Magnetic Tower of Hanoi
The Magnetic Tower of Hanoi (MToH) puzzle is a variation of the classical Tower of Hanoi puzzle (ToH), where each disk has two distinct sides, for example, with different colors "red" and "blue". The rules of the MToH puzzle are the same as the rules of the original puzzle, with the added constraints that each disk is flipped as it is moved, and that two disks may not be placed one on another if their touching sides have the same color. Each disk has a North and South pole, with similar poles repelling one another and opposite poles attracting one another. Magnets inside each disk physically prevent illegal moves.[1]


One of the striking features of the classical ToH puzzle is its relation to the base 2: the minimum number of total moves required to solve the puzzle is 2n − 1 (where n is the number of disks), while the minimum number of moves made by disk k is 2k − 1 (disks are numbered bottom up so that k = 1 being the largest disk, and k = n being the smallest). It will be shown below that just as the original ToH puzzle is related to base 2, so the MToH is related to base 3, though in a more complex manner.[2]
Origin
Mathematically equivalent puzzles to certain variations of the MToH have been known for some time. For example, an equivalent puzzle to one of the colored variations of the MToH appears in Concrete Mathematics.[3] In this puzzle moves are only allowed between certain posts, which is equivalent to assigning permanent colors to the posts (e.g. if two posts have the same permanent color assigned to them, then direct moves are not allowed between the two posts).
The free (non-colored) MToH first appeared publicly on the internet[4] around 2000 (though under the name of "Domino Hanoi") as part of a detailed review by the Mathematician Fred Lunnon of the different variations of the original Tower of Hanoi puzzle.
The MToH was independently invented by the Physicist Uri Levy in the summer of 1984, who also coined the name and the analogy to magnetism. [5] Dr Levy later published a series of papers [1][6][7] dealing with the mathematical aspects of the MToH.
Puzzle description

The MToH puzzle consists of three posts labeled source (S), destination (D), and intermediate (I), and a stack of n different sized disks with each side of a disk having a different color, either Red or Blue. At the beginning of the puzzle the disks are stacked on the S post in order of decreasing size (i.e. the largest disk is at the bottom), and such that all disks have their Red side facing upwards. The objective of the puzzle (in its "basic" version) is to move the entire stack, one disk at a time, to the D post, maintaining the order from largest to smallest disk, but with the Blue sides facing upwards.

The rules governing the movement of the disks are as follows:
- A larger disk cannot be laid on top of a smaller disk (as in the original ToH)
- When a disk is moved, it is flipped, i.e. the color that was facing up now faces down
- Two sides of different disks with the same color may not touch each other (for example, a disk with its Blue side facing downwards cannot be placed on top of a disk that has its Blue side facing upwards).
Puzzle solution for n = 2 and n = 3
In order to illustrate the rules of the MToH, and also show the route to a more general solution, it is useful to work through examples for n = 2 and n = 3. For the case of n = 2, four steps are required, as shown in the accompanying figure, compared to three steps in the n = 2 case of the original ToH. The extra step is required because after the second step the small disk cannot be moved directly from the I post to the D post, as this would mean that its Blue side would be facing downwards. Thus, an extra step is required to flip the color of the small disk, so that it can then be placed on the D post with its Blue side facing upwards.

For the n = 3 case, the solution involves the following steps:
- Numbering the disks 1 to 3 from largest to smallest, one first moves disks 2 and 3 from the S post to the I post (four moves)
This first stage is similar to the n = 2 puzzle described above, which also takes four moves, where the D and I posts are interchanged. However, it is not identical to the n = 2 puzzle due to the presence of the large disk on the S post, which "colors" it red. This means that a disk can only be placed on this post with its red side facing upwards.
