Nanodisc
A nanodisc is a synthetic model membrane system which assists in the study of membrane proteins.[1] It is composed of a lipid bilayer of phospholipids with the hydrophobic edge screened by two amphipathic proteins. These proteins are called membrane scaffolding proteins (MSP) and align in double belt formation.[2][3][4] Nanodiscs are structurally very similar to discoidal high-density lipoproteins (HDL) and the MSPs are modified versions of apolipoprotein A1 (apoA1), the main constituent in HDL. Nanodiscs are useful in the study of membrane proteins because they can solubilise and stabilise membrane proteins[5] and represent a more native environment than liposomes, detergent micelles, bicelles and amphipols.
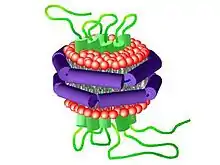
The art of making nanodiscs has progressed past using only the MSPs and lipids to make particles, leading to alternative strategies like peptide nanodiscs that use simpler proteins and synthetic nanodiscs that do not need any proteins for stabilization.
MSP nanodisc
The original nanodisc was produced by apoA1-derived MSPs from 2002.[2] The size and stability of these discs depend on the size of these proteins, which can be adjusted by truncation and fusion. In general, MSP1 proteins consist of one repeat, and MSP2s are double-sized.[6][7]
Peptide nanodisc
In peptide nanodiscs, the lipid bilayer is screened by amphipathic peptides instead of two MSPs. Peptide nanodiscs are structurally similar to MSP nanodiscs and the peptides also align in a double belt. They can stabilise membrane proteins,[8] but have higher polydispersity and are structurally less stable than MSP nanodiscs. Recent studies, however, showed that dimerization[9] and polymerization[10] of the peptides make them more stable.
Synthetic nanodisc
Another way to mimic the native lipid membrane are synthetic polymers. Styrene-maleic acid co-polymers (SMAs)[11] and Diisobutylene-maleic acid (DIBMA)[12] are such synthetic polymers. They can solubilize membrane proteins directly from cells or raw extract. It was discovered that all synthetic polymers which contained a styrene and maleic acid group can solubilize proteins.[13]
References
- Liszewski, Kathy (1 October 2015). "Dissecting the Structure of Membrane Proteins". Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News. 35 (17): 16–18, 21. doi:10.1089/gen.35.07.09.
Nanodiscs are self-assembling nanoscale phospholipid bilayers that are stabilized using engineered membrane scaffold proteins.
(subscription required) - Bayburt, T. H.; Grinkova, Y. V.; Sligar, S. G. (2002). "Self-Assembly of Discoidal Phospholipid Bilayer Nanoparticles with Membrane Scaffold Proteins". Nano Letters. 2 (8): 853–856. doi:10.1021/nl025623k.
- Bayburt, T.H.; Sligar, S.G. (2010). "Membrane protein assembly into Nanodiscs". FEBS Letters. 584 (9): 1721–1727. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2009.10.024. PMC 4758813. PMID 19836392.
- Skar-Gislinge, N.; Simonsen, J.B.; Mortensen, K.; Feidenhans'l, R.; Sligar, S.G.; Lindberg Møller, B.; Bjørnholm, T.; Arleth, L. (2010). "Elliptical structure of phospholipid bilayer nanodiscs encapsulated by scaffold proteins: casting the roles of the lipids and the protein". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 132 (39): 13713–22. doi:10.1021/ja1030613. PMC 4120756. PMID 20828154.
- Denisov, I. G.; Sligar, S. G. (2011). "Cytochromes P450 in Nanodiscs". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Proteins and Proteomics. 1814 (1): 223–229. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.05.017. PMC 2974961. PMID 20685623.
- Denisov, IG; Grinkova, YV; Lazarides, AA; Sligar, SG (24 March 2004). "Directed self-assembly of monodisperse phospholipid bilayer Nanodiscs with controlled size". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 126 (11): 3477–87. doi:10.1021/ja0393574. PMID 15025475.
- Grinkova, YV; Denisov, IG; Sligar, SG (November 2010). "Engineering extended membrane scaffold proteins for self-assembly of soluble nanoscale lipid bilayers". Protein Engineering, Design & Selection : PEDS. 23 (11): 843–8. doi:10.1093/protein/gzq060. PMC 2953958. PMID 20817758.
