South China-Vietnam subtropical evergreen forests
The South China-Vietnam subtropical evergreen forests ecoregion (WWF ID:IM0149) covers the mountainous coastal region of southeastern China and northeastern Vietnam. The ecoregional also covers the coastal plain along the South China Sea and Hainan Island. The area has significant biodoversity and ecological importance, with high levels of both endemic and threatened species. Rapid urban expansion is reducing biologically-rich forests and wetlands. Ecologically, the suptropical forests are at the northeastern extent of the Indomalayan realm.[1][2][3]
| Ecoregion: South China-Vietnam subtropical evergreen forests | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) Lianjiang, Zhanjiang, Guangdong, China | |
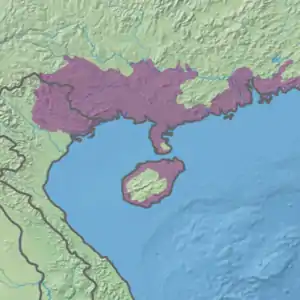 Ecoregion territory (in purple) | |
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Indomalayan |
| Biome | tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests |
| Borders | |
| Geography | |
| Area | 224,293 km2 (86,600 sq mi) |
| Countries | China and Vietnam |
| Provinces and regions of China | Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Hong Kong and Macau |
| Coordinates | 21°40′N 110°00′E |
Location and description
The ecoregion stretches from the northeastern corner of Vietnam, across the lower half of southeastern China, and down into coastal Hainan Island. To the north is the watershed of the Pearl River, to the south is the South China Sea. The terrain is mountainous for the most part, except along the coasts and around the Leizhou Peninsula. The ecoregion runs across the southern half of Guangxi and Guangdong Provinces, with the major Guangzhou/Shenzhen/Hong Kong urban area in its east.
.jpg.webp)
Climate
The climate of the ecoregion is Dry-winter humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification (Cwa)). This climate is characterized as having no month averaging below 0 °C (32 °F), at least one month averaging above 22 °C (72 °F), and four months averaging over 10 °C (50 °F). Precipitation in the wet summer months is ten time or more the average of the winter months.[4][5] The ecoregion is mostly below 23d 30m latitude, and below the frost line.
Flora and fauna
Tropical genera represent 80% of the flora of the ecoregion.[6] The forests of the area are under pressure from the increase in rubber and pulp plantations, and commercial agricultural crops in the understory[6] As of 2012, the region supported 117 threatened species (out of a total of 1,114 species), 28 of which were endemic.[3]
See also
References
- "South China-Vietnam subtropical evergreen forests". World Wildlife Federation. Retrieved February 23, 2020.
- "Map of Ecoregions 2017". Resolve, using WWF data. Retrieved September 14, 2019.
- "Urban expansion dynamics and natural habitat loss in China: a multiscale landscape perspective" (PDF). Global Change Biology (2014). Retrieved February 26, 2020.
- Kottek, M., J. Grieser, C. Beck, B. Rudolf, and F. Rubel, 2006. "World Map of Koppen-Geiger Climate Classification Updated" (PDF). Gebrüder Borntraeger 2006. Retrieved September 14, 2019.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- "Dataset - Koppen climate classifications". World Bank. Retrieved September 14, 2019.
- "The Tropical Forests of Southern China and Conservation of Biodiversity". Botanical Review. Retrieved February 26, 2020.