authors continued to compile Udmurt dictionaries and grammars, but all of them remained in manuscripts at that time. These works used the Russian Cyrillic alphabet, sometimes with the addition of individual characters, such as j and g, as well as the superscript circumflex diacritic mark (ˆ).[8]
From the beginning of the 19th century, the question of translating Orthodox literature into the Udmurt language, primarily the Gospels, was raised. The first translations were made in 1803, but for various reasons, their release was constantly postponed and dragged on for more than 40 years.[8] Finally, in 1847–1849, the first Udmurt books were published, with 5 titles at once (the dating of the first Udmurt books in 1823 is erroneous[9]). These were the Gospel of Matthew and the Gospel of Mark in the Glazov dialect, the Gospel of Matthew in the Sarapul dialect and two alphabets - one in the Glazov dialect, the other in the Sarapul dialect.[10] The alphabets contain the following alphabet:[11] А а, Б б, В в, Г г, Д д, Е е, Ж ж, G g, З з, И и, І і, К к, Л л, М м, Н н, О о, П п, Р р, С с, Т т, У у, Ф ф, Х х, Ц ц, Ч ч, Ш ш, Щ щ, Ъ ъ, Ы ы, Ь ь, Ѣ ѣ, Э э, Ю ю, Я я, Ѳ ѳ, Ѵ ѵ. In fact, the alphabets also used the iô digraph.[12] A similar graphic system was used in the Gospels. The sound, now denoted by the letter ӝ, was transmitted through ж and дж; ӟ - through з and дз; ч - through с, ц and ч; ӵ - through ч; ӧ - through е, э and о.[13] These alphabets are graphically based on the alphabet of the first Udmurt grammar of 1775.[14]
From the middle of the XIX century
After the first Udmurt books appeared and until the early 1870s, new Udmurt publications appeared sporadically. Their alphabets continued the graphic traditions of 1775 grammar and represented Russian practical transcription.[15] For example, the alphabet “Лыдзонъ” published in 1867 contained all the letters of the then Russian alphabet without any additional characters for specific sounds of the Udmurt language.[16]

In the mid-70s of the XIX century, the enlightener Nikolay Ilminsky developed a uniform graphic system (based on the transcriptional alphabet adopted in the then Russian linguistics on the Cyrillic basis) for the languages of the peoples of the Ural-Volga region (Mari, Udmurt, Chuvash, baptized Tatar). Unlike the alphabet of the previous time and from the modern Udmurt writing, Ilminsky's writing was based not on the syllabic, but on the phonemic principle.[15]
In 1895, Grigoriy Vereshchagin, in his work "О книгах на вотском языке" (About books in the Votyak Language), examined the graphic systems used in the Udmurt books of the 1880s and 1890s and proposed his own version of the alphabet, which, however, did not find practical application. Vereshchagin's alphabet project looked like this:[18] А а, Б б, В в, Г г, Д д, Е е, Э э, Ж ж, З з, Ԫ ԫ, Ꚉ ꚉ, І і, Ј ј, К к, Л л, М м, Н н, О о, Ӧ ӧ, П п, Р р, Ԛ ԛ, С с, Т т, У у, Ц ц, Ч ч, Ӵ ӵ, Ш ш, ЧШ чш (ligature), Ы ы.
