Methacrolein diacetate
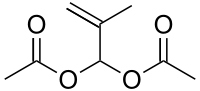
Methacrolein diacetate is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C8H12O4 and a molecular weight of 172.17848.[1] It is a colorless liquid.[2] It is listed as an extremely hazardous substance by the Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act, and the National Institute of Health identifies it as "an irritant of the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract."[3]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Methyl-1-propene-3,3-diyl diacetate | |
| Other names
2-Methyl-2-propene-1,1-diol diacetate; 2-Methylallylidene diacetate; 3,3-Diacetoxy-2-methyl-1-propene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.873 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H12O4 | |
| Molar mass | 172.180 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Production
According to the National Center for Biotechnology Information, "the common esters & diesters of the common polyols are prepared commercially by esterifying the particular polyol with the acid, acid anhydride, or acid chloride of choice in presence of a catalyst. Mono- or diesters result, depending upon the proportions of each reactant employed."[1]
Toxicity
Methacrolein diacetate is extremely toxic, capable of causing severe eye injuries, burns on the skin, and hazards when inhaled. According to the NCBI, "Rabbit eye studies showed the material to cause severe irritation & corneal injury, being rated 9 on a scale of 10. It is markedly irritating to the skin & can cause a burn, but greater hazard is that of skin absorption ... It is hazardous from inhalation also. All rats exposed for 1 hr to essentially saturated vapors died, & five of six rats exposed to 63.5 ppm for 4 hr died."[1]
References
- CID 25305 from PubChem
- "NJ Hazardous Substance Fact Sheet" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services. Retrieved July 9, 2012.
- "METHACROLEIN DIACETATE - National Library of Medicine HSDB Database". Toxnet.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2012-07-09.