Stoke-on-Trent Green Belt
The Stoke-on-Trent Green Belt is a green belt environmental and planning policy that regulates the rural space throughout mainly the West Midlands region of England. It is contained within the counties of Cheshire and Staffordshire. Essentially, the function of the designated area is to prevent surrounding towns and villages within the Stoke-on-Trent conurbation from further convergence.[1] It is managed by local planning authorities on guidance from central government.
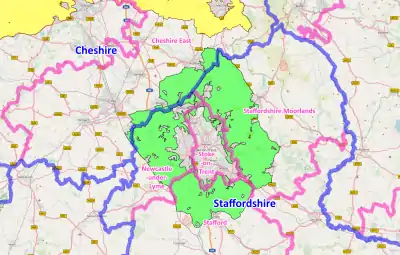
Stoke green belt showing extents, districts and counties.
Purpose
The following policy was stated for the creation of the green belt area by Staffordshire County Council in 1967:[2]
- "To limit the expansion into adjoining open country of the urban areas of North Staffordshire forming part of the Potteries Conurbation.
- To prevent the following towns and settlements in the adjoining open area from merging with the Potteries Conurbation and with other settlements;
- a) The built up areas of Kidsgrove and Biddulph;
- b) The settlements of Brown Edge, Endon, Stanley, Bagnall, Stanley Moor, Norton Green, Baddeley Green, Baddeley Edge, Light Oaks, Werrington, Cellarhead, Caverswall, Cookshill, Blythe Bridge, Forsbrook, Meir Heath, Barlaston, Alsagers Bank, Halmer End, Miles Green, Wood Lane, Bignall End and Audley.
- To prevent the coalescence of the following towns and settlements around the Potteries Conurbation:
- Leek with Longsdon; Leek with Cheddleton; Longsdon with Cheddleton; Longsdon with Endon; Cheddleton with Folly Lane; Folly Lane with Wetley Rocks; Wetley Rocks with Cellarhead; Cheadle with Kingsley Holt; Kingsley with Kingsley Holt; Cheadle with Dihorne; Cheadle with Forsbrook; Fulford with Meir Heath; Stone with Oulton; Stone with Yarfield; Tittensor with Barlaston; Barlaston with Stone; Madeley Heath with Madeley; Betley with Audley.
- To maintain the present open character of the land within the North Staffordshire Green Belt and to prevent the coalescence of smaller settlements not mentioned above."
Cheshire County Council set out their policy in 1961:[3]
- "Prevent the outward spread of development from Greater Manchester, Merseyside and the Potteries"
Geography
Land area taken up by the green belt is 43,836 hectares (438.36 km2; 169.25 sq mi), 0.5% of the total land area of England (2010).[4] The main coverage of the area is within northern Staffordshire, extending into southern Cheshire.[5] The North West Green Belt area surrounding Macclesfield lies close to the Stoke-on-Trent green belt, being just over a mile away at its closest extent from the River Dane which forms the northern boundary for the area.
Landscape facilities and features within the green belt area include the Cudmore Fisheries, Meaford Energy Centre, Millennium Topograph in Downs Banks, JCB Harewood Estate, Rudyard Lake, Meir Heath, Barlaston Common, Chatterley Whitfield Country Park and enterprise centre, Bucknall Reservoir, the Trent & Mersey and Caldon canals, the River Blythe and Trent, Wedgwood Museum and estate, Strongford Sewage Treatment Works, and Trent Vale Pumping Station.
A large portion of the western boundary is formed by the West Coast Main Line railway. Towns on the outer extents of the green belt include Alsager, Cheadle, Congleton, Crewe, Leek, and Stone. Towns and villages within the area include Biddulph, Endon, Kidsgrove, Rudyard, Scholar Green and Swynnerton. Due to the green belt lying across county borders, responsibility and co-ordination lies with several district councils and unitary authorities as these are the local planning authorities.
See also
References
- Fawcett, Tony. "Green Belts: A greener future - Campaign to Protect Rural England".
- "Joint local plan Green Belt assessment november 2017 - Stoke-on-Trent". www.stoke.gov.uk.
- "Cheshire East Local Plan Evidence Base Green Belt Assessment - September 2013" (PDF). www.cheshireeast.gov.uk. Cheshire East Council.
...the original intent for the area of Green Belt in Cheshire East was to prevent the outward spread of development from Greater Manchester and the Potteries. These original draft Green Belt proposals were submitted to the Ministry of Housing and Local Government in 1961 and although they were not formally approved at this time, Green Belt control has been operated in the area concerned ever since submission.
- "Green Belts in England: Key facts - A series of factsheets on England's 14 Green Belts".
- Cheshire East Council. "Cheshire East Local Plan Local Plan Strategy 2010 - 2030 Adopted 27 July 2017" (PDF). www.cheshireeast.gov.uk.
2.83 The North Staffordshire Green Belt surrounds Stoke and Newcastle with its northernmost extent covering part of Cheshire East (known locally as the South Cheshire Green Belt) – south of Alsager and Congleton and south east of Crewe.