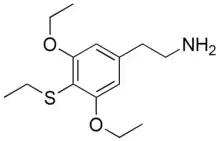
Thiotrisescaline
Thiotrisescaline (T-TRIS) is a series of lesser-known phenethylamines prepared as potential psychedelic drugs. There are two isomers, 3-T-TRIS and 4-T-TRIS, each similar in structure to trisescaline with a sulfur atom in a place of a different oxygen atom. They were first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and described in his book PiHKAL.[1][2] Very little is known about their dangers or toxicity.
T-TRIS compounds
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.