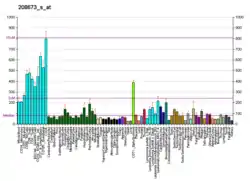
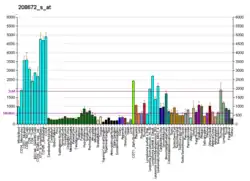
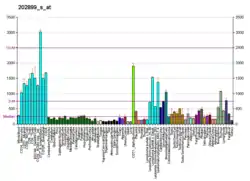
SFRS3
Splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SFRS3 gene.[5][6]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000112081 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000071172 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Zahler AM; Lane WS; Stolk JA; Roth MB (Jun 1992). "SR proteins: a conserved family of pre-mRNA splicing factors". Genes Dev. 6 (5): 837–47. doi:10.1101/gad.6.5.837. PMID 1577277.
- "Entrez Gene: SFRS3 splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 3".
- Guo, Taylor B; Boros Laszlo G; Chan Kam C; Hikim Amiya P Sinha; Hudson Alan P; Swerdloff Ronald S; Mitchell Aaron P; Salameh Wael A (2003). "Spermatogenetic expression of RNA-binding motif protein 7, a protein that interacts with splicing factors". J. Androl. 24 (2): 204–14. doi:10.1002/j.1939-4640.2003.tb02664.x. ISSN 0196-3635. PMID 12634307.
Further reading
- Ayane M; Preuss U; Köhler G; Nielsen PJ (1991). "A differentially expressed murine RNA encoding a protein with similarities to two types of nucleic acid binding motifs". Nucleic Acids Res. 19 (6): 1273–8. doi:10.1093/nar/19.6.1273. PMC 333853. PMID 2030943.
- Gui JF; Lane WS; Fu XD (1994). "A serine kinase regulates intracellular localization of splicing factors in the cell cycle". Nature. 369 (6482): 678–82. Bibcode:1994Natur.369..678G. doi:10.1038/369678a0. PMID 8208298. S2CID 4275539.
- Cáceres JF; Screaton GR; Krainer AR (1998). "A specific subset of SR proteins shuttles continuously between the nucleus and the cytoplasm". Genes Dev. 12 (1): 55–66. doi:10.1101/gad.12.1.55. PMC 316398. PMID 9420331.
- Zhang WJ; Wu JY (1998). "Sip1, a novel RS domain-containing protein essential for pre-mRNA splicing". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (2): 676–84. doi:10.1128/MCB.18.2.676. PMC 108778. PMID 9447963.
- Tripodis N, Mason R, Humphray SJ, et al. (1999). "Physical map of human 6p21.2-6p21.3: region flanking the centromeric end of the major histocompatibility complex". Genome Res. 8 (6): 631–43. doi:10.1101/gr.8.6.631. PMC 310739. PMID 9647638.
- Papoutsopoulou S, Nikolakaki E, Chalepakis G, et al. (1999). "SR protein-specific kinase 1 is highly expressed in testis and phosphorylates protamine 1". Nucleic Acids Res. 27 (14): 2972–80. doi:10.1093/nar/27.14.2972. PMC 148514. PMID 10390541.
- Barnard DC; Patton JG (2000). "Identification and characterization of a novel serine-arginine-rich splicing regulatory protein". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (9): 3049–57. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.9.3049-3057.2000. PMC 85584. PMID 10757789.
- Shnyreva M, Schullery DS, Suzuki H, et al. (2000). "Interaction of two multifunctional proteins. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K and Y-box-binding protein". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (20): 15498–503. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.20.15498. PMID 10809782.
- Elliott DJ, Bourgeois CF, Klink A, et al. (2000). "A mammalian germ cell-specific RNA-binding protein interacts with ubiquitously expressed proteins involved in splice site selection". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (11): 5717–22. Bibcode:2000PNAS...97.5717E. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.11.5717. PMC 18499. PMID 10823932.
- Huang Y; Steitz JA (2001). "Splicing factors SRp20 and 9G8 promote the nucleocytoplasmic export of mRNA". Mol. Cell. 7 (4): 899–905. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00233-7. PMID 11336712.
- Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, et al. (2002). "Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus". Curr. Biol. 12 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00650-9. PMID 11790298. S2CID 14132033.
- Barnard DC; Li J; Peng R; Patton JG (2002). "Regulation of alternative splicing by SRrp86 through coactivation and repression of specific SR proteins". RNA. 8 (4): 526–33. doi:10.1017/S1355838202029928. PMC 1370273. PMID 11991645.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Guo TB, Boros LG, Chan KC, et al. (2003). "Spermatogenetic expression of RNA-binding motif protein 7, a protein that interacts with splicing factors". J. Androl. 24 (2): 204–14. doi:10.1002/j.1939-4640.2003.tb02664.x. PMID 12634307.
- Tai HH, Geisterfer M, Bell JC, et al. (2003). "CHD1 associates with NCoR and histone deacetylase as well as with RNA splicing proteins". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 308 (1): 170–6. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)01354-8. PMID 12890497.
- Li J, Hawkins IC, Harvey CD, et al. (2003). "Regulation of alternative splicing by SRrp86 and its interacting proteins". Mol. Cell. Biol. 23 (21): 7437–47. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.21.7437-7447.2003. PMC 207616. PMID 14559993.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Dettwiler S, Aringhieri C, Cardinale S, et al. (2005). "Distinct sequence motifs within the 68-kDa subunit of cleavage factor Im mediate RNA binding, protein-protein interactions, and subcellular localization" (PDF). J. Biol. Chem. 279 (34): 35788–97. doi:10.1074/jbc.M403927200. PMID 15169763. S2CID 39752996.
- Lehner B; Sanderson CM (2004). "A protein interaction framework for human mRNA degradation". Genome Res. 14 (7): 1315–23. doi:10.1101/gr.2122004. PMC 442147. PMID 15231747.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.