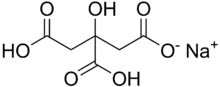
Monosodium citrate
Monosodium citrate, more correctly, sodium dihydrogen citrate (Latin: natrium citricum acidulatum), is an acid salt of citric acid. Disodium citrate and trisodium citrate are also known. It can be prepared by partial neutralisation of an aqueous solution of sodium bicarbonate or carbonate with citric acid.
- NaHCO3 + C6H8O7 → NaC6H7O7 + CO2 + H2O
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
sodium dihydrogen 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.038.834 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E331i (antioxidants, ...) |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H7NaO7 | |
| Molar mass | 214.105 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white powder hygroscopic |
| Odor | odorless |
| Melting point | 212 °C (414 °F; 485 K) |
| soluble | |
| Solubility | negligible in ethanol |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.50 - 3.80 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is highly soluble in water and practically insoluble in ethanol. Monosodium citrate is used as an anticoagulant in donated blood.[1]
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.