Pennsic War
The Pennsic War is an annual American medieval camping event held by the Society for Creative Anachronism (SCA), a "war" between two large regional SCA groups: the Kingdom of the East and the Middle Kingdom. It is the single largest annual SCA event, with more than 10,000 people attending each year, from as far as China, South Korea, Sweden, Germany, France, Italy, Greece, and Australia.[1] The Tuchux, a non-member splinter group of the SCA, are also frequent participants, holding no allegiance to either Kingdom. [2]

Pennsic is held in late summer and lasts for 17 days (begins on a Friday, ends on the second Sunday).[3] The event centers on pre-17th century history and culture with all campers dressing in historically relevant clothing. The winners of the battles and other activities receive war points, and the Kingdom with the most war points wins that Pennsic.[4]
The Pennsic War uses numbers to identify each war rather than the year it was held, so the 2019 event was known as "Pennsic War 48", there having been 47 previous events. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, no Pennsic event was held in 2020.[3]
History
The Pennsic War takes place in late July/early August.[3] Prior to 2007, Pennsic took place during the first two weeks of August, and some of the earliest Pennsics were held during September.
- The first Pennsic was held in 1972, at Newton's Campground (now Shorehaven Campground) in Waterford, Pennsylvania.
- The second was held at St. Clair Beach Campground near Pittsburgh.
- The third was held on a private farm in Wexford, Pennsylvania.
- The fourth, often called "Pennsic Pour" or "Pennsic Puddle", was held at Spencer Farm on Aquilla Road near Chardon, Ohio and was marred by massive flooding and mudslides. This is celebrated in song by performer Duke Moonwulf Starkadderson in "Pennsic War IV".
- The fifth was held at the Berlin Reservoir outside Alliance, Ohio, after a site in West Virginia was rejected.
- The sixth and all subsequent Pennsics have been held at Coopers Lake Campground in Worth Township near Slippery Rock, Pennsylvania near the intersection of Interstate 79 and US 422. The site is easily visible from the I-79 southbound lanes.[4]
According to the HERSTAĐR-SAGA: An Incomplete History of Pennsic,
One day, almost 30 years ago, Cariadoc of the Bow, the King of the Middle, got bored with peace and declared war upon the East, loser to take Pittsburgh. The King of the East read the declaration of war, filed it away and forgot about it. Time passed. Cariadoc moved to New York and subsequently became King of the East, whereupon he retrieved the declaration from the file cabinet and said, "Let’s fight." The Middle won, and Cariadoc has the distinction of being the only king who declared war upon himself and lost.[5]
People
Since Pennsic XXV in 1996, the event has gathered over 10,000 participants most years.[6] These include not only SCA members from across the globe, but also members of various other historical re-enactment groups such as Markland; and martial arts–based organizations, such as the Tuchux or Rome. Pennsic is, however, an SCA event; members of other groups are welcome, but are generally expected to follow SCA rules—especially in regards to armor, weapons and behavior on the battlefield for the various fighting scenarios. According to the official Pennsic website, the final count for 2015 was 10,556.[7]
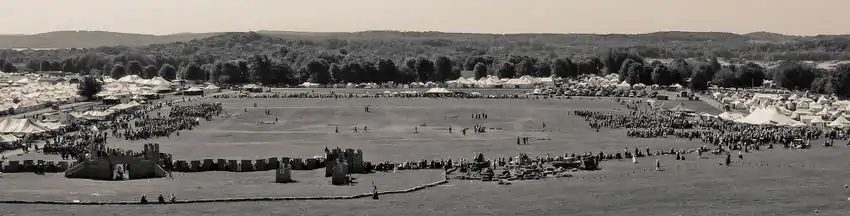
Activities
Martial
- Archery
- SCA Heavy Combat
- Rapier Combat
- Thrown Weapons
- Youth Combat
Non-martial
- Pennsic University (and its offshoot, Bog U): a framework of classes where attendees learn period skills, trades, and performing arts.
- Arts and Sciences Exhibition.
- Youth Arts and Sciences Exhibition.
- Performing Arts: which include acrobatics, busking, comedy, dance, magic, music, juggling, and theatre.
- Period Games: where one can play board games such as Go, Chess and Tafl games, card games such as Tarot card games and dice games.
- Pennsic Choir.
- Dancing: including Renaissance dances, Middle Eastern Dance, South Asian Dance, and East Asian Dance.
- Shopping (roughly 250 vendors)
Local impact
With over 10,000 people, Pennsic becomes the fourth largest populated place in Butler County, PA (after Cranberry and Butler Townships, and the City of Butler). Pennsic's annual economic impact on the immediate area amounts to $1.8 million dropped into the Butler County economy, with many local businesses citing the period during Pennsic being among their busiest of the year.[8][9] During the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic when no Pennsic was held, regular Pennsic attendees who were aware of the event's historically positive impact on businesses organized fundraising for charities local to the area.[10]
See also
- Estrella War—another war held by the SCA
References
- Ganster, Kathleen (August 14, 2005). "10,000 Renaissance buffs converge on Butler County for annual Pennsic War". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette.
- "Tuchux". everything2.com. November 22, 2019.
- http://www.pennsicwar.org/penn43/GENERAL/deadlines.html
- http://www.pennsicwar.org/ANNUAL/pwhistory.html
- F.L. Watkins (Fólki Þorgilsson). 2005. HERSTAĐR-SAGA: An Incomplete History of Pennsic © Folump Enterprises
- "Pennsic War History". PennsicWar.org. Retrieved August 15, 2016.
- "Pennsic 44". PennsicWar.org. Retrieved August 15, 2016.
- Gerard, Joseph (July 2011). "Getting Medieval". Challenge Magazine. Archived from the original on December 6, 2014. Retrieved August 15, 2016.
- Miles, Elizabeth (August 9, 2015). "At the Pennsic Wars, Play's the Thing". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. Retrieved August 15, 2016.
- https://100kfromthesca.org/
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pennsic War. |