Symphyotrichum ascendens
Symphyotrichum ascendens (formerly Aster ascendens) is a species of aster known by the common names western aster[1] and long-leaved aster.[2] It is native to western North America from British Columbia to Saskatchewan, the Sierra Nevada in California, to Arizona and New Mexico. It grows in many types of habitat, including disturbed areas.
| Symphyotrichum ascendens | |
|---|---|
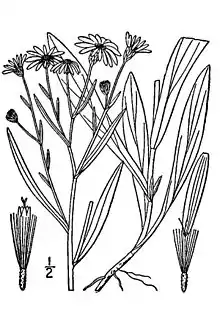 | |
| Botanical illustration | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Genus: | Symphyotrichum |
| Species: | S. ascendens |
| Binomial name | |
| Symphyotrichum ascendens | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Aster ascendens Lindl. | |
Description
This is a rhizomatous perennial herb growing a branching, erect stem to heights between 20 and 60 centimeters. Leaves are widely lance-shaped to oblong and pointed, the largest ones near the base of the stem reaching up to 15 centimeters long. The stem and leaves are roughly hairy in places.
The inflorescence is an array of many flower heads with many narrow violet to nearly white ray florets around a center of golden disc florets. The fruit is a hairy achene with a long pappus.[3]
References
- "Symphyotrichum ascendens". Natural Resources Conservation Service PLANTS Database. USDA. Retrieved 6 December 2015.
- "BSBI List 2007". Botanical Society of Britain and Ireland. Archived from the original (xls) on 2015-01-25. Retrieved 2014-10-17.
- Jepson Manual Treatment - Symphyotrichum ascendens
External links
 Media related to Symphyotrichum ascendens at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Symphyotrichum ascendens at Wikimedia Commons Data related to Symphyotrichum ascendens at Wikispecies
Data related to Symphyotrichum ascendens at Wikispecies- Symphyotrichum ascendens - Photo gallery