Triethoxysilane
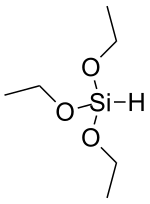
Triethoxysilane is an organosilicon compound with the formula HSi(OC2H5)3. It is a colourless liquid used in precious metal-catalysed hydrosilylation reactions. The resulting triethoxysilyl groups are often valued for attachment to silica surfaces.[1] Compared to most compounds with Si-H bonds, triethoxysilane exhibits relatively low reactivity. Like most silyl ethers, triethoxysilane is susceptible to hydrolysis. As reducing agent, triethoxysilane can for example be used in reduction of amides, reduction of carbonyl compounds in the presence of cobalt(II) chloride as catalyst, Cu-catalyzed reductive hydroxymethylation of styrenes, and Rh-catalyzed hydrodediazoniation. [2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Triethoxysilane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.409 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H16O3Si | |
| Molar mass | 164.276 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colourless liquid |
| Density | 0.89 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 134–135 °C (273–275 °F; 407–408 K) |
| organic solvents | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Robert J. P. Corriu, Christian Guérin, Karl A. Scheidt, Robert B. Lettan II, George Nikonov, Lidia Yunnikova "Triethoxysilane" e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2001 John Wiley & Sons doi:10.1002/047084289X.rt215.pub3
- https://www.organic-chemistry.org/chemicals/reductions/triethoxysilane.shtm
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.