Tone name
In tonal languages, tone names are the names given to the tones these languages use.

Pitch contours of the four Mandarin tones
- In contemporary standard Chinese (Mandarin), the tones are numbered from 1 to 4. They are descended from but not identical to the historical four tones of Middle Chinese, namely level (Chinese: 平; pinyin: píng), rising (Chinese: 上; pinyin: shǎng), departing (Chinese: 去; pinyin: qù), and entering (Chinese: 入; pinyin: rù), each split into yin (Chinese: 陰; pinyin: yīn) and yang (Chinese: 陽; pinyin: yáng) registers, and the categories of high and low syllables.
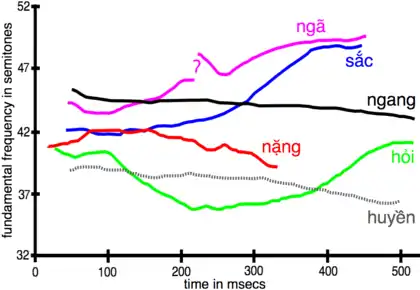
Northern Vietnamese (non-Hanoi) tones as uttered by a male speaker in isolation. From Nguyễn & Edmondson (1998)
- Standard Vietnamese has six tones, known as ngang, sắc, huyền, hỏi, ngã, and nặng tones.
- Thai has five phonemic tones: mid, low, falling, high and rising, sometimes referred to in older reference works as rectus, gravis, circumflexus, altus and demissus, respectively.[1] The table shows an example of both the phonemic tones and their phonetic realization, in the IPA.

Thai language tone chart
| Tone | Thai | Example | Phonemic | Phonetic | Example meaning in English |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mid | สามัญ | นา | /nāː/ | [naː˧] | paddy field |
| low | เอก | หน่า | /nàː/ | [naː˩] | (a nickname) |
| falling | โท | หน้า | /nâː/ | [naː˥˩] | face |
| high | ตรี | น้า | /náː/ | [naː˧˥] or [naː˥] | maternal aunt or uncle younger than one's mother |
| rising | จัตวา | หนา | /nǎː/ | [naː˩˩˦] or [naː˩˦] | thick |
See also
- Tone letter
- Tone number
- Archaic & modern four tones in Chinese
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.