Ricinoleic acid
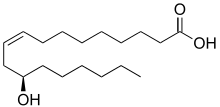
Ricinoleic acid, formally called 12-hydroxy-9-cis-octadecenoic acid is a fatty acid. It is an unsaturated omega-9 fatty acid[1] and a hydroxy acid. It is a major component of the seed oil obtained from mature castor plant (Ricinus communis L., Euphorbiaceae) seeds or in sclerotium of ergot (Claviceps purpurea Tul., Clavicipitaceae). About 90% of the fatty acid content in castor oil is the triglyceride formed from ricinoleic acid.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(9Z,12R)-12-Hydroxyoctadec-9-enoic acid | |
| Other names
(R)-12-Hydroxy-9-cis-octadecenoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.974 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H34O3 | |
| Molar mass | 298.461 g/mol |
| Density | 0.945 g/cm3 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Production
Ricinoleic acid is manufactured for industries by saponification or fractional distillation of hydrolyzed castor oil.[2]
The first attempts to prepare ricinoleic acid were made by Friedrich Krafft in 1888.[3]
Use
Sebacic acid ((CH2)8(CO2H)2), which is used in preparing certain nylons, is produced by cleavage of ricinoleic acid. The coproduct is 2-octanol.[4]
The zinc salt is used in personal care products such as deodorants.[5]
Biological activities
Ricinoleic acid exerts analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.[6]
Ricinoleic acid specifically activates the EP3 prostanoid receptor for prostaglandin E2.[7]
Ricinoleic acid acts as a specific algicide for the control of cyanobacteria (formerly called blue-green algae).[8]
See also
- Castor oil
- Lesquerolic acid, a similar chemical, which could be described as ricinoleic acid with -CH2-CH2- group inserted between carboxyl group and the double bound.
- Polyglycerol polyricinoleate, a polymer of glycerol with ricinoleic acid side chains, used as an emulsifier in chocolate
- Ricinelaidic acid, the trans isomer of ricinoleic acid
- Ricinolein, the triglyceride of ricinoleic acid
- Sodium ricinoleate, the sodium salt of ricinoleic acid
- Undecylenic acid, a product of pyrolysis of ricinoleic acid
References
- Frank D. Gunstone; John L. Harwood; Albert J. Dijkstra (2007). The Lipid Handbook. 10: CRC Press. p. 1472. ISBN 978-1420009675.CS1 maint: location (link)
- James AT, Hadaway HC, Webb JP (May 1965). "The biosynthesis of ricinoleic acid". Biochem. J. 95 (2): 448–52. doi:10.1042/bj0950448. PMC 1214342. PMID 14340094.
- Rider, T. H. (November 1931). "The Purification of Sodium Ricinoleate". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 53 (11): 4130–4133. doi:10.1021/ja01362a031.
- Cornils, Boy; Lappe, Peter (2000). "Dicarboxylic Acids, Aliphatic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a08_523.
- Tom's of Maine - About Our Products
- Vieira C, Evangelista S, Cirillo R, Lippi A, Maggi CA, Manzini S (2000). "Effect of ricinoleic acid in acute and subchronic experimental models of inflammation". Mediators Inflamm. 9 (5): 223–8. doi:10.1080/09629350020025737. PMC 1781768. PMID 11200362.
- Tunaru S, Althoff TF, Nüsing RM, Diener M, Offermanns S (2012). "Castor oil induces laxation and uterus contraction via ricinoleic acid activating prostaglandin EP3 receptors". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109 (23): 9179–9184. Bibcode:2012PNAS..109.9179T. doi:10.1073/pnas.1201627109. PMC 3384204. PMID 22615395.
- US 4398937, "Selective algaecides for control of cyanochloronta", published 1983