Proton-enhanced nuclear induction spectroscopy
Proton-enhanced nuclear induction spectroscopy (PENIS), also called cross-polarisation (CP),[1] is a nuclear magnetic resonance technique invented by Michael Gibby and Alexander Pines while they were graduate students in the lab of Professor John S. Waugh at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.[2] Due to the suggestive nature of its acronym, the latter name is used more often. This technique is an integral part of most solid-state NMR experiments involving spin-1/2 nuclei.[3][1]
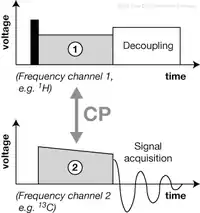
PENIS was one of the first of Pines' experiments transferring spin orientation from one atomic nucleus to another, which has been one of the running themes throughout his career as a leading pioneer in the applications of NMR to the study of non-liquid samples. The PENIS technique was patented in 1972.[4]
Technique
In this technique the natural polarization of an abundant spin (1H, the "proton" which begins the name of the technique) is exploited to increase the polarization of a rare spin (such as 13C) by irradiating the sample with radio waves at the frequency which corresponds to the difference between the rotation frequencies of the two different spins.[5]
Besides its utility for boosting signals from dilute spins, transferring spin-polarization can also be used by surface-scientists to selectively enhance the spin-polarization of molecules on a sample's surface over the spins in the bulk by transferring spin-polarization from a gas to the surface.[6]
References
- Oshiro, C.M. (1 June 1982). Optically enhanced nuclear cross polarization in acridine-doped fluorene (Thesis). doi:10.2172/5193797. OSTI 5193797.
- Pines, A.; Gibby, M.G.; Waugh, J.S. (August 1972). "Proton-enhanced nuclear induction spectroscopy 13C chemical shielding anisotropy in some organic solids". Chemical Physics Letters. 15 (3): 373–376. Bibcode:1972CPL....15..373P. doi:10.1016/0009-2614(72)80191-X.
- Weber, Daniel K.; Bader, Taysir; Larsen, Erik K.; Wang, Songlin; Gopinath, Tata; Distefano, Mark; Veglia, Gianluigi (2019). "Cysteine-ethylation of tissue-extracted membrane proteins as a tool to detect conformational states by solid-state NMR spectroscopy". Methods in Enzymology. 621. pp. 281–304. doi:10.1016/bs.mie.2019.02.001. ISBN 978-0-12-818117-1. PMC 7418180. PMID 31128784.
- US 3792346, "Proton-enhanced nuclear induction spectroscopy"
- Pines, A.; Gibby, M. G.; Waugh, J. S. (15 July 1973). "Proton‐enhanced NMR of dilute spins in solids". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 59 (2): 569–590. Bibcode:1973JChPh..59..569P. doi:10.1063/1.1680061. S2CID 40114590.
- Raftery, Daniel; MacNamara, Ernesto; Fisher, Gregory; Rice, Charles V.; Smith, Jay (September 1997). "Optical Pumping and Magic Angle Spinning: Sensitivity and Resolution Enhancement for Surface NMR Obtained with Laser-Polarized Xenon". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 119 (37): 8746–8747. doi:10.1021/ja972035d.