Northern dry deciduous forests
The Northern dry deciduous forests, also known as the North Deccan dry deciduous forests, is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion of east-central India.
| Northern dry deciduous forests | |
|---|---|
 | |
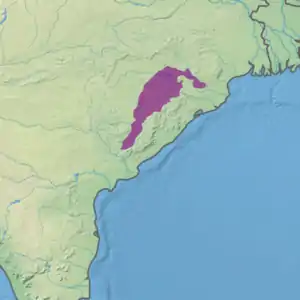 Ecoregion territory (in purple) | |
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Indomalayan |
| Biome | tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests |
| Borders | Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests |
| Geography | |
| Area | 58,154 km2 (22,453 sq mi) |
| Country | India |
| States | Odisha and Chhattisgarh |
| Conservation | |
| Conservation status | critical/endangered |
| Protected | 1,604 km² (3%)[1] |
Geography
It covers an area of 58,200 square kilometers (22,500 sq mi), mostly in western Odisha state, with portions in neighboring Chhattisgarh. The region extends northeast-southwest in the dry western rain shadow of the Eastern Ghats range, which block the moisture-laden monsoon winds from the Bay of Bengal to the east. It is surrounded by the more humid Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests ecoregion.
The ecoregion lies mostly in the middle basin of the Mahanadi River and its tributary the Tel. The southern portion of the ecoregion lies in the upper basin of the Indravati River, a tributary of the Godavari.
Flora
The original vegetation was a multi-storied forest of mostly dry-season deciduous trees, dominated by sal (Shorea robusta). Little of the original forest remains. Teak (Tectona grandis), which favors drier conditions, is more common in the remaining forests. Frequent fires, intensive grazing, and over-harvesting trees for firewood and fodder has reduced other areas to open scrubland or savanna. Much of the ecoregion has been converted to agriculture or pasture.[2]
Fauna
The ecoregion has 68 native mammal species. Threatened mammals include the tiger (Panthera tigris), dhole (Cuon alpinus), sloth bear (Melursus ursinus), and chousingha (Tetracerus quadricornis).[2]
There are 261 bird species in the ecoregion. They include the Indian grey hornbill (Ocyceros birostris) and Oriental pied hornbill (Anthracoceros albirostris).[2]
Conservation
A 1997 assessment found that more than three-quarters of the ecoregion's natural habitat had been cleared or degraded. Four protected areas encompassed about 2.5 percent of the ecoregion's area.[3] A 2017 assessment estimated that 1,604 km², or 3%, of the ecoregion is in protected areas. Another 12% is forested but unprotected.[4]
- Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary, Odisha (340 km²)
- Gomarda Wildlife Sanctuary, Raigarh district, Chhattisgarh (290 km²)
- Kanger Ghati National Park, Chhattisgarh (230 km²)
- Sunabeda Tiger Reserve, Nuapada district, Odisha (591 km²)
See also
External links
- "Northern dry deciduous forests". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.
References
- Eric Dinerstein, David Olson, et al. (2017). An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm, BioScience, Volume 67, Issue 6, June 2017, Pages 534–545; Supplemental material 2 table S1b.
- "Northern dry-deciduous forests". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.
- Wikramanayake, Eric; Eric Dinerstein; Colby J. Loucks; et al. (2002). Terrestrial Ecoregions of the Indo-Pacific: a Conservation Assessment. Island Press; Washington, DC. pp. 321-322
- Eric Dinerstein, David Olson, et al. (2017). An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm, BioScience, Volume 67, Issue 6, June 2017, Pages 534–545; Supplemental material 2 table S1b.