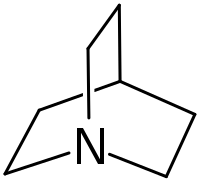
Quinuclidine
Quinuclidine is an organic compound and a bicyclic amine and used as a catalyst and a chemical building block. It is a strong base with pKa of the conjugate acid of 11.0.[3] It can be prepared by reduction of quinuclidone.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octane[2] | |||
| Other names
Quinuclidine[2] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.625 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H13N | |||
| Molar mass | 111.188 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 0.97 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 157 to 160 °C (315 to 320 °F; 430 to 433 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 149.5 °C (301.1 °F; 422.6 K) at 760 mmHg | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 11.0 (conjugate acid) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | 36.5 °C (97.7 °F; 309.6 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
In alkane solvents quinuclidine is a Lewis base that forms adducts with a variety of Lewis acids.
The compound is structurally related to DABCO, in which the other bridgehead is also nitrogen, and to tropane, which has a slightly different carbon frame.
Quinuclidine is found as a structural component of some biomolecules including quinine.
References
- Quinuclidine Archived October 15, 2007, at the Wayback Machine at Sigma-Aldrich
- Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 169. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
The name quinuclidine is retained for general nomenclature only (see Table 2.6).
- Hext, N. M.; Hansen, J.; Blake, A. J.; Hibbs, D. E.; Hursthouse, M. B.; Shishkin, O. V.; Mascal, M. (1998). "Azatriquinanes: Synthesis, Structure, and Reactivity". J. Org. Chem. 63 (17): 6016–6020. doi:10.1021/jo980788s. PMID 11672206.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.