- Move disk 1 from S to D (one move)
At this stage one might be tempted to again make use of the n = 2 puzzle, and try to move disks 2 and 3 from I to D in 4 moves. However, here again care is needed. Due to the presence of disk 1 on D, D is now "colored" Blue, i.e. another disk can be placed on it only if it has its Blue side facing up. Furthermore, with the n = 2 puzzle the disks have their red side facing upwards in the starting position, whereas here they have their blue sides facing upwards. Thus, this intermediate configuration is not equivalent to the n = 2 MToH. Instead, we proceed as follows:
- Move disk 3 from I to D via S (2 moves)
- Move disk 2 from I to S (1 move)
- Move disk 3 from D to I (1 move)
- Move disk 2 from S to D (1 move)
- Move disk 3 from I to D (1 move)
Thus, the solution requires 11 steps altogether. As just shown, it is natural to try to use the n = 2 solution to solve parts of the n = 3 puzzle in a recursive manner, as typically used for solving the classical ToH puzzle. However, in contrast to the classical ToH, here the n = 2 solution cannot be blindly applied due to the coloring of the posts and disks. This point illustrates that to achieve a more general solution for the n-disk MToH puzzle, it is necessary to consider variants of the puzzle where the posts are pre-colored (either Blue or Red). By considering these variants it is possible to develop full recursive relations for the MToH puzzle, and thus find a general solution.
Colored variations of the MToH puzzle
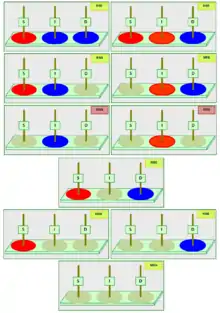
The above description of the MToH puzzle assumes that while the disks themselves are colored, the posts are neutral. This means that an empty post may accept a disk with either its Red side or Blue side facing up. This basic version of the MToH is called the "free" MToH.
Other variations of the MToH puzzle are possible whereby the posts themselves are colored, as shown in the accompanying figure. If a post is pre-colored Red/Blue, then only disks with their Red/Blue side facing upwards may be placed on this pre-colored post. The different variations of the MToH may be named using a 3 letter label "SID", where S,I D refer to the color of the Source, Intermediate and Destination posts respectively, and may assume the values R (Red), B (Blue), or N (Neutral - no color). Thus, the "NNN" puzzle refers to the free MToH, while the "RBB" puzzle refers to the variation where the S post is pre-colored Red, while the I and D posts are pre-colored Blue.
While the variations of the MToH are puzzles within their own right, they also play a key role in solving the free MToH. As seen above, intermediate states of the free MToH can be considered as colored variations, since a post with a disk already on it assume the corresponding color of the disk (meaning that only disk with the same color facing upwards can be placed on the post).
For example, in the free n = 3 MToH puzzle described above, after 5 moves an intermediate state is reached where the large disk is on the D post. From this point on, the D post is considered to be colored Blue, and the puzzle becomes equivalent to the "NNB" puzzle. If a solution is known for the n = 2 "NNB" puzzle, it could immediately be applied to complete the n = 3 free puzzle.
Symmetry relations
Not all of the different colored variations are distinct puzzles, since symmetry means that some pre-colored puzzle variations are identical to others. For example, if we solve the RBB puzzle backwards, then this is the same as solving the RRB puzzle in the regular forward direction (note: the Blue and Red colors have been swapped to keep the rule that at the start of the puzzle all disks must be on the source post with their Red side facing up). Thus, the RBB and RRB puzzles form a time reversal symmetry pair. This means that they share the same characteristics with respect to the number of optimal moves required, even though each puzzle requires a distinct algorithm to solve it. In fact, it will be shown below that puzzles forming a time reversal symmetry pair are interdependent one on the other, in the sense that the solving algorithm of one makes use of the solving algorithm of the other.
Solutions
As with the classical ToH puzzle, one of the simplest and most instructive methods for solving the MToH is to use recursive algorithms. Such algorithms are presented below for selected variations of the puzzle, and the optimality of the solutions is proved. Using these algorithms recursive relations, and subsequently closed form expressions, can be derived for the number of total moves required to solve the puzzle, and the number of moves each disk makes during the solution.
