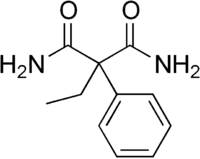
Phenylethylmalonamide
Phenylethylmalonamide (PEMA) is an active metabolite of the anticonvulsant drug primidone, although it is produced in a much lower concentration than phenobarbital, the other active metabolite.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Ethyl-2-phenylmalonamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.027.804 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H14N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 206.24 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- El-Masri HA, Portier CJ (June 1998). "Physiologically based pharmacokinetics model of primidone and its metabolites phenobarbital and phenylethylmalonamide in humans, rats, and mice". Drug Metab. Dispos. 26 (6): 585–94. PMID 9616196.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.