Q-plate
A q-plate is an optical device which can generate light beams with orbital angular momentum of light (OAM) from a beam with well-defined Spin angular momentum of light (SAM). It is currently realized using liquid crystals, polymers or sub-wavelength gratings.
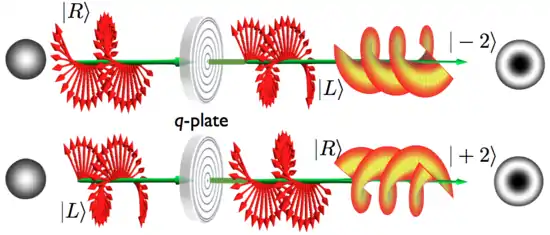
A q-plate can convert a right-polarized beam into a beam with an OAM of -2ħ, and a left-polarized beam into a +2ħ state.
A method for generating orbital angular momentum of light (OAM) is based on the SAM-OAM coupling that may occur in a medium which is both anisotropic and inhomogeneous. In the case of the q-plate, the OAM sign is controlled by the input polarization.[1][2]
References
- Marrucci, L.; Manzo, C.; Paparo, D. (2006-04-28). "Optical Spin-to-Orbital Angular Momentum Conversion in Inhomogeneous Anisotropic Media". Physical Review Letters. 96 (16): 163905. arXiv:0712.0099. Bibcode:2006PhRvL..96p3905M. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.163905. PMID 16712234.
- Karimi, Ebrahim; Piccirillo, Bruno; Nagali, Eleonora; Marrucci, Lorenzo; Santamato, Enrico (2009-06-08). "Efficient generation and sorting of orbital angular momentum eigenmodes of light by thermally tuned q-plates". Applied Physics Letters. 94 (23): 231124. arXiv:0905.0562. Bibcode:2009ApPhL..94w1124K. doi:10.1063/1.3154549. ISSN 0003-6951.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.