In 1897, Kazan publishers adopted a compromise graphic system based on a modernized Russian alphabet using additional glyphs with diacritics (partly borrowed from Ilminsky's letter, partly invented again after his model). It is this system that underlies the modern Udmurt writing.[15] So, in the “Краткий славяно-вотский словарь” (Concise Slavic-Votyak Dictionary), published in Kazan in 1897, the Russian alphabet and additional letters Ӝ ӝ, Ӟ ӟ, І і, Ј ј, Ӥ ӥ, Ӧ ӧ, Ў ў, Ӵ ӵ are used.[19] In 1898, an alphabet of this type appeared in the educational literature.[20] The first Udmurt newspaper «Войнаысь ивор», which began to be published in 1915, was of great importance for the stabilization of the alphabet and spelling. The newspaper materials contained the letters Ӝ ӝ, Ӟ ӟ, Ӧ ӧ, Ӵ ӵ, Ы̆ ы̆.[19]
In 1924, the first edition of the textbook “Удмурт кылрадъян” was published. In it, the Udmurt alphabet already had an almost modern look, with the exception of the letters Ф ф, Х х, Ц у, Щ щ. At the same time, it was stipulated that these letters could be used in Russian words. In the early 1930s, the letters Ф ф, Х х, Ц у, Щ щ were introduced into the Udmurt alphabet, and it took on a modern form. This was finally approved at a language conference in 1937. Since then, the Udmurt alphabet has not been changed, only the spelling has been refined.[19]
- Primer for baptized votyaks. Kazan, 1875, 1882: there are letters Ӓ ӓ, Ӗ ӗ,
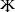
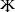 , І і, J ȷ, Ӆ ӆ, Ҥ ҥ, Ԣ ԣ, Ŏ ŏ, Ҫ ҫ, Ꚋ ꚋ, Ӱ ӱ, Ѳ ѳ, Ы̆ ы̆. None letters Ё ё, Ӝ ӝ, Ӟ ӟ, Ӥ ӥ, Й й, Ц ц, Ӵ ӵ, Щ щ, ъ, ь.
, І і, J ȷ, Ӆ ӆ, Ҥ ҥ, Ԣ ԣ, Ŏ ŏ, Ҫ ҫ, Ꚋ ꚋ, Ӱ ӱ, Ѳ ѳ, Ы̆ ы̆. None letters Ё ё, Ӝ ӝ, Ӟ ӟ, Ӥ ӥ, Й й, Ц ц, Ӵ ӵ, Щ щ, ъ, ь. - Primer for Votyak children of the Sarapul uyezd. Kazan, 1882: J ȷ, Ԡ ԡ, Ҥ ҥ, Ԣ ԣ, Ҫ ҫ, Ꚋ ꚋ, Ӳ ӳ, Ѣ ѣ, Ѳ ѳ. None letters Ё ё, Ӝ ӝ, Ӟ ӟ, Ӥ ӥ, Й й, Ц ц, Ӵ ӵ, Щ щ.
- Primer and first educational book for votyaks of the Yelabuga uyezd. Kazan, 1889: there are letters І і, Ҥ ҥ, Ŏ ŏ, Ҷ ҷ. None letters Ӝ ӝ, Ӟ ӟ, Ӥ ӥ, Й й, Ӧ ӧ, Ф ф, Х х, Ц ц, Ӵ ӵ, Щ щ.
- Primer for Votyak children. Kazan, 1898, 1907: there are letters І і, J ȷ. None letters Ф ф, Х х, Ц ц, Щ щ.
- Primer for Votyak children. Kazan, 1912, 1917: there are letters І і, J ȷ, Ҥ ҥ. None letters Ф ф, Х х, Ц ц, Щ щ.
- «Вуоно улон — огъя улон». Izhevsk, 1924: None letters Ф ф, Х х, Ц ц, Щ щ, Ъ ъ.
Modern alphabet
The Udmurt alphabet consists of 38 letters:[20]
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | Ӝ ӝ | З з |
| Ӟ ӟ | И и | Ӥ ӥ | Й й | К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | Ӧ ӧ |
| П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф | Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ӵ ӵ |
| Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
The Udmurt alphabet includes all 33 letters of the Russian alphabet, as well as 5 additional letters. The rules for reading them are similar to those in Russian, which allows you to borrow Russian words while preserving their spelling. The letters Ф ф, Х х, Ц у, Щ щ are not used in words of Udmurt origin.[21]
The letter Ӥ ӥ ("dot-son I") denotes the same vowel as the letter И и and, but, unlike it, does not cause the softness of the preceding consonant. The letter Ӧ ӧ denotes a special uncorrupted middle-rise back vowel ([ʌ] in IPA). The letters Ӝ ӝ, Ӟ ӟ, Ӵ ӵ are used for specific affricates - combinations of two conjointly pronounced consonants. The letter Ӵ ӵ represents the affricate /t͡ʃ/ and is a hard variant of Ч ч. The letter Ӝ ӝ is the affricate /d͡ʒ/ and is a voiced variant of Ӵ ӵ. The letter Ӟ ӟ is an affricate /d͡ʑ/, a soft version Ӝ ӝ and a voiced version of Ч ч.[22]
Unaccepted reform
.png.webp)
.jpg.webp)
