Oxycarboxin
Oxycarboxin is an organic compound used as a fungicide.[1][2] It is an anilide.[3]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
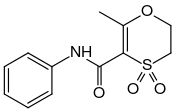
| IUPAC name
6-methyl-4,4-dioxo-N-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1,4-oxathiine-5-carboxamide | |
| Other names
Oxycarboxine; Dcmod; Oxicarboxin, Vitavax sulfone, Plantvax, Carbojet, 5,6-dihydro-2-methyl-1,4-oxathi-ine-3-carboxanilide-4,4-dioxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.023.697 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H13NO4S | |
| Molar mass | 267.30 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 120 °C (248 °F; 393 K) |
| moderate | |
| Solubility | acetone, DMF, ethanol, and methanol |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Triforine, Triclopyr |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Uses
Oxycarboxin is used to control rust diseases (e.g. soybean rust).[2]
History
Oxycarboxin has been commercially available since 1966.[1]
Preparation
Oxycarboxin is prepared from acetoacetanilide and 2-mercaptoethanol.[1]
References
- Ackermann, Peter; Margot, Paul; Müller, Franz (2000). "Fungicides, Agricultural". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a12_085. ISBN 3527306730.
- Shanmugasundaram, S.; Yeh, C.C.; Hartman, G.L.; Talekar, N.S. (1991). Vegetable Soybean Research Needs for Production and Quality Improvement (PDF). Taipei: Asian Vegetable Research and Development Center. pp. 86–87. ISBN 9789290580478. Retrieved 6 February 2016.
- PubChem. "Oxycarboxin". PubChem. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 2020-12-06.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.