Mitochondrial disease
Mitochondrial disease is a group of disorders caused by mitochondrial dysfunction. Mitochondria, are the organelles that generate energy for the cell and are found in every cell of the human body except red blood cells. They convert the energy of food molecules into the ATP that powers most cell functions.
| Mitochondrial disease | |
|---|---|
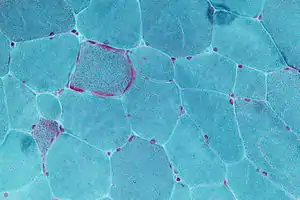 | |
| Micrograph showing ragged red fibers, a finding seen in various types of mitochondrial diseases. Muscle biopsy. Gomori trichrome stain. | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
Mitochondrial diseases take on unique characteristics both because of the way the diseases are often inherited and because mitochondria are so critical to cell function. A subclass of these diseases that have neuromuscular symptoms are known as mitochondrial myopathies.
Conditions
Examples of mitochondrial diseases include:
- Mitochondrial myopathy
- Diabetes mellitus and deafness (DAD)
- this combination at an early age can be due to mitochondrial disease
- Diabetes mellitus and deafness can be found together for other reasons
- Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON)
- visual loss beginning in young adulthood
- eye disorder characterized by progressive loss of central vision due to degeneration of the optic nerves and retina
- affects 1 in 50,000 people in Finland
- Leigh syndrome, subacute sclerosing encephalopathy
- after normal development the disease usually begins late in the first year of life, although onset may occur in adulthood
- a rapid decline in function occurs and is marked by seizures, altered states of consciousness, dementia, ventilatory failure
- Neuropathy, ataxia, retinitis pigmentosa, and ptosis (NARP)
- progressive symptoms as described in the acronym
- dementia
- Myoneurogenic gastrointestinal encephalopathy (MNGIE)
- gastrointestinal pseudo-obstruction
- neuropathy
- MERRF syndrome
- progressive myoclonic epilepsy
- "Ragged Red Fibers" are clumps of diseased mitochondria that accumulate in the subsarcolemmal region of the muscle fiber and appear when muscle is stained with modified Gömöri trichrome stain
- short stature
- hearing loss
- lactic acidosis
- exercise intolerance
- MELAS syndrome
- Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome
Conditions such as Friedreich's ataxia can affect the mitochondria but are not associated with mitochondrial proteins.
Associated conditions
Acquired conditions in which mitochondrial dysfunction has been involved are:
- diabetes
- Huntington's disease
- cancer
- Alzheimer's disease
- Parkinson's disease
- bipolar disorder,[1][2][3] schizophrenia, aging and senescence, anxiety disorders[4]
- cardiovascular disease
- sarcopenia
- chronic fatigue syndrome[2]
The body, and each mutation, is modulated by other genome variants; the mutation that in one individual may cause liver disease might in another person cause a brain disorder. The severity of the specific defect may also be great or small. Some defects include exercise intolerance. Defects often affect the operation of the mitochondria and multiple tissues more severely, leading to multi-system diseases.[5]
As a rule, mitochondrial diseases are worse when the defective mitochondria are present in the muscles, cerebrum, or nerves,[6] because these cells use more energy than most other cells in the body.
Although mitochondrial diseases vary greatly in presentation from person to person, several major clinical categories of these conditions have been defined, based on the most common phenotypic features, symptoms, and signs associated with the particular mutations that tend to cause them.
An outstanding question and area of research is whether ATP depletion or reactive oxygen species are in fact responsible for the observed phenotypic consequences.
