Marjorie Joyner
Marjorie Joyner (née Stewart; October 24, 1896 – December 27, 1994) was an American businesswoman, hair care entrepreneur, philanthropist, educator and activist. Joyner is noted for being the first African-American woman to create and patent a permanent hair-wave machine.[2] In addition to her career in hair care, Joyner was highly visible in the African-American community in Chicago, once serving as head of the Chicago Defender Charity network, helping organize the Bud Billiken Day Parade and fundraiser for various schools.[1][3]
Marjorie Joyner | |
|---|---|
 Joyner c. 1950s. | |
| Born | Marjorie Stewart October 24, 1896[1] Monterey, Virginia, U.S. |
| Died | December 27, 1994 (aged 98) Chicago, Illinois, U.S. |
| Nationality | American |
| Education | Bethune-Cookman College |
| Occupation |
|
| Known for | Being the first African-American woman create and patent a permanent hair-wave machine. |
| Spouse(s) | Robert E. Joyner
(m. 1916; died 1973) |
| Children | 2 |
Biography
Early life and education
Born in 1896 in Monterey, Virginia, Joyner was the daughter of George Emmanuel Stewart, a teacher and Annie Stewart (née Daugherty).[1] Joyner was the granddaughter of a slave and a white slave-owner. Joyner's family relocated to Dayton, Ohio in 1904 and her parents divorced three years later. After the divorce of her parents, Joyner lived with various relatives between Ohio and Virginia.[1] In 1912, aged 16, Joyner relocated to Chicago, Illinois to live with her mother. After arriving to Chicago, Joyner received a certificate for dramatic art and expression from Chicago Musical College in 1914.[1] Joyner began studying cosmetology, graduating A.B. Molar Beauty School in 1916, becoming the first African American to graduate from the school.[2] Joyner later received her high school diploma in 1935.[3] In 1973, at the age of 77, Joyner was awarded a bachelor's degree in psychology from Bethune-Cookman College.
Career

Shortly after graduating from beauty school, Joyner opened her salon.[4] Joyner later met Madam C. J. Walker, an African American beauty entrepreneur, and the owner of a cosmetic empire. Joyner worked for Walker as a sales representative. In 1920, Joyner oversaw 200 of Madam Walker's beauty schools as the national adviser. Joyner taught some 15,000 stylists and served as an instructor to coaching Walker's sales representatives door-to-door.[2][1] After her time with Walker beauty schools, Joyner served as a leader in developing new products, such as her permanent wave machine. Joyner helped write the first cosmetology laws for the state of Illinois in the early 1940s. On October 27, 1945, Dr. Joyner, along with renowned educator, Dr. Mary McLeod Bethune and U.S. Congressman William Dawson, founded a sorority and fraternity dedicated to the advancement and promotion of the beauty industry, Alpha Chi Pi Omega. In 1945, Joyner along with Mary McLeod Bethune founded the United Beauty School Owners and Teachers Association, a national association for African-American beauticians.[2] In the 1940s, Joyner was an advisor to the Democratic National Committee and advised several New Deal agencies trying to reach out to African-American women.
Permanent wave design
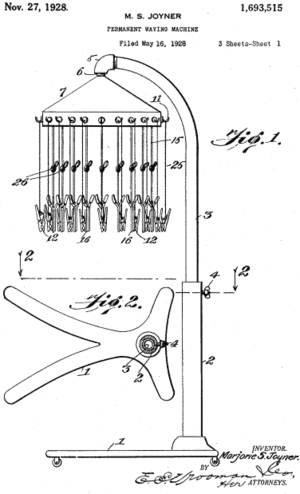
In 1939, Joyner started looking for an easier way for women to curl their hair, taking her inspiration from a pot roast cooking with paper pins to quicken preparation time. Joyner experimented initially with these paper rods and soon designed a table that could be used to curl or straighten hair by wrapping hair. This method allowed hairstyles to last several days. At the beginning of her invention, there were complaints from people that it was uncomfortable.
That was when Joyner improved it with the simple idea of having a scalp protector while the lady is curling her hair.[5] Her patent for this design, (U.S. pat. #1,693,515) established her as the first African American woman to receive a patent. This claim is disputed by some who say that Sarah E. Goode was the first African American woman to hold a patent. It is sometimes falsely cited that Joyner was the original inventor of this type of the machine, called the permanent wave, or perm. Joyner's design was an alternative version of Karl Nessler's groundbreaking invention, invented in England during the late 19th century and patented in London in 1909 and again in the United States in 1925. (U.S. Patent 1,522,258) Joyner's design was popular in salons with both African American and white women. The patent was credited to Madame Walker's company and she received almost no money for it.
Personal life and death
Joyner was married once and had two children. On April 4, 1916, aged 19, she married podiatrist Robert E. Joyner. They remained married until his death in 1973. Together they had two daughters, Anne and Barbara Joyner.[1] Joyner died on December 27, 1994 of heart failure at her home in the Bronzeville neighborhood of Chicago, Illinois, aged 98.[2]
Legacy
In 1987, the Smithsonian Institution in Washington opened an exhibit featuring Joyner's permanent wave machine and a replica of her original salon.[6] On October 24, 1990, Joyner's 95th birthday, she was honored by the city of Chicago, proclaiming her birthday Marjorie Stewart Joyner Day within the city.[3] Currently, her papers reside in the Vivian G. Harsh Research Collection of African-American History and Literature at the Chicago Public Library.
See also
References
- Encyclopedia of African American Business: Updated and Revised Edition, 2nd ..., edited by Jessie Smith.Retrieved March 27, 2020.
- Women of Invention: Life-Changing Ideas by Remarkable Women, By Charlotte Montague.Retrieved March 27, 2020.
- Black Firsts: 4,000 Ground-Breaking and Pioneering Historical Events, By Jessie Carney Smith.Retrieved March 27, 2020.
- "Majorie Joyner". lemelson.mit.edu.
- 1941-, Sullivan, Otha Richard (2002). African American women scientists and inventors. Haskins, James, 1941-2005. New York: Wiley. ISBN 047138707X. OCLC 46456247.CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- Jessie Carney Smith, ed., Encyclopedia of African American Popular Culture (2010) pp 435-38.
- "Invention at Play: Marjorie Joyner". Lemelson Center for the Study of Invention and Innovation. Archived from the original on 2006-10-04. Retrieved 2006-07-24.