- Midtgaard, S.R.; Pedersen, M.C.; Kirkensgaard, J.J.K.; Sørensen, K.K.; Mortensen, K.; Jensen, K.J.; Arleth, L. (2016). "Self-assembling peptides form nanodiscs that stabilize membrane proteins". Soft Matter. 10 (5): 738–752. doi:10.1039/c3sm51727f. PMID 24651399.
- Larsen, A.N.; Sørensen, K.K.; Johansen, N.T.; Martel, A.; Kirkensgaard, J.J.K.; Jensen, K.J.; Arleth, L; Midtgaard, S. Roi (2016). "Dimeric peptides with three different linkers self- assemble with phospholipids to form peptide nanodiscs that stabilize membrane proteins". Soft Matter. 12 (27): 5937–5949. doi:10.1039/c6sm00495d. PMID 27306692.
- Kondo, H; Ikeda, K; Nakano, M (2016). "Formation of size-controlled, denaturation-resistant lipid nanodiscs by an amphiphilic self-polymerizing peptide". Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. 146: 423–430. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.06.040. PMID 27393815.
- Knowles, Timothy J.; Finka, Rachael; Smith, Corinne; Lin, Yu-Pin; Dafforn, Tim; Overduin, Michael (2009-06-10). "Membrane Proteins Solubilized Intact in Lipid Containing Nanoparticles Bounded by Styrene Maleic Acid Copolymer". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 131 (22): 7484–7485. doi:10.1021/ja810046q. ISSN 0002-7863. PMID 19449872.
- Oluwole, Abraham Olusegun; Klingler, Johannes; Danielczak, Bartholomäus; Babalola, Jonathan Oyebamiji; Vargas, Carolyn; Pabst, Georg; Keller, Sandro (2017-12-06). "Formation of Lipid-Bilayer Nanodiscs by Diisobutylene/Maleic Acid (DIBMA) Copolymer". Langmuir. 33 (50): 14378–14388. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b03742. ISSN 0743-7463. PMID 29160078.
- "Diisobutylene-maleic acid (DIBMA)". Cube Biotech. Retrieved 2019-02-21.
External links
- Nanodisc Technology from the Stephen Sligar laboratory
- Assembled nanodiscs for application with cell-free lysates
- HDL and Nanodiscs an overview of nanodisc technology at UIUC
- Phospholipid Bilayer Nanodiscs A summary from the Atkins lab at the University of Washington
- Purchase the MSP The plasmid for the MSP is available from AddGene
Further reading
Roos, C; Kai, L; Haberstock, S; Proverbio, D; Ghoshdastider, U; Ma, Y; Filipek, S; Wang, X; Dötsch, V; Bernhard, F (2014). "High-Level Cell-Free Production of Membrane Proteins with Nanodiscs". Cell-Free Protein Synthesis. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1118. pp. 109–30. doi:10.1007/978-1-62703-782-2_7. ISBN 978-1-62703-781-5. PMID 24395412.
Roos, C; Kai, L; Proverbio, D; Ghoshdastider, U; Filipek, S; Dötsch, V; Bernhard, F (2013). "Co-translational association of cell-free expressed membrane proteins with supplied lipid bilayers". Molecular Membrane Biology. 30 (1): 75–89. doi:10.3109/09687688.2012.693212. PMID 22716775.
Ritchie, T. K.; Grinkova, Y. V.; Bayburt, T. H.; Denisov, I. G.; Zolnerciks, J. K.; Atkins, W. M.; Sligar, S. G. (2009). "Chapter 11 Reconstitution of Membrane Proteins in Phospholipid Bilayer Nanodiscs". Methods in Enzymology Volume 464. Methods in Enzymology. 464. pp. 211–231. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(09)64011-8. ISBN 9780123749697. PMC 4196316. PMID 19903557.
Kijac, A.; Shih, A. Y.; Nieuwkoop, A. J.; Schulten, K.; Sligar, S. G.; Rienstra, C. M. (2010). "Lipid−Protein Correlations in Nanoscale Phospholipid Bilayers Determined by Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance". Biochemistry. 49 (43): 9190–9198. doi:10.1021/bi1013722. PMC 3136391. PMID 20804175.
Bayburt, T. H.; Sligar, S. G. (2010). "Membrane protein assembly into Nanodiscs". FEBS Letters. 584 (9): 1721–1727. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2009.10.024. PMC 4758813. PMID 19836392.
