Paint robot
Industrial paint robots have been used for decades in automotive paint applications.

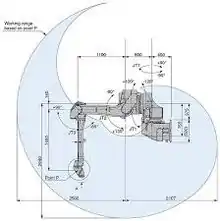
Early paint robots were hydraulic versions - which are still in use today but are of inferior quality and safety - to the latest electronic offerings.[1][2][3] The newest robots are accurate and deliver results with uniform film builds and exact thicknesses.
Originally industrial paint robots were large and expensive, but robot prices have come down to the point that general industry can now afford the same level of automation used by the large automotive manufacturers.
The selection of modern paint robot varies much more in size and payload to allow many configurations for painting items of all sizes.
Painting robots generally have five or six axis motion, three for the base motions and up to three for applicator orientation. These robots can be used in any explosion hazard Class 1 Division 1 environment.
Uses
Automotive Industry
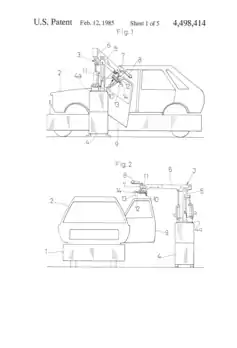
Painting robots are used by vehicle manufacturers to do detailing work on their cars in a consistent and systematic way. Some of these robots are designed with a robotic arm that moves vertically and horizontally, to apply paint on all parts of the car.[4] A patent granted in 1985 to the Mazda Motor Corporation also includes a door handler (a small mechanical hand) that can open and close doors on a vehicle and paint the interior.[4] [Picture of blueprints]
Companies like FANUC continue to mass-produce industrial painting robots that are then sold to manufacturers for use.[5] According to FANUC's website, these robots are useful in limiting safety hazard such as the toxicity of paint, reducing wasted materials through consistent application, and increasing productivity.[5]
Future
There are multiple ideas people have come up with to increase the presence of painting robots in various industries. One such idea comes from technology professors; an interior wall painting robot. The design aims to make the robots “roller-based” so that it can move freely along walls and apply paint to them.[7] The hope is to get people out of the toxicity of interior painting and decrease the amount of time it takes to finish walls.[7] According to the designers, the robot can be made inexpensively as to make it more commercially available.
CloudPainter is a company that designs robots, who's take on the painting robot shifts from simple filling of color to a robot that has “computational creativity,” and can paint more detailed and original designs.[8] The robot has a 3-D printed paint-head with multiple robotic arms and is programmed with artificial intelligence and deep learning.[8]
[include picture for this paragraph] A painting robot designed by Shunsuke Kudoh is equipped with fingered hands and stereo vision. It is capable of looking (with a digital camera eye) at an object, then, using its fingers, pick up a paintbrush and copy the object onto a canvas.[9] The robot is relatively small and can paint small things, such as an apple.[9]
Other designs for painting robots outside of the automotive industry focus on making artwork. One painting robot was able to copy the style and even brushstrokes of Rembrandt, and creating original portraits using that style.[10]
History
Painting Robots have been around since at least 1985.[4] The main use of these robots was found in the automotive industry, but the concept of what a painting robot is capable of has been expanded by many people.
Industrial robots, including painting ones, were created to keep people out of "dangerous" jobs as well as increase productivity.[11] Since their creation, robots have been working side by side with people in manufacturing companies (Hinds, 2008).[12]
In recent years, the painting robot has evolved past industrial use; Many inventors have taken on the idea of creating robots that can create works of art, rather than paint in just a solid color.[9] Besides making them more creative, others have looked for ways to make the robots affordable and accessible for commercial use in places such as interior wall painting.[7]
References
- "abb.com" (PDF).
- "Robotics Online". Robotics Online.
- Rola, Martin D. "Robotic Painting". www.pfonline.com.
- Vehicle body painting robot, 1982-11-29, retrieved 2018-03-26
- "Painting Robots - Robots for Painting & Coating | FANUC America". www.fanucamerica.com. Retrieved 2018-03-26.
- Vehicle body painting robot, 1982-11-29, retrieved 2018-04-09
- Sorour, Mohamed; Abdellatif, Mohamed; Ramadan, Ahmed; A Abo-Ismail, Ahmed (2011-11-01). "Development of Roller-Based Interior Wall Painting Robot". Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Home". cloudpainter - an artificially intelligent painting robot. Retrieved 2018-03-26.
- Kudoh, Shunsuke; Ogawara, Koichi; Ruchanurucks, Miti; Ikeuchi, Katsushi (2009-03-31). "Painting robot with multi-fingered hands and stereo vision". Robotics and Autonomous Systems. 57 (3): 279–288. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.77.2630. doi:10.1016/j.robot.2008.10.007. ISSN 0921-8890.
- Reynolds, Emily. "This fake Rembrandt was created by an algorithm". Retrieved 2018-03-26.
- Wallen, Johanna (May 2008). "History of the industrial robot" (PDF). doi:10.18411/a-2017-023 – via Department of Electrical Engineering, Linkopings Universitet. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Hinds, Pamela J.; Roberts, Teresa L.; Jones, Hank (June 2004). "Whose Job is It Anyway? A Study of Human-Robot Interaction in a Collaborative Task". Human–Computer Interaction. 19 (1–2): 151–181. doi:10.1207/s15327051hci1901&2_7. S2CID 102882.
