Priority encoder
A priority encoder is a circuit or algorithm that compresses multiple binary inputs into a smaller number of outputs. The output of a priority encoder is the binary representation of the original number starting from zero of the most significant input bit. They are often used to control interrupt requests by acting on the highest priority interrupt input.

If two or more inputs are given at the same time, the input having the highest priority will take precedence.[1] An example of a single bit 4 to 2 encoder is shown, where highest-priority inputs are to the left and "x" indicates an irrelevant value - i.e. any input value there yields the same output since it is superseded by higher-priority input. The output V indicates if the input is valid.
| I3 | I2 | I1 | I0 | O1 | O0 | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | x | x | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | x | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | x | x | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | x | x | x | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Priority encoders can be easily connected in arrays to make larger encoders, such as one 16-to-4 encoder made from six 4-to-2 priority encoders - four 4-to-2 encoders having the signal source connected to their inputs, and the two remaining encoders take the output of the first four as input. The priority encoder is an improvement on a simple encoder circuit, in terms of handling all possible input configurations.
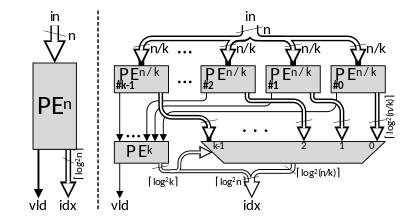
Recursive construction of priority encoders[2][3][4]
A priority-encoder, also called leading zero detector (LZD) or leading zero counter (LZC), receives an -bit input vector and detects the index of the first binary ‘1’ in the input vector. A valid signal indicates if any binary ‘1’ was detected in the input vector, hence the index is valid.
Priority-encoders can be efficiently constructed by recursion. The input vector is split into equal fragments with bits. A priority encoder with a narrower width of 𝑛/𝑘 is applied for each fragment. The valid bit of each of the ‘s goes to a bit to detect the first valid fragment. The location of this fragment is the higher part of the overall index, and steers the exact location within the fragment itself to produce the lower part of the overall index.
The depth of the proposed structure is , while the hardware area complexity is . If Altera’s Stratix V or equivalent device is used, is recommended to achieve higher performance and area compression, since the mux can be implemented using 6-LUT, hence an entire ALM.
An open-source Verilog generator for the recursive priority-encoder is available online.[5]
A behavioral description of priority encoder in Verilog is as follows.[6]
// behavioural description of priority enconder;
// https://github.com/AmeerAbdelhadi/Indirectly-Indexed-2D-Binary-Content-Addressable-Memory-BCAM
module pe_bhv
#( parameter OHW = 512 ) // encoder one-hot input width
( input clk , // clock for pipelined priority encoder
input rst , // registers reset for pipelined priority encoder
input [ OHW -1:0] oht , // one-hot input / [ OHW -1:0]
output reg [`log2(OHW)-1:0] bin , // first '1' index/ [`log2(OHW)-1:0]
output reg vld ); // binary is valid if one was found
// use while loop for non fixed loop length
// synthesizable well with Intel's QuartusII
always @(*) begin
bin = {`log2(OHW){1'b0}};
vld = oht[bin] ;
while ((!vld) && (bin!=(OHW-1))) begin
bin = bin + 1 ;
vld = oht[bin];
end
end
endmodule
Simple encoder
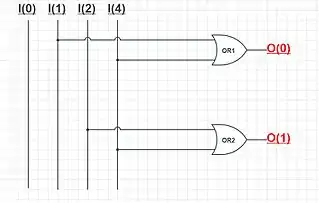
A simple encoder circuit is a one-hot to binary converter. That is, if there are 2n input lines, and at most only one of them will ever be high, the binary code of this 'hot' line is produced on the n-bit output lines.
References
- M. Morris Mano, Michael D. Ciletti, "Digital Design", 4th Edition, Prentice Hall, 2006, ISBN 978-0-13-198924-5.
- Abdelhadi, Ameer M. S. (2016). Architecture of block-RAM-based massively parallel memory structures : multi-ported memories and content-addressable memories (Thesis). University of British Columbia.
- Abdelhadi, Ameer M.S.; Lemieux, Guy G.F. (May 2015). "Modular SRAM-Based Binary Content-Addressable Memories". 2015 IEEE 23rd Annual International Symposium on Field-Programmable Custom Computing Machines: 207–214. doi:10.1109/FCCM.2015.69. ISBN 978-1-4799-9969-9.
- Abdelhadi, Ameer M. S.; Lemieux, Guy G. F. (December 2014). "Deep and narrow binary content-addressable memories using FPGA-based BRAMs". 2014 International Conference on Field-Programmable Technology (FPT): 318–321. doi:10.1109/FPT.2014.7082808. ISBN 978-1-4799-6245-7.
- "https://github.com/AmeerAbdelhadi/Indirectly-Indexed-2D-Binary-Content-Addressable-Memory-BCAM/blob/master/pe". External link in
|title=(help) - "AmeerAbdelhadi/Indirectly-Indexed-2D-Binary-Content-Addressable-Memory-BCAM". GitHub. Retrieved 2020-02-29.