Morrissey, J. H.; Pureza, V.; Davis-Harrison, R. L.; Sligar, S. G.; Rienstra, C. M.; Kijac, A. Z.; Ohkubo, Y. Z.; Tajkhorshid, E. (2009). "Protein-membrane interactions: Blood clotting on nanoscale bilayers". Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 7 (Suppl 1): 169–172. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03390.x. PMC 2839880. PMID 19630793.
Shih, A. Y.; Sligar, S. G.; Schulten, K. (2009). "Maturation of high-density lipoproteins". Journal of the Royal Society Interface. 6 (39): 863–871. doi:10.1098/rsif.2009.0173. PMC 2805102. PMID 19570799.
Das, A.; Zhao, J.; Schatz, G. C.; Sligar, S. G.; Van Duyne, R. P. (2009). "Screening of Type I and II Drug Binding to Human Cytochrome P450-3A4 in Nanodiscs by Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Spectroscopy". Analytical Chemistry. 81 (10): 3754–3759. doi:10.1021/ac802612z. PMC 4757437. PMID 19364136.
Shih, A.Y., Freddolino, P.L., Arkhipov, A., Sligar, S.G., and Schulten, K. (2008) Molecular Modeling of the Structural Properties and Formation of High-Density Lipoprotein Particles Current Topics in Membranes 60, 313-342. ISBN 978-0-12-373893-6
Goluch, E. D.; Shaw, A. W.; Sligar, S. G.; Liu, C. (2008). "Microfluidic patterning of nanodisc lipid bilayers and multiplexed analysis of protein interaction". Lab on a Chip. 8 (10): 1723–1728. doi:10.1039/b806733c. PMID 18813396.
Zhao, J.; Das, A.; Zhang, X.; Schatz, G. C.; Sligar, S. G.; Van Duyne, R. P. (2006). "Resonance Surface Plasmon Spectroscopy: Low Molecular Weight Substrate Binding to Cytochrome P450". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 128 (34): 11004–11005. doi:10.1021/ja0636082. PMID 16925400.
Borch, J.; Torta, F.; Sligar, S. G.; Roepstorff, P. (2008). "Nanodiscs for Immobilization of Lipid Bilayers and Membrane Receptors: Kinetic Analysis of Cholera Toxin Binding to a Glycolipid Receptor". Analytical Chemistry. 80 (16): 6245–6252. doi:10.1021/ac8000644. PMID 18616345.
Morrissey, J. H.; Pureza, V.; Davis-Harrison, R. L.; Sligar, S. G.; Ohkubo, Y. Z.; Tajkhorshid, E. (2008). "Blood clotting reactions on nanoscale phospholipid bilayers". Thrombosis Research. 122 (Suppl 1): S23–S26. doi:10.1016/S0049-3848(08)70014-8. PMC 2836762. PMID 18691494.
Marin, V. L.; Bayburt, T. H.; Sligar, S. G.; Mrksich, M. (2007). "Functional Assays of Membrane-Bound Proteins with SAMDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 46 (46): 8796–8798. doi:10.1002/anie.200702694. PMC 2790068. PMID 17943935.
Kijac, A. Z.; Li, Y.; Sligar, S. G.; Rienstra, C. M. (2007). "Magic-Angle Spinning Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy of Nanodisc-Embedded Human CYP3A4†". Biochemistry. 46 (48): 13696–13703. doi:10.1021/bi701411g. PMC 2571072. PMID 17985934.
Shih, A. Y.; Arkhipov, A.; Freddolino, P. L.; Sligar, S. G.; Schulten, K. (2007). "Assembly of Lipids and Proteins into Lipoprotein Particles". The Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 111 (38): 11095–11104. doi:10.1021/jp072320b. PMID 17696388.
Shih, A. Y.; Freddolino, P. L.; Sligar, S. G.; Schulten, K. (2007). "Disassembly of Nanodiscs with Cholate". Nano Letters. 7 (6): 1692–1696. doi:10.1021/nl0706906. PMID 17503871.
Bayburt, T. H.; Leitz, A. J.; Xie, G.; Oprian, D. D.; Sligar, S. G. (2007). "Transducin Activation by Nanoscale Lipid Bilayers Containing One and Two Rhodopsins". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 282 (20): 14875–14881. doi:10.1074/jbc.M701433200. PMID 17395586.
Nath, A.; Atkins, W. M.; Sligar, S. G. (2007). "Applications of Phospholipid Bilayer Nanodiscs in the Study of Membranes and Membrane Proteins†". Biochemistry. 46 (8): 2059–2069. doi:10.1021/bi602371n. PMID 17263563.