Sedaxane
Sedaxane is a chemical developed as a fungicide in the European Union.
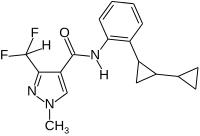 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2’-[1,1’-bicycloprop-2-yl]-3-(difluoromethyl)-1-methylpyrazole-4-carboxanilide | |
| Other names
SYN524464 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.214.982 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H19F2N3O | |
| Molar mass | 331.367 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White powder[1] |
| Odor | Odorless[1] |
| Density | 1.23 g/cm3 (26 °C)[1] |
| Melting point | 121.4 °C (250.5 °F; 394.5 K)[1] |
| Very slightly soluble (0.67 g/L, 20 °C)[1] | |
| Solubility in other solvents | Slightly soluble in acetone (410 g/L) and dichloromethane (500 g/L)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The molecular grouping to which it belongs is a pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid amide; its method of action is as a succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor (SDHI).[2]
It is approved in Austria, and pending approval in Germany and Switzerland.
References
- William Donovan. "Sedaxane" (PDF). United States Environmental Protection Agency.
- Ronald Zeun, Gabriel Scalliet and Michael Oostendorp (2013). "Biological activity of sedaxane - a novel broad-spectrum fungicide for seed treatment" (PDF). Pest Management Science. 69 (4): 527–534. doi:10.1002/ps.3405. PMID 23044852.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.