o-Cymene
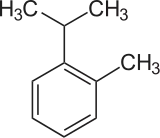
o-Cymene is an organic compound classified as an aromatic hydrocarbon. Its structure consists of a benzene ring ortho-substituted with a methyl group and an isopropyl group. It is a flammable colorless liquid which is nearly insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-methyl-2-propan-2-ylbenzene | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14 | |
| Molar mass | 134.22 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.88 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −71.5 °C (−96.7 °F; 201.7 K) |
| Boiling point | 178 °C (352 °F; 451 K) |
| 23.3 mg/L | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Flammable |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H226 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P280, P303+361+353, P370+378, P403+235, P501 | |
| Flash point | 50.6 °C (123.1 °F; 323.8 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Isomers and production
In addition to o-cymene, there are two other geometric isomers called m-cymene, in which the alkyl groups are meta-substituted, and p-cymene, in which they are para-substituted. p-Cymene is the most common natural isomer, o-cymene is also found naturally rarely, documented in the plant species Echinophora platyloba D.C.[1] The three isomers form the group of cymenes.
Cymenes can be produced by alkylation of toluene with propylene.[2][3]
References
- Hashemi, Mohammad; Ehsani, Ali; Hosseini Jazani, Nima; Aliakbarlu, Javad; Mahmoudi, Razzaqh (2013). "Chemical composition and in vitro antibacterial activity of essential oil and methanol extract of Echinophora platyloba D.C against some of food-borne pathogenic bacteria". Veterinary Research Forum: An International Quarterly Journal. 4 (2): 123–127. ISSN 2008-8140. PMC 4313014. PMID 25653784.
- Vora, Bipin V.; Kocal, Joseph A.; Barger, Paul T.; Schmidt, Robert J.; Johnson, James A. (2003). "Alkylation". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. Kirk‐Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0112112508011313.a01.pub2. ISBN 0471238961.
- Griesbaum, Karl; Behr, Arno; Biedenkapp, Dieter; Voges, Heinz-Werner; Garbe, Dorothea; Paetz, Christian; Collin, Gerd; Mayer, Dieter; Höke (2002). "Hydrocarbons". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a13_227.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.