North Creek (conservation area)
North Creek (conservation area) is a wildland in the George Washington and Jefferson National Forests of western Virginia that has been recognized by the Wilderness Society as a special place worthy of protection from logging and road construction. Tall evergreen and hardwood trees in the area around Apple Orchard Falls tower above ferns and wildflowers.[1] The area includes a valley which extends from Sunset Fields in the east to its western border near the North Creek Camping Area.[2]
| North Creek (conservation area) | |
|---|---|
IUCN category VI (protected area with sustainable use of natural resources) | |
_looking_northeast_from_Middle_Creek_Rd%252C_Fall_2019.jpg.webp) | |
 Location of North Creek wildarea in Virginia | |
| Location | Glenwood, Virginia, Botetourt County, Virginia, Virginia, United States |
| Coordinates | 37°30′44″N 79°32′31″W |
| Area | 5,131 acres (20.76 km2) |
The area is part of the Glenwood Cluster.
Location and access

The area, located in the Appalachian Mountains of Southwestern Virginia about 7 miles northeast of Buchanan, Virginia, is between the Blue Ridge Parkway on the east, Middle Creek Road (Rt. 3101) on the west and Parkers Gap Road (Va 612) on the north.[3]
The Forest Service 2015 Motor Vehicle Use Map shows roads and trails in the forest and gives the type of vehicle allowed on each route with possible seasonal restrictions. The map covering the North Creek area is included in the gallery below.[4]
Trails into the area include[3]
- Appalachian Trail (Thunder Hill Section), 1.3 mile section in wildland includes Thunder Hill Shelter.[5]
- Apple Orchard Falls, FS Trail 17, 3.4 miles, moderate difficulty, blue blazed
- Cornelius Creek, FS Trail 18, 2.9 miles, moderate difficulty, blue blazed
- Cornelius Creek (2), FS Trail 18a, 2.8 miles, easy, yellow blazed
The boundary of the wildland as determined by the Wilderness Society is shown in the adjacent map.[1] Additional roads and trails are given on National Geographic Map 789.[3] A great variety of information, including topographic maps, aerial views, satellite data and weather information, is obtained by selecting the link with the wildland’s coordinates in the upper right of this page. Beyond maintained trails, old logging roads can be used to explore the area. The Appalachian Mountains were extensively timbered in the early twentieth century leaving logging roads that are becoming overgrown but still passable.,[6] Old logging roads and railroad grades can be located by consulting the historical topographic maps available from the United States Geological Survey (USGS). The North Creek wildland is covered by USGS topographic maps Arnold Valley and Peaks of Otter.[1] A key to the topographic maps for the northern half of the Jefferson National Forest is in the gallery below.
Natural history
The habitat of the southern Appalachians is rich in its biological diversity with nearly 10,000 species, some not found anywhere else. The great diversity is related to the many ridges and valleys which form isolated communities in which species evolve separately from one another. The region lies south of the glaciers that covered North America 11,000 years ago. To escape the glaciers, northern species retreated south to find refuge in the southern Appalachians. When the glaciers retreated, many of these species remained along with the southern species that were native to the area. The diversity includes trees, mosses, millipedes and salamanders.[7]
The wildland contains parts of two special biological areas, Apple Orchard Mountain and Camping Ridge. Special biological areas have large biological diversity with rare fauna and significant forest communities.[2] There are over 1300 acres of possible old growth trees, with a large section near Floyd Mountain and the Cornelius Creek Shelter and smaller tracts scattered throughout the valley. Much of the area on the eastern side has trees at least 140 years old.[1][2] The area includes part of the 5200-acres North Creek Special Management Area, a designation intended to protect hiking and recreation resources, fauna such as songbirds that depend on interior forest habitat, and the creek which is eligible for protection under the Wild and Scenic Rivers Act.[2] Large infestations of invasive species, such as tree of heaven, are found throughout the area, especially in places that have been clearcut.[2]
Wild natural trout streams in Virginia are classified by the Department of Game and Inland Fisheries by their water quality, with class i the highest and class iv the lowest.[8] North Creek and Cornelius Creek are ranked as a class ii trout streams.[2]
To protect the creek for future generations, North Creek has been designated as an Exceptional State Water (Tier III), thus prohibiting new or increased point source discharges.[9][10][11][12]
Topography
At an elevation of 4206 feet,[13] Apple Orchard Mountain dominates the region. It is the highest elevation on the Appalachian Trail within 200 miles.[5] The name comes from the weathered northern red oaks that give the appearance of a deserted orchard.[5] The headwaters of North Creek are within the wildland. The creek flows along the base of the southern slope of Pine Mountain into Jennings Creek. Cornelius Creek, between Floyd Mountain and Backbone Ridge, flows into North Creek.
