Polyozellin
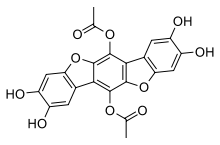
Polyozellin is a chemical which occurs in the mushroom Polyozellus multiplex. It inhibits prolyl endopeptidase, an enzyme that has a role in processing proteins (specifically, amyloid precursor protein) in Alzheimer's disease. Chemicals that inhibit prolyl endopeptidase have attracted research interest due to their potential therapeutic effects.[1] Structurally related dibenzofuranyl derivatives of polyozellin are known as kynapcins.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
6,12-Diacetoxy-2,3,8,9-tetrahydroxybenzo[1,2-b;4,5-b']bisbenzofuran | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H14O10 | |
| Molar mass | 438.344 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Hwang JS, Song KS, Kim WG, Lee TH, Koshino H, Yoo ID (1997). "Polyozellin, a new inhibitor of prolyl endopeptidase from Polyozellus multiplex". The Journal of Antibiotics. 50 (9): 773–77. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.50.773. PMID 9360624.
- Kim SI, Park IH, Song KS (2002). "kynapcin-13 and -28, new benzofuran prolyl endopeptidase inhibitors from Polyozellus multiplex". The Journal of Antibiotics. 55 (7): 623–28. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.55.623. PMID 12243451.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.