The recursive relations can also be presented and analyzed using a Markov type analysis, which is also discussed.
Recursive solving algorithms and proof of their optimality
It is instructive to first consider the time reversal symmetry pair of puzzles RBB and RRB. As it turns out, these two puzzles are the simplest to solve in that their recursive algorithms depend only one on the other, and not on other variations of the puzzle.
In contrast, solutions for the semi-colored variations (where one or more posts are neutral) and the fully free variation are solved by more complex recursion relations. The RBB(n) and RRB(n) puzzles can be solved using the following pair of optimal algorithms:
For RBB(n):
- Move the n − 1 smallest disks from S to I using the RBB(n − 1) algorithm
- Move disk 1 from S to D
- Move n − 1 disks from I to S using the RRB(n − 1) algorithm
- Move n − 1 disks from S to D using the RBB(n − 1) algorithm
For RRB(n):
- Move the n − 1 smallest disks from S to D using the RRB(n − 1) algorithm
- Move n − 1 disks from D to I using the RBB(n − 1) algorithm
- Move disk 1 from S to D
- Move n − 1 disks from I to D using the RRB(n − 1) algorithm
The optimality of this pair of algorithms is proved via induction, as follows (this proof also forms a detailed explanation of the algorithms):
For n = 1 it is obvious that the algorithms are optimal, since there is only a single move. Next, it is assumed that the algorithms are optimal for n − 1, and using this assumption, it is shown that they are optimal for n.
Beginning with the RBB(n) algorithm, it is clear that before disk 1 can be placed on the D post, it must first be on the S post (which is the only post colored Red), and the rest of the disks must be on the I post. Thus, the solution must pass through this intermediate state, and, by assumption, the optimal way to achieve this intermediate state is to use the RBB(n − 1) algorithm with the D and I posts interchanged.
Next, disk 1 has to be moved from S to D, since it must be moved at least once.
Next, it is shown that from this state the final solution can only be reached via an intermediate state where all n − 1 disks are on the S post. For disk 2 to be placed on the D post, it must first be on the S post (the only Red post), while the other n − 2 disks must be on the I post. However, before disk 3 can be placed on the I post, it must first be on the S post on top of disk 2. This reasoning can proceed through all the disks, each of which must first be on the S post before passing to the I post, thus showing that the solution must pass through an intermediate state where all n − 1 disk are on the S post.
To achieve this intermediate state, it is necessary to use an optimal algorithm which transfers n − 1 disks from the Blue I post to the Red S post via the Blue D post, i.e. the optimal BBR(n − 1) algorithm, which is equivalent to the RRB(n − 1) algorithm (the colors are just swapped).
Finally, it is necessary to transfer the n − 1 smallest disks from the S to the D post via the I post. This of course is just the RBB(n − 1) algorithm.
Similar reasoning can be applied to show that the RRB(n) algorithm above is optimal. Solving algorithms can also be written, and their optimality proved, for other time-reversal pairs of the puzzles, namely:
- The RBN and NRB pair
- The RNB and BNR pair
- The RNN and NNB pair
These algorithms are generally more complex, and make use of the fully colored RBB and RRB algorithms described above. Full details of these algorithms and proofs of their optimality can be found in.[7]
To conclude this section, the solving algorithm of the fully free NNN puzzle is listed. The proof of optimality can also be found in.[7]
- Move the smallest n − 1 disk from S to I via D, using the RNN(n − 1) algorithm
- Move disk 1 from S to D.
- Move the smallest n − 2 disks from I to S via D, using the RRB(n − 2) algorithm (which is equivalent to the BBR(n-2) algorithm)
- Move the smallest n − 2 disks from S to D via I, using the RBB(n − 2) algorithm
- Move disk 2 from I to S
- Move the smallest n − 2 disks from D to I via S, using the RBN(n − 2) algorithm (which is equivalent to the BRN(n − 2) algorithm)
- Move disk 2 from S to D
- Move the smallest n − 2 disks from I to D via S, using the NNB algorithm
Recurrence relations and their solutions
Once the solving algorithms are found, they can be used to derive recurrence relations for the total number of moves made during the execution of the algorithm, as well as for the number of moves made by each disk.