At the turn of the 1920s and 1930s, the process of latinisation was going on in the USSR - the translation of the written languages of the peoples of the country to a Latin graphic basis. As part of this process, a discussion about the reform of the Udmurt alphabet flared up. In the late 1920s, a number of proposals related to the reform of the existing Cyrillic alphabet. So, in 1928, Innaki Kelda proposed replacing the three in the letters ӝ, ӟ, ӧ, ӵ with check marks at the top; the softness of the letters д, з, л, н, с, т should be denoted with a sub-letter comma, and at the beginning of a word, instead of iotated vowels, write the letter ј. At the same time, D.I. Korepanov proposed to introduce special iotated letters to denote the sounds [йы] and [йӧ]. Dmitriy Bubrikh proposed to exclude iotated vowels from the alphabet and replace и with i.[19]
The question of translating the Udmurt alphabet into the Latin alphabet was first raised in 1927 by the academic center of the Votyak regional department of public education. In 1928, the first draft of the Latinized alphabet was drawn up. In May 1930, at a regional party conference, a discussion took place about the possible romanization and the appearance of the new alphabet. At the same time it was decided to develop a unified Latinized alphabet for closely related Udmurt and Komi languages, which was done in 1931.[23] In the summer of 1931, the unified Komi-Udmurt Latinized alphabet was approved, after which its introduction into life was to begin. However, if the Komi alphabet was introduced a year later, then in Udmurtia no real steps were taken to implement this project. B. Grande wrote that by December 1932 no steps had been taken towards a real transition to the Latin script, the reason for which was the negative attitude of the regional authorities towards the reform in general and the lack of funding.[24]
As a result, by the mid-1930s, the transition of the Udmurt script to the Latin alphabet was still not implemented, but by that time the state policy in relation to the scripts of national minorities had changed - the transition to the Cyrillic alphabet began. Thus, the graphical system of Udmurt writing remained unchanged.[25][26]
See also
References
- Ившин 2010, p. 18—19.
- Ившин 2010, p. 28.
- Ившин 2010, p. 32.
- Ившин 2010, p. 46.
- Ившин 2010, p. 51.
- Ившин 2010, p. 59.
- Ившин 2010, p. 86.
- Ившин 2010, p. 212.
- И. Анисимов (1847). Азбука, составленная из российских, церковной и гражданской печати, букв, для обучения вотских детей чтению на их наречии (по глазовскому). Казань. p. 2.
- Ившин 2010, p. 98.
- Ившин 2010, p. 116.
- Ившин 2010, p. 209.
- Д. М. Сахарных (2005). "1". О периодизации истории удмуртской письменности. Ижевск. pp. 63—65/.
- Н. Блинов (1867). Лыдзонъ = Азбука для вотских детей. Вятка: Тип. Губерн. правл.
- Букварь для крещеных вотяков. Казань. 1882.
- Г. Е. Верещагин (1895). О книгах на вотском языке. Вятка. p. 8.
- И. В. Тараканов (2007). Удмуртский язык: становление и развитие. Ижевск: Удмуртия. pp. 76—84/288. ISBN 978-5-7659-0417-6.
- И. В. Тараканов (2000). Алфавит. Ижевск: "Удмуртия". pp. 168/800. ISBN 5-7659-0732-6.
- В. М. Вахрушев, В. Н. Денисов (1992). Современный удмуртский язык (1000 экз ed.). Ижевск: Удмуртия. pp. 88–102. ISBN 5-7659-0244-8.
- К. М. Мусаев (1993). Языки и письменности народов Евразии (100 экз ed.). Алматы: «Гылым». pp. 117–120. ISBN 5-628-01418-4.
- Б. Гранде (1933). Латинизация письма в Удмуртской АО.
- М. И. Исаев (1979). Языковое строительство в СССР (2650 экз ed.). М.: «Наука». pp. 251–270.
- Д. М. Сахарных (2002). Латинизация: очерк из истории удмуртской письменности. М.: "Наталис". pp. 97—106/.
Further reading
- Ившин, Л. М. (2010). Становление и развитие удмуртской графики и орфографии в XVIII — первой половине XIX века. Екатеринбург — Ижевск: УрО РАН. p. 236. ISBN 978-5-7691-2135-7.