Transition metal boryl complex
In chemistry, a transition metal boryl complex is a molecular species with a formally anionic boron center coordinated to a transition metal.[1] They have the formula LnM-BR2 or LnM-(BR2LB) (L = ligand, R = H, organic substituent, LB = Lewis base). One example is (C5Me5)Mn(CO)2(BH2PMe3) (Me = methyl).[2] Such compounds, especially those derived from catecholborane and the related pinacolborane, are intermediates in transition metal-catalyzed borylation reactions.
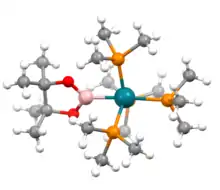
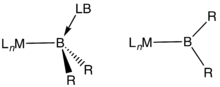
Structure of boryl ligands in metal complexes.
References
- Geoffrey J. Irvine; M. J. Gerald Lesley; Todd B. Marder; Nicholas C. Norman; Craig R. Rice; Edward G. Robins; Warren R. Roper; George R. Whittell; L. James Wright (1998). "Transition Metal−Boryl Compounds: Synthesis, Reactivity, and Structure". Chem. Rev. 98: 2685–2722. doi:10.1021/cr9500085.
- Staubitz, A.; Robertson, A. P. M.; Sloan, M. E.; Manners, I. (2010). "Amine− and Phosphine−Borane Adducts: New Interest in Old Molecules". Chem. Rev. 110: 4023–4078. doi:10.1021/cr100105a.
- C.Borner; K.Brandhorst; C.Kleeberg (2015). "Selective B–B bond activation in an unsymmetrical diborane(4) by [(Me3P)4Rh–X] (X = Me, OtBu): a switch of mechanism?". Dalton Trans. 44: 8600. doi:10.1039/C5DT00618J.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.