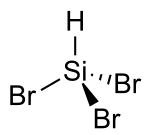
Tribromosilane
Tribromosilane is a chemical compound containing silicon, hydrogen, and bromine. At high temperatures, it decomposes to produce silicon, and is an alternative to purified trichlorosilane of ultrapure silicon in the semiconductor industry.
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Tribromosilane | |||
| Other names
Silicobromoform; Tribromomonosilane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.250 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Br3HSi | |||
| Molar mass | 268.805 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
The Schumacher Process of silicon deposition uses tribromosilane gas to produce polysilicon, but it has a number of cost and safety advantages over the Siemens Process to make polysilicon.[1]
It may be prepared by heating crystalline silicon with gaseous hydrogen bromide at high temperature.[2] It spontaneously combusts when exposed to air.[3]
References
- The Schumacher Process
- Schumb WC, Young RC (April 1930). "A study of the reaction of hydrogen bromide with silicon". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 52 (4): 1464–1469. doi:10.1021/ja01367a025.
- Schumb WC (December 1942). "The Halides and Oxyhalides of Silicon". Chemical Reviews. 31 (3): 587–595. doi:10.1021/cr60100a004.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.