Cerebellar atrophy or hypoplasia has sometimes been reported to be associated.[7]
Causes
Mitochondrial disorders may be caused by mutations (acquired or inherited), in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), or in nuclear genes that code for mitochondrial components. They may also be the result of acquired mitochondrial dysfunction due to adverse effects of drugs, infections, or other environmental causes.[8] Oxalate may enter cells where it is known to cause mitochondrial dysfunction.[9]
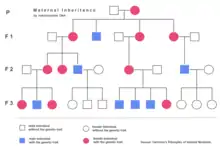
Nuclear DNA has two copies per cell (except for sperm and egg cells), one copy being inherited from the father and the other from the mother. Mitochondrial DNA, however, is inherited from the mother only (with some exceptions) and each mitochondrion typically contains between 2 and 10 mtDNA copies. During cell division the mitochondria segregate randomly between the two new cells. Those mitochondria make more copies, normally reaching 500 mitochondria per cell. As mtDNA is copied when mitochondria proliferate, they can accumulate random mutations, a phenomenon called heteroplasmy. If only a few of the mtDNA copies inherited from the mother are defective, mitochondrial division may cause most of the defective copies to end up in just one of the new mitochondria (for more detailed inheritance patterns, see human mitochondrial genetics). Mitochondrial disease may become clinically apparent once the number of affected mitochondria reaches a certain level; this phenomenon is called "threshold expression".
Mitochondria possess many of the same DNA repair pathways as nuclei do—but not all of them;[10] therefore, mutations occur more frequently in mitochondrial DNA than in nuclear DNA (see Mutation rate). This means that mitochondrial DNA disorders may occur spontaneously and relatively often. Defects in enzymes that control mitochondrial DNA replication (all of which are encoded for by genes in the nuclear DNA) may also cause mitochondrial DNA mutations.
Most mitochondrial function and biogenesis is controlled by nuclear DNA. Human mitochondrial DNA encodes 13 proteins of the respiratory chain, while most of the estimated 1,500 proteins and components targeted to mitochondria are nuclear-encoded. Defects in nuclear-encoded mitochondrial genes are associated with hundreds of clinical disease phenotypes including anemia, dementia, hypertension, lymphoma, retinopathy, seizures, and neurodevelopmental disorders.[11]
A study by Yale University researchers (published in the February 12, 2004, issue of the New England Journal of Medicine) explored the role of mitochondria in insulin resistance among the offspring of patients with type 2 diabetes.[12] Other studies have shown that the mechanism may involve the interruption of the mitochondrial signaling process in body cells (intramyocellular lipids). A study conducted at the Pennington Biomedical Research Center in Baton Rouge, Louisiana[13] showed that this, in turn, partially disables the genes that produce mitochondria.
Mechanisms
The effective overall energy unit for the available body energy is referred to as the daily glycogen generation capacity,[14][15][16] and is used to compare the mitochondrial output of healthy individuals to that of afflicted or chronically glycogen-depleted individuals. This value is slow to change in a given individual, as it takes between 18 and 24 months to complete a full cycle.[15]
The glycogen generation capacity is entirely dependent on, and determined by, the operating levels of the mitochondria in all of the cells of the human body;[17] however, the relation between the energy generated by the mitochondria and the glycogen capacity is very loose and is mediated by many biochemical pathways.[14] The energy output of full healthy mitochondrial function can be predicted exactly by a complicated theoretical argument, but this argument is not straightforward, as most energy is consumed by the brain and is not easily measurable.
Diagnosis
Mitochondrial diseases are usually detected by analysing muscle samples, where the presence of these organelles is higher. The most common tests for the detection of these diseases are:
- Southern blot to detect big deletions or duplications
- Polymerase chain reaction and specific mutation testing
- Sequencing
Treatments
Although research is ongoing, treatment options are currently limited; vitamins are frequently prescribed, though the evidence for their effectiveness is limited.[18] Pyruvate has been proposed in 2007 as a treatment option.[19] N-acetyl cysteine reverses many models of mitochondrial dysfunction.[20] In the case of mood disorders, specifically bipolar disorder, it is hypothesized that N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC), acetyl-L-carnitine (ALCAR), S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe), coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), creatine monohydrate (CM), and melatonin could be potential treatment options.[21]
Gene therapy prior to conception
Mitochondrial replacement therapy (MRT) , where the nuclear DNA is transferred to another healthy egg cell leaving the defective mitochondrial DNA behind, is an IVF treatment procedure.[22] Using a similar pronuclear transfer technique, researchers at Newcastle University led by Douglass Turnbull successfully transplanted healthy DNA in human eggs from women with mitochondrial disease into the eggs of women donors who were unaffected.[23][24] In such cases, ethical questions have been raised regarding biological motherhood, since the child receives genes and gene regulatory molecules from two different women. Using genetic engineering in attempts to produce babies free of mitochondrial disease is controversial in some circles and raises important ethical issues.[25][26] A male baby was born in Mexico in 2016 from a mother with Leigh syndrome using MRT.[27]
In September 2012 a public consultation was launched in the UK to explore the ethical issues involved.[28] Human genetic engineering was used on a small scale to allow infertile women with genetic defects in their mitochondria to have children.[29] In June 2013, the United Kingdom government agreed to develop legislation that would legalize the 'three-person IVF' procedure as a treatment to fix or eliminate mitochondrial diseases that are passed on from mother to child. The procedure could be offered from 29 October 2015 once regulations had been established.[30][31][32] Embryonic mitochondrial transplant and protofection have been proposed as a possible treatment for inherited mitochondrial disease, and allotopic expression of mitochondrial proteins as a radical treatment for mtDNA mutation load.
