Musculair
Musculair 1 and Musculair 2 are two human-powered aircraft designed and built by German academic and engineer Günther Rochelt.
Rochelt designed Musculair 1 and completed building it in 1984, allowing his son Holger to win two Kremer prizes for the flight over "the eight" in four minutes and 25 seconds in 1984. In the same year, he set a world speed record at 35.7 kilometres per hour (22.2 mph) to receive a second Kremer prize. Later that year, Holger and his sister Katrin, at that time still a child, became the first passenger flight in a human powered aircraft.
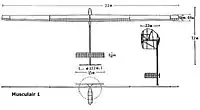
- Length: 7.20 m
- Wingspan: 22.00 m
- Wing area: 16.50 m2
- Glide ratio: 1:38
- Height: 2.20 m
- Mass of the aircraft: 28 kg
- Propeller diameter: 2.72 m
- required minimum power: 200 watts
- required performance (11m / s): 280 Watts
Having slimmed down to just 41 kilograms (90 lb), Günther designed Musculair 2, Holger set a new speed world record of 44.26 kilometres per hour (27.50 mph) in 1985.[1]
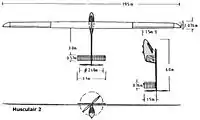

- Length: 6.00 m
- Wingspan: 19.50 m
- Wing area: 11.70 m2
- Glide ratio: 1:37
- Height: 1.50 m
- Mass of the plane: 25 kg
- Propeller diameter: 2.68 m
Today, Musculair I is on display at the main Deutsches Museum, Munich. Musculair 2 is on display at the specialist Deutsches Museum Flugwerft Schleissheim in Oberschleißheim.
See also
References
- "Holger Rochelt (FRG) (389)". www.fai.org. 2017-10-10. Retrieved 2020-12-04.