Stewartia sinensis
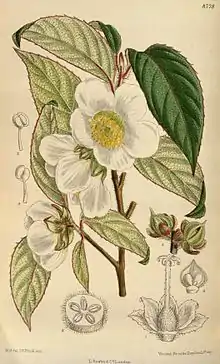
Stewartia sinensis is a species of flowering plant in the camellia family Theaceae, native to central and eastern China. It is typically a small deciduous tree or large shrub, commonly growing to about 9 m (30 ft) tall.[1] It is highly regarded horticulturally for the combination of its attractive, cinnamon-colored peeling bark, numerous cup-shaped, fragrant white flowers to 10 cm (4 in) in midsummer, and generally intensely red fall foliage. The species also has an attractive multiply-branched growth habit and low maintenance requirements.
| Stewartia sinensis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Theaceae |
| Genus: | Stewartia |
| Species: | S. sinensis |
| Binomial name | |
| Stewartia sinensis | |
In its native forests, S. sinensis has been known to achieve a maximum height of 20 m (66 ft) tall by 7 m (23 ft) broad[2] but it generally does not achieve these proportions in cultivation, where competition for sunlight is less of a concern. This has led to its recommendation for use where larger trees are inadvisable, e.g. under power lines.[3][4][5] When not grown in forested settings, S. sinensis generally takes the form of a multiply-branched, large shrub.
Preferred growing conditions for S. sinensis are similar to those of the more commonly cultivated and closely related Japanese stewartia (S. pseudocamellia), though the latter is somewhat more cold-tolerant. Stewartia sinensis prefers full sun to part shade and moist, well-drained slightly acid soil in a protected location, but may be grown as a specimen tree in climates that do not test its cold-tolerance. It is hardy to USDA zone 5, but it has been suggested that young trees may be more susceptible to cold than older specimens, and should thus be protected during very cold temperatures until they reach mature sizes.[6]
In the UK S.sinensis has gained the Royal Horticultural Society’s Award of Garden Merit.[7][8]
References
- "Stewartia sinensis". Flora of China.
- RHS A-Z encyclopedia of garden plants. United Kingdom: Dorling Kindersley. 2008. p. 1136. ISBN 1405332964.
- "Planting near power lines. pub # 10809 00-06" (PDF). BC Hydro. 2000.
- "Trees compatible with power lines" (PDF). Connecticut Light and Power. 2010.
- "Small trees for small places: 100 tree species for use adjacent to power lines" (PDF). Pacific Power. 2010.
- http://www.bluebellnursery.com/catalogue/trees/Stewartia/S/2967
- "RHS Plantfinder - Stewartia sinensis". Retrieved 21 November 2018.
- "AGM Plants - Ornamental" (PDF). Royal Horticultural Society. July 2017. p. 99. Retrieved 21 November 2018.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Stewartia sinensis. |