In June 2018 Australian Senate's Senate Community Affairs References Committee recommended a move towards legalising Mitochondrial replacement therapy (MRT). Research and clinical applications of MRT were overseen by laws made by federal and state governments. State laws were, for the most part, consistent with federal law. In all states, legislation prohibited the use of MRT techniques in the clinic, and except for Western Australia, research on a limited range of MRT was permissible up to day 14 of embryo development, subject to a license being granted. In 2010, the Hon. Mark Butler MP, then Federal Minister for Mental Health and Ageing, had appointed an independent committee to review the two relevant acts: the Prohibition of Human Cloning for Reproduction Act 2002 and the Research Involving Human Embryos Act 2002. The committee’s report, released in July 2011, recommended the existing legislation remain unchanged
Currently, human clinical trials are underway at GenSight Biologics (ClinicalTrials.gov # NCT02064569) and the University of Miami (ClinicalTrials.gov # NCT02161380) to examine the safety and efficacy of mitochondrial gene therapy in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy.
Epidemiology
About 1 in 4,000 children in the United States will develop mitochondrial disease by the age of 10 years. Up to 4,000 children per year in the US are born with a type of mitochondrial disease.[33] Because mitochondrial disorders contain many variations and subsets, some particular mitochondrial disorders are very rare.
The average number of births per year among women at risk for transmitting mtDNA disease is estimated to approximately 150 in the United Kingdom and 800 in the United States.[34]
History
The first pathogenic mutation in mitochondrial DNA was identified in 1988; from that time to 2016, around 275 other disease-causing mutations were identified.[35]:37
Notable cases
Notable people who suffered from mitochondrial disease include:
- Mattie Stepanek, a poet, peace advocate, and motivational speaker who suffered from dysautonomic mitochondrial myopathy, and who died at age 13.
- Rocco Baldelli, a coach and former center fielder in Major League Baseball who had to retire from active play at age 29 due to mitochondrial channelopathy.
- Charlie Gard, a British boy who suffered from mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome; decisions about his care were taken to various law courts.
References
- Stork, C; Renshaw, P F (2005). "Mitochondrial dysfunction in bipolar disorder: Evidence from magnetic resonance spectroscopy research". Molecular Psychiatry. 10 (10): 900–19. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001711. PMID 16027739.
- Pieczenik, Steve R; Neustadt, John (2007). "Mitochondrial dysfunction and molecular pathways of disease". Experimental and Molecular Pathology. 83 (1): 84–92. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2006.09.008. PMID 17239370.
- Nierenberg, Andrew A; Kansky, Christine; Brennan, Brian P; Shelton, Richard C; Perlis, Roy; Iosifescu, Dan V (2012). "Mitochondrial modulators for bipolar disorder: A pathophysiologically informed paradigm for new drug development". Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry. 47 (1): 26–42. doi:10.1177/0004867412449303. PMID 22711881.