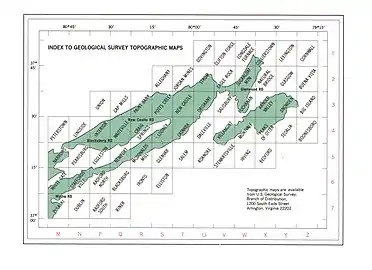 Index to topographic maps covering the northern section of the Jefferson National Forest
Index to topographic maps covering the northern section of the Jefferson National Forest Motor Vehicle Use Map31 for the North Creek (conservation area)
Motor Vehicle Use Map31 for the North Creek (conservation area)
Forest Service management
The Forest Service has conducted a survey of their lands to determine their potential for wilderness designation. Wilderness designation provides a high degree of protection from development. The areas that were found suitable are referred to as inventoried roadless areas. Later a Roadless Rule was adopted that limited road construction in these areas. The rule provided some degree of protection by reducing the negative environmental impact of road construction and thus promoting the conservation of roadless areas. The North Creek wildland was not included in the inventoried roadless areas, and therefore not protected from possible road construction and timber sales.[1]
There have been numerous proposed timber sales in the area. Notice for the Stave Hollow-Colon Hollow-Thomas Mountain Timbers sale was given in 1993. The Parkers Gap timber sale of 145 acres, with construction of spur roads, was approved in 2003. Environmental groups objected to the sale because of its location in the Peaks of Otter salamander conservation area, the habitat of one of the rarest salamanders in North America.[14] The project was completed in 2010 with 106 acres actually logged.[2]
Nearby Wildlands
Nearby wilderness areas and wildlands recognized as one of Virginia's "Mountain Treasures" by the Wilderness Society are:[1]
References
- Virginia's Mountain Treasures, report issued by The Wilderness Society, May, 1999
- Bamford, Sherman (February 2013). A Review of the Virginia Mountain Treasures of the Jefferson National Forest. Blacksburg, Virginia: Sierra Club, OCLC: 893635467.
- Trails Illustrated Maps (2007). Lexington, Blue Ridge Mts. Hiking Map (Trails Illustrated Hiking Maps, 789). Washington, D. C.: National Geographic Society. ISBN 978-1566952330.
- "US Forest Service, Motor Vehicle Use Map".
- Appalachian Trail Guide, Central Virginia (3rd ed.). Harpersville, West Virginia: Appalachian Trail Conference. 2014. pp. 138–139. ISBN 978-1-889386-88-1.
- Sarvis, Will (2011). The Jefferson National Forest. Knoxville, Tennessee: University of Tennessee Press. ISBN 978-1-57233-828-9.
- "Biodiversity of Southern Appalachians". Highlands Biological Station. Retrieved 6 December 2015.
- Virginia Stream Classification: 9VAC25-260-370. Classification Column., accessdate: June 18, 2017
- "Exceptional State Waters" (PDF). Virginia Department of Environmental Quality. Retrieved 9 December 2017.
- "Exceptional State Waters (Tier III)". Virginia Department of Environmental Quality. Retrieved 9 December 2017.
- "Map, North Creek". Virginia Department of Environmental Quality.
- "Photos, North Creek" (PDF). Virginia Department of Environmental Quality.
- "Apple Orchard Mountain". United States Geological Survey.
- "Upcoming Project on the Jefferson and George Washington National Forest". Southern Appalachian Forest Coalition. Retrieved 11 December 2017.