Picramic acid
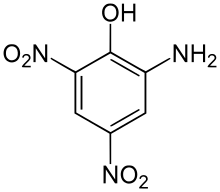
Picramic acid, also known as 2-amino-4,6-dinitrophenol,[2] is an acid obtained by neutralizing an alcoholic solution of picric acid with ammonium hydroxide. Hydrogen sulfide is then added to the resulting solution, which turns red, yielding sulfur and red crystals. These are the ammonium salts of picramic acid, from which it can be extracted using acetic acid.[3]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Amino-4,6-dinitrophenol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.314 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H5N3O5 | |
| Molar mass | 199.12 g/mol |
| Appearance | Brown paste |
| Density | 1.749 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 169 °C (336 °F; 442 K) |
| Boiling point | 386.3 °C (727.3 °F; 659.5 K) |
| log P | 2.41840[1] |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.73 [1] |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases (outdated) | 2, 4, 23/24/25 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | 28, 35, 37, 45 |
| Flash point | 187.5 °C (369.5 °F; 460.6 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Picramic acid is explosive and very toxic. It has a bitter taste.[4]
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.