Denoting the total number of moves made by the optimal algorithms of the RBB and RRB puzzles as and , then referring to the solving algorithm listed above, it is easy to show that the following recurrence relation holds:
where use has been made of the fact that the RBB and RRB puzzles form a time reversal symmetry pair, and thus .
It is also possible to list a recursion relation for the total number of moves made by disk k, which we denote by and for the RBB and RRB algorithms respectively (note that is independent of the total number of disks n in the puzzle). Again working through the algorithms, and using the equality , it is simple to show that
From these recursive relations, it is quite simple to derive closed form expressions for and , which are given by
As can be seen, these quantities scale as 3n, in contrast to the classical ToH puzzle which scales as 2n. In fact, as shown in,[7] all variations of the MToH puzzle satisfy the asymptotic relations
with the factors s, p given by the following table:
| Puzzle Variations | s | p |
|---|---|---|
| RRB / RBB | 1/2 | 1 |
| RBN / NRB | 5/11 | 10/11 |
| RNB | 4/11 | 8/11 |
| RNN / NNB | 7/22 | 14/22 |
| NNN | 10/33 | 20/33 |
Finally, while the integer sequences generated by the expression for and are well known and listed in the Online Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences (OEIS),[8] the integer sequences generated by the other puzzle variations are far less trivial, and were not found in OEIS prior to the analysis of the MToH. These new sequences, 15 in number, are now all listed.
Markov type solution
A powerful method of analyzing the MToH puzzle (and other similar puzzles), suggested by Fred Lunnon and presented in his review of Tower puzzles variations,[4] is a matrix method.
In this method no effort is made to separate the various puzzles into independent groups whose solving algorithms depend only one on the other. Instead the solving algorithms are written in the most direct way so that algorithms of all the puzzle variations are interdependent. Once this has been done, the total number of moves (S,I,D being equal to R,B,N) for each puzzle variation can be written as follows:
Note that in contrast to the other variations and the general rule, MToH variations NNR and NBR end with the red sides of the disks facing upwards. This is a natural consequence of the destination post being colored red.
If we now define a vector
Then
and the recursion relations can be written in the following matrix form
where the Markov matrix is defined by

The equation for can now be written as
The characteristic polynomial of is given by
having the following eight roots
and eight eigenvectors such that
We can now express using the eight eigenvectors
so that
Now, since for all , it is clear that
Thus, as before we obtain the following asymptotic relation for all puzzle variations
with the factor s given by the following table:
| Puzzle Variation | s |
|---|---|
| NNN | 20/66 |
| RNN | 21/66 |
| NNR | 39/66 |
| NBR | 42/66 |
| RNB | 24/66 |
| RBN | 30/66 |
| RRB | 33/66 |
References
- Levy, Uri (2010). "The Magnetic Tower of Hanoi". arXiv:1003.0225 [math.CO].
- "Tower of Hanoi, the Hard Way". This is another variation of the ToH which relates to base 3.
- R.L. Graham; D.E. Knuth & O. Patashnik (1989). Concrete Mathematics. Addisson Wesley. p. 17.
- Lunnon, Fred. "The Tower of Hanoi and Variations". Archived from the original on 2013-09-05. Retrieved 2013-01-25.
- Cutrofello, Tom (2010). "Tower of Hanoi and Other Recursive Puzzles". Games (November 2010).
- Levy, Uri (2010). "The Magnetic Tower of Hanoi". Journal of Recreational Mathematics. 35 (3): 173.
- Levy, Uri (2010). "Magnetic Towers of Hanoi and their Optimal Solutions". arXiv:1011.3843 [math.CO].
- "The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences (OEIS)".