Psychosine
Psychosine is a highly cytotoxic lipid that accumulates in the nervous system in the absence of galactosylceramidase.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
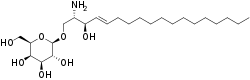
| IUPAC name
(2S,3R,4E)-2-Amino-3-hydroxy-4-octadecen-1-yl β-D-galactopyranoside | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.357 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H47NO7 | |
| Molar mass | 461.640 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Chemically, it is a galactoside of sphingosine.
References
- Hawkins-Salsbury, J. A.; Parameswar, A. R.; Jiang, X; Schlesinger, P. H.; Bongarzone, E; Ory, D. S.; Demchenko, A. V.; Sands, M. S. (2013). "Psychosine, the cytotoxic sphingolipid that accumulates in globoid cell leukodystrophy, alters membrane architecture". The Journal of Lipid Research. 54 (12): 3303–3311. doi:10.1194/jlr.M039610. PMC 3826678. PMID 24006512.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.