- Misiewicz, Zuzanna; Iurato, Stella; Kulesskaya, Natalia; Salminen, Laura; Rodrigues, Luis; Maccarrone, Giuseppina; Martins, Jade; Czamara, Darina; Laine, Mikaela A.; Sokolowska, Ewa; Trontti, Kalevi; Rewerts, Christiane; Novak, Bozidar; Volk, Naama; Park, Dong Ik; Jokitalo, Eija; Paulin, Lars; Auvinen, Petri; Voikar, Vootele; Chen, Alon; Erhardt, Angelika; Turck, Christoph W.; Hovatta, Iiris (2019-09-26). "Multi-omics analysis identifies mitochondrial pathways associated with anxiety-related behavior". PLOS Genetics. 15 (9): e1008358. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1008358. ISSN 1553-7404. PMC 6762065. PMID 31557158.
- Nunnari J, Suomalainen A (2012). "Mitochondria: in sickness and in health". Cell. 148 (6): 1145–59. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.035. PMC 5381524. PMID 22424226.
- Finsterer, Josef (2007). "Hematological Manifestations of Primary Mitochondrial Disorders". Acta Haematologica. 118 (2): 88–98. doi:10.1159/000105676. PMID 17637511.
- Lax, Nichola Zoe; Hepplewhite, Philippa Denis; Reeve, Amy Katherine; Nesbitt, Victoria; McFarland, Robert; Jaros, Evelyn; Taylor, Robert William; Turnbull, Douglass Matthew (2012). "Cerebellar Ataxia in Patients with Mitochondrial DNA Disease". Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology. 71 (2): 148–61. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e318244477d. PMC 3272439. PMID 22249460.
- "Mitochondrial diseases". MeSH. Retrieved 2 August 2019.
- Patel, Mikita; Yarlagadda, Vidhush; Adedoyin, Oreoluwa; Saini, Vikram; Assimos, Dean G.; Holmes, Ross P.; Mitchell, Tanecia (May 2018). "Oxalate induces mitochondrial dysfunction and disrupts redox homeostasis in a human monocyte derived cell line". Redox Biology. 15: 207–215. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2017.12.003. PMC 5975227. PMID 29272854.
- Alexeyev M, Shokolenko I, Wilson G, LeDoux S (May 2013). "The maintenance of mitochondrial DNA integrity--critical analysis and update". Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. 5 (5): a012641. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a012641. PMC 3632056. PMID 23637283.
- Scharfe C, Lu HH, Neuenburg JK, Allen EA, Li GC, Klopstock T, Cowan TM, Enns GM, Davis RW (2009). Rzhetsky A (ed.). "Mapping gene associations in human mitochondria using clinical disease phenotypes". PLOS Comput Biol. 5 (4): e1000374. Bibcode:2009PLSCB...5E0374S. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000374. PMC 2668170. PMID 19390613.
- Petersen, Kitt Falk; Dufour, Sylvie; Befroy, Douglas; Garcia, Rina; Shulman, Gerald I. (2004). "Impaired Mitochondrial Activity in the Insulin-Resistant Offspring of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes". New England Journal of Medicine. 350 (7): 664–671. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa031314. ISSN 0028-4793. PMC 2995502. PMID 14960743.
- Diabetes 54, 2005 1926-33
- Mitchell, Peter. "David Keilin's respiratory chain concept and its chemiosmotic consequences" (PDF). Nobel institute.
- Michelakis, Evangelos (January 2007). "A Mitochondria-K+ Channel Axis Is Suppressed in Cancer and Its Normalization Promotes Apoptosis and Inhibits Cancer Growth". University of Alberta. University of Alberta, 2007. 11 (1): 37–51. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.10.020. PMID 17222789.
- Lorini & Ciman, M, & M (1962). "Hypoglycaemic action of Diisopropylammonium salts in experimental diabetes". Institute of Biochemistry, University of Padua, September 1962. Biochemical Pharmacology. 11 (9): 823–827. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(62)90177-6. PMID 14466716.
- Stacpoole PW, Henderson GN, Yan Z, James MO (1998). "Clinical pharmacology and toxicology of dichloroacetate". Environ. Health Perspect. 106 Suppl 4: 989–94. doi:10.1289/ehp.98106s4989. PMC 1533324. PMID 9703483.
- Marriage B, Clandinin MT, Glerum DM (2003). "Nutritional cofactor treatment in mitochondrial disorders". J Am Diet Assoc. 103 (8): 1029–38. doi:10.1016/S0002-8223(03)00476-0. PMID 12891154.
