UNECE Environmental Performance Reviews
The UNECE Environmental Performance Review (EPR) (French: Examen des performances environnementales – EPE) is an assessment process to evaluate the progress made by individual countries in improving their environmental policies. The EPRs are carried out under the auspices of the Committee on Environmental Policy of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE).
 | |
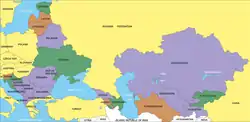 Map showing countries reviewed by the UNECE Environmental Performance Review programme. Countries in brown went through the 1st cycle of EPR, green through the 2nd cycle and violet through the 3rd cycle. | |
| Abbreviation | EPR |
|---|---|
| Formation | 1996 |
| Type | Programme |
| Legal status | Active |
Parent organization | UNECE |
| Website | UNECE EPR |
Objective
EPRs provide countries with independent, external assessment of how they handle the pollution reduction process, manage their natural resources and protect nature and environment. EPRs also evaluate progress made by governments in meeting their international commitments on environment and sustainable development such as the Sustainable Development Goals.
History
The UNECE Programme on EPRs was inspired by a sister programme launched by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) for its member States in 1991. In 1993 at the second "Environment for Europe" Ministerial Conference in Lucerne, Switzerland, UNECE was asked to run an EPR Programme for its member States that were not covered by the OECD EPR Programme.[1] Therefore, the UNECE EPRs focus on the countries of Eastern Europe, Caucasus, Central Asia and South-Eastern Europe known as economies in transition.
The first EPR cycle established the baseline conditions regarding state of environment and national environmental policies. The second EPR cycle looked into the implementation and financing of environmental policies, integration of environmental concerns into economic sectors, and promotion of sustainable development.[2] By now, almost all eligible UNECE member countries have been reviewed twice.
The third review cycle was initiated at the seventh “Environment for Europe” Ministerial Conference (Astana, Kazakhstan, 2011).[3] It focuses on environmental governance and green economy. It also analyses countries’ cooperation with international community and environmental mainstreaming in priority sectors.
EPR topics
Topics for the EPR report are selected by the country which requests an EPR. EPRs cover horizontal issues such as legislation and policy development, compliance and enforcement, use of economic instruments for environmental protection, environmental information and education. They discuss in detail the issues of water management, air protection, waste management, biodiversity and protected areas, and integration of environmental considerations into selected sectors such as agriculture, energy, forestry, industry, transport, or health. Cross-cutting issues, such as environmental monitoring and climate change, are also addressed in the EPRs.
EPR process
The EPR is a voluntary exercise undertaken only at the request of a country. Once the request is received, the UNECE secretariat organizes a preparatory mission to the country during which the structure of the review is agreed.
Upon completion of preparatory activities, international experts embark on a review mission to the country where they meet with national and local governmental representatives, international organizations, civil society groups and the private sector to gain an in-depth understanding of specific environmental issues. International experts are provided by governments and international organizations, such as OECD, United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA), United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (UNISDR), United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA), European Environment Agency (EEA), World Health Organization (WHO) and World Bank (WB). At the end of the review mission, the experts prepare chapters that are compiled into a draft EPR report.[4]
The draft EPR report is first reviewed by the EPR Expert Group, which consists of representatives from ten UNECE member countries elected for three years. During the review, the members of the Expert Group discuss the draft EPR report, with particular attention given to the conclusions and recommendations. Delegation from the reviewed country is invited to participate in the meeting and interact with the Expert Group. At the end of review, the report is amended and submitted to the Committee on Environmental Policy for peer review.[5]
At the annual session of the Committee on Environmental Policy, UNECE member States and a high-level delegation from the country discuss and review EPR recommendations. The Committee on Environmental Policy adopts the recommendations of the EPR report and the country commits to implement them.
The report is then finalized and published. An official launch event of the EPR publication usually takes place in the country under review. Typically, the launch event is accompanied by a press conference with high-level governmental representation.
When an EPR is conducted in the country for the second or the third time, governmental officials usually prepare a self-evaluation of implementation of recommendations of the previous review. The outcomes of self-evaluation are reviewed by the team of international experts and become part of the EPR report.
Countries reviewed
List of countries reviewed.[6]
In 2012 – 2013, the UNECE EPR Programme undertook a review of a non-UNECE country – Morocco.[7] The EPR of Morocco [8] was carried out in cooperation with UNECA to facilitate the transfer of the EPR methodology and know-how from UNECE to UNECA.[9] In 2017, the UNECE EPR Programme undertook a review of another non-UNECE country –Mongolia. The review was carried out in cooperation with ESCAP.
Practical value of EPRs
By providing concrete, tailor-made, recommendations, the EPR reports assist countries to reconcile their economic and social development with environmental protection.
Unlike for ratified international treaties, the countries do not have a formal legal obligation to implement EPR recommendations. However, governments do make serious efforts to implement the recommendations. The average rate of implementation of EPR recommendations is about 75 per cent.
The practical measures that have been implemented as a result of the EPRs include the strengthening of environmental institutions and governance, the adoption of new legislation and policy documents, introduction of economic instruments for environmental protection, better integration of environmental considerations into sectoral policies, increase of governmental expenditures for environmental protection and other measures.
EPRs and the global agenda
Since 2017, EPRs include the review of relevant goals and targets of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and provide recommendations to the countries on the achievement of SDGs.[10]
References
- "Second Ministerial Conference "Environment for Europe" (28-30 April 1993, Lucerne, Switzerland)".
- "UNECE EPR programme".
- "Seventh "Environment for Europe" Ministerial Conference (21-23 September 2011, Astana, Kazakhstan)".
- "What UNECE does for you" (PDF).
- "Environmental Performance Reviews".
- "UNECE EPR programme".
- "Experts meet in Rabat to discuss recommendations to Morocco in the first Environmental Performance Review undertaken by UNECE outside the region, 11 September 2013".
- "EPR of Morocco".
- "The Environmental Performance Review, a powerful tool for achieving Sustainable Development. Lessons learnt from the Moroccan Experience, UNECA, 2014".
- "Role of Environmental Performance Reviews in supporting the achievement and monitoring of Sustainable Development Goals in the pan-European region" (PDF).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Environmental Performance Reviews. |