Schneekopf
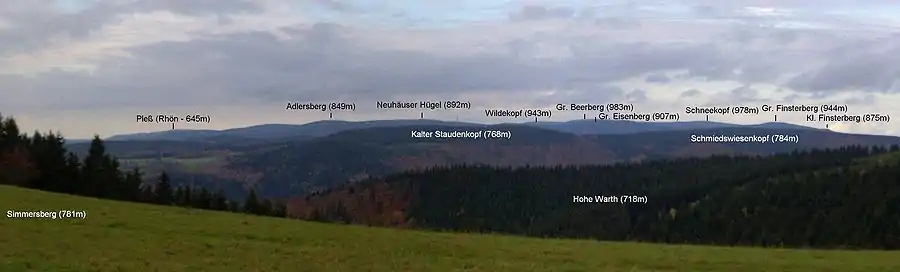
The Schneekopf near Gehlberg in the Thuringian county of Ilm-Kreis is 978 m above sea level (NHN)[1] and thus the second highest peak in the Thuringian Forest after its western neighbour, the Großer Beerberg (983 m). The Adler Saddle between them is only about 59.4 metres lower than the two summits. To the east some distance away is its subpeak, the Sachsenstein (915 m), to the south are the Teufelskreise (967 m) and Fichtenkopf (944 m). The Goldlauterberg (866 m) further south marks the transition to the mountain of Großer Finsterberg (944 m).
| Schneekopf | |
|---|---|
 View from the Großer Finsterberg of the Großer Beerberg (l) and the Schneekopf (r, tower) | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 978 m above sea level (NHN) (3,208.7 ft) [1] |
| Prominence | 59.4 m ↓ Adler |
| Isolation | 1.6 km → Großer Beerberg |
| Coordinates | 50°39′57″N 10°45′52″E |
| Geography | |
| Parent range | Thuringian Forest |
| Geology | |
| Type of rock | Porphyry |
Description
The mountain is of volcanic origin and consists of porphyry. It is known for the Schneekopf balls (Schneekopfkugel), balls of porphyry (druse) that occur here that form agate in the interior of crystals. They were formed during a volcanic eruption in the Permian. On the northern slopes of the mountain rises the Wilde Gera stream.
From the summit plateau there is a good all round view of other summits in the Thuringian Forest and the Rhön mountains, over the Thuringian Basin as far as the Ettersberg near Weimar and of the winter sports resort of Oberhof. In very good visibility, for example during winter inversion weather conditions, the view extends as far as the Brocken in the Harz Mountains, the Schneeberg and the western Ore Mountains. In addition, the Wilde Gera Viaduct (on the A 71), which has a span of 252 metres - the largest arch bridge in Germany, is also visible.
 View from the Schneekopf of the Wilde Gera Viaduct (A 71)
View from the Schneekopf of the Wilde Gera Viaduct (A 71) Communications tower on the Schneekopf in winter
Communications tower on the Schneekopf in winter The observation tower on the Schneekopf
The observation tower on the Schneekopf The New Gehlberger Hut
The New Gehlberger Hut View from the Schneekopf in winter
View from the Schneekopf in winter
Literature
- Ludwig Bechstein: Sagenbuch des Schneekopfs und des Thüringischen Henneberger Landes. Veröffentlichung 1837; Verlag Rockstuhl, Bad Langensalza, Reprint 2009, ISBN 978-3-86777-063-7
References
- Map services of the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Schneekopf. |
- Von der Gemeinde Gehlberg betriebene „offizielle“ Website des Schneekopfs (mit Webcams)
- Historie des Schneekopfes (Neue Gehlberger Hütte)
- Das Richtfunknetz der Partei (SED) u. d. NVA