Tazabagyab culture
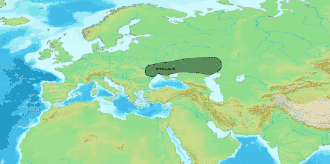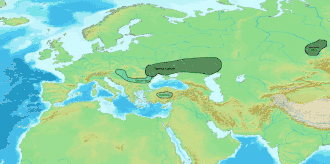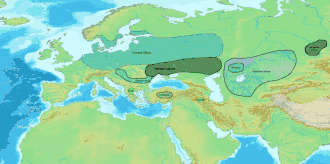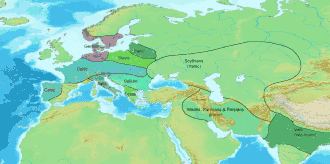
The Tazabagyab culture is a late Bronze Age culture which flourished along the lower Amu Darya and on the south shore of the Aral Sea from ca. 1500 BC to 1100 BC. It was a southern offshoot of the Andronovo culture, and was composed of Indo-Iranians.[1]
 | |
| Geographical range | Lower Amu Darya |
|---|---|
| Period | Late Bronze Age |
| Dates | ca. 1500–1100 BC |
| Preceded by | Andronovo culture |
| Followed by | ? |
| Part of a series on |
| Indo-European topics |
|---|
 |
Origins
The Tazabagyab culture emerged in 1500 BC as a southern variant of the Andronovo culture.[2][3][4] Unlike the Andronovo peoples further to the north, who were largely pastoral, the people of the Tazabagyab culture were largely agricultural.[1]
It is probable that they were descended from Indo-Iranian steppe pastoralists from the north who had expanded southwards and founded agricultural communities.[1]
Characteristics
Tazabagyab settlements show evidence of small-scale irrigation agriculture.[3] About fifty settlements have been discovered.[5] These contained subterranean rectangular houses, usually three per village.[5] Tazabagyav houses are generally large, some being more than 10 x 10 m in dimensions. They are built of clay and the reeds are supported by timber posts. Ca. 100 individuals, belonging to around ten families,[3] would have inhabited a Tazabagyav village. Figurines and remains of horses have been found.[1]
In Tazabagyav burials, males are buried on their left, while females are buried on their right. This is similar to contemporary Indo-European cultures in the region, such as the Andronovo culture,[3] Bishkent culture, the Swat culture and the Vakhsh culture,[1] and the earlier Corded Ware culture of central and eastern Europe.[6][7][8] This practice has been identified as a typical Indo-Iranian tradition.[9]
Metal objects of the Tazabagyab culture are similar to those of the Andronovo culture in Kazakhstan, and of the Srubnaya culture further west.[1] Archaeological evidence show that Tazabagyab settlements included metal-working craftsmen.[5]
Its ceramics were of the Namazga VI type which was common throughout Central Asia at the time.[1] Tazabagyav pottery appears throughout a wide area.[4]
The Tazabagyab people appears to have controlled the trade in minerals such as copper, tin and turquoise, and pastoral products such as horses, dairy and leather. This must have given them great political power in the old oasis towns of the Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex. Their mastery of chariot warfare must have given them military control. This probably encouraged social, political and also military integration.[10]
Successors
David W. Anthony suggests that Tazabagyav culture might have been a predecessor of early Indo-Aryan peoples such as the compilers of the Rigveda and the Mitanni.[10]
References
- Mallory & Adams 1997, pp. 566-567.
- Mallory & Adams 1997, p. 20.
- Mallory 1991, p. 230.
- Anthony 2007, p. 452.
- Masson 1992, p. 350.
- Mallory & Adams 1997, p. 68.
- Mallory & Adams 1997, p. 589.
- Mallory 1991, p. 244.
- Mallory & Adams 1997, p. 558.
- Anthony 2007, pp. 453-454.
Bibliography
- Anthony, David W. (2010). The Horse, the Wheel, and Language: How Bronze-Age Riders from the Eurasian Steppes Shaped the Modern World. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-1-4008-3110-4.
- Mallory, J. P. (1991). In Search of the Indo-Europeans: Language Archeology and Myth. Thames & Hudson.
- Mallory, J. P.; Adams, Douglas Q. (1997). "Tazabagyab Culture". Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. Taylor & Francis. pp. 566–567. ISBN 1884964982.
- Masson, V. M. (1992). "The Decline of the Bronze Age Civilization and Movements of the Tribes". In Dani, A. H.; Masson, V. M. (eds.). History of Civilizations of Central Asia: The Dawn of Civilization. 1. UNESCO. pp. 337–431. ISBN 9231027190.
Further reading
- Kuzmina, Elena E. (2007). Mallory, J. P. (ed.). The Origin of the Indo-Iranians. BRILL. ISBN 978-9004160545.