- Tanaka M, Nishigaki Y, Fuku N, Ibi T, Sahashi K, Koga Y (2007). "Therapeutic potential of pyruvate therapy for mitochondrial diseases". Mitochondrion. 7 (6): 399–401. doi:10.1016/j.mito.2007.07.002. PMID 17881297.
- Frantz MC, Wipf P (Jun 2010). "Mitochondria as a target in treatment". Environ Mol Mutagen. 51 (5): 462–75. doi:10.1002/em.20554. PMC 2920596. PMID 20175113.
- Nierenberg, Andrew A, Kansky, Christine, Brennan, Brian P, Shelton, Richard C, Perlis, Roy, Iosifescu, Dan V (2012). "Mitochondrial modulators for bipolar disorder: A pathophysiologically informed paradigm for new drug development". Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry. 47 (1): 26–42. doi:10.1177/0004867412449303. PMID 22711881.
- Tachibana M, Sparman M, Sritanaudomchai H, Ma H, Clepper L, Woodward J, Li Y, Ramsey C, Kolotushkina O, Mitalipov S (September 2009). "Mitochondrial gene replacement in primate offspring and embryonic stem cells". Nature. 461 (7262): 367–372. Bibcode:2009Natur.461..367T. doi:10.1038/nature08368. PMC 2774772. PMID 19710649.
- Boseley, Sarah (2010-04-14). "Scientists reveal gene-swapping technique to thwart inherited diseases". Guardian. London.
- Craven, Lyndsey; Tuppen, Helen A.; Greggains, Gareth D.; Harbottle, Stephen J.; Murphy, Julie L.; Cree, Lynsey M.; Murdoch, Alison P.; Chinnery, Patrick F.; Taylor, Robert W.; Lightowlers, Robert N.; Herbert, Mary; Turnbull, Douglass M. (2010). "Pronuclear transfer in human embryos to prevent transmission of mitochondrial DNA disease". Nature. 465 (7294): 82–85. Bibcode:2010Natur.465...82C. doi:10.1038/nature08958. PMC 2875160. PMID 20393463.

- "UK urged to permit IVF procedure to prevent fatal genetic diseases". The Guardian. London. 2015-04-30.
- "Three parent baby law is 'irresponsible' says Church of England ahead of vote". The Telegraph. London. 2015-04-30.
- Hamzelou, Jessica (2016-09-27). "Exclusive: World's first baby born with new "3 parent" technique". New Scientist. Retrieved 2016-11-26.
- Sample, Ian (2012-09-17). "Regulator to consult public over plans for new fertility treatments". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 8 October 2012.
- "Genetically altered babies born". BBC News. 2001-05-04. Retrieved 2008-04-26.
- The Human Fertilisation and Embryology (Mitochondrial Donation) Regulations 2015 No. 572
- "UK government backs three-person IVF". BBC News. 27 June 2013.
- Knapton, Sarah (1 March 2014) 'Three-parent babies' could be born in Britain next year The Daily Telegraph Science News, Retrieved 1 March 2014
- The Mitochondrial and Metabolic Disease Center
- Gorman, Gráinne S.; Grady, John P.; Ng, Yi; Schaefer, Andrew M.; McNally, Richard J.; Chinnery, Patrick F.; Yu-Wai-Man, Patrick; Herbert, Mary; Taylor, Robert W.; McFarland, Robert; Turnbull, Doug M. (2015). "Mitochondrial Donation — How Many Women Could Benefit?". New England Journal of Medicine. 372 (9): 885–887. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1500960. ISSN 0028-4793. PMC 4481295. PMID 25629662.
- Committee on the Ethical and Social Policy Considerations of Novel Techniques for Prevention of Maternal Transmission of Mitochondrial DNA Diseases; Board on Health Sciences Policy; Institute of Medicine (2016). Claiborne, Anne; English, Rebecca; Kahn, Jeffrey (eds.). Mitochondrial Replacement Techniques: Ethical, Social, and Policy Considerations. National Academies Press. ISBN 978-0-309-38870-2. Index page with links to summaries including one page summary flyer.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mitochondrial diseases. |