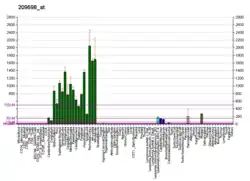
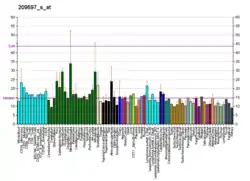
PNMA2
Paraneoplastic antigen Ma2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PNMA2 gene.[5][6]
| PNMA2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | PNMA2, MA2, MM2, RGAG2, paraneoplastic Ma antigen 2, PNMA family member 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 603970 MGI: 2444129 HomoloGene: 5249 GeneCards: PNMA2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 8: 26.5 – 26.51 Mb | Chr 14: 66.91 – 66.92 Mb | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000240694 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000046204 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Voltz R, Gultekin SH, Rosenfeld MR, Gerstner E, Eichen J, Posner JB, Dalmau J (Jun 1999). "A serologic marker of paraneoplastic limbic and brain-stem encephalitis in patients with testicular cancer". N Engl J Med. 340 (23): 1788–95. doi:10.1056/NEJM199906103402303. PMID 10362822.
- "Entrez Gene: PNMA2 paraneoplastic antigen MA2".
Further reading
- Hillier LD, Lennon G, Becker M, et al. (1997). "Generation and analysis of 280,000 human expressed sequence tags". Genome Res. 6 (9): 807–28. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.807. PMID 8889549.
- Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Suyama M, et al. (1999). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XII. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 5 (6): 355–64. doi:10.1093/dnares/5.6.355. PMID 10048485.
- Dalmau J, Gultekin SH, Voltz R, et al. (1999). "Ma1, a novel neuron- and testis-specific protein, is recognized by the serum of patients with paraneoplastic neurological disorders". Brain. 122 (1): 27–39. doi:10.1093/brain/122.1.27. PMID 10050892.
- Rosenfeld MR, Eichen JG, Wade DF, et al. (2001). "Molecular and clinical diversity in paraneoplastic immunity to Ma proteins". Ann. Neurol. 50 (3): 339–48. doi:10.1002/ana.1288. PMID 11558790. S2CID 24518861.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, et al. (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
- Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, et al. (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. 3 (1): 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.