List of extreme points of China
This is a list of the extreme points of China, compared both globally and within the country.
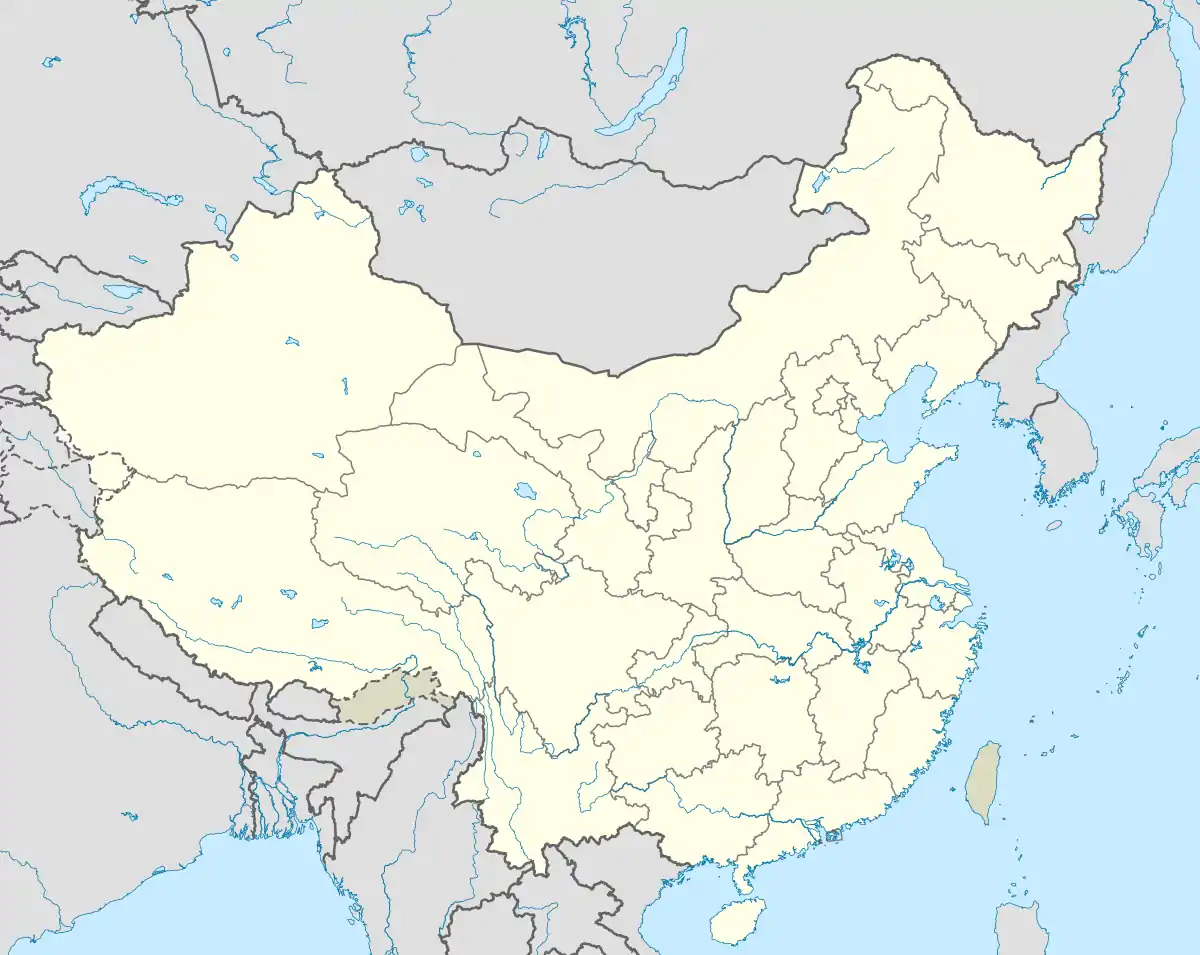
North
West
Lowest
Highest
Extreme points of China (approximate)
Global extreme points in China
Altitude
- The highest point measured from sea level is the summit of Mount Everest, Tibet Autonomous Region on the Sino-Nepalese border. While measurements of its height vary slightly, the elevation of its peak is usually given as 8,848 m (29,029 ft) above sea level.
- The lowest point in Central Asia is 154 metres (505 ft) below sea level at Ayding Lake within the Turpan Depression, near the oasis city of Turpan Pendi, Xinjiang.
Highest attainable by transportation
The following are all located partially or completely in the Tibet Autonomous Region.
- Road (mountain pass): Possibly Semo La 5,565 m (18,258 ft), depending on definition of "attainable by transportation". There may be higher motorable passes in Tibet in areas affected by lack of information and restricted access. See Khardung La, 5,359 m (17,582 ft) for more information.
- Train: Tanggula Mountain Pass, in the Tanggula Mountains, on the Qinghai–Tibet border 5,072 m (16,640 ft)
- Airport: Daocheng Yading Airport, Sichuan province 4,411 metres (14,472 ft)[1]
Highest geographical features
The following are all located partially or completely in the Tibet Autonomous Region.
- Lake: Lhagba Pool on the northeast slopes of Mount Everest, at an altitude of 6,368 metres (20,892 ft).[2]
- River: One candidate from among many possibilities is the Ating Ho (meaning Ho river), which flows into the Aong Tso (Hagung Tso), a large lake about 6,100 metres (20,013 ft) at its source at 32°49′30″N 81°03′45″E. A very large high river is the Yarlung Tsangpo, the Tibetan section of the Brahmaputra River, whose main stem, the Maquan River has its source at about 6,020 metres (19,751 ft) above sea level at 30°48′59″N 82°42′45″E.[3]
- Island: There are a number of islands in the Orba Co lake, which is located at an altitude of 5,209 metres (17,090 ft).[4]
Remoteness
- The Eurasian pole of inaccessibility, the point on land farthest from any ocean, is located approximately 320 km (199 mi) from Ürümqi, Xinjiang, at 46°16.8′N 86°40.2′E (in the Dzoosotoyn Elisen Desert). This position is at a distance of approximately 2,648 km (1,645 mi) from the nearest coastline.
Country extreme points
Altitude
- Maximum: Mount Everest, Tibet, 8,849.87 m (29,035.0 ft) 27°59′17″N 86°55′31″E
- Minimal: Ayding Lake, Turfan Depression, Xinjiang, −154 m (−505 ft) 42.78°N 89.34°E
Continent
- North: Mohe County, Heilongjiang 53°33′N 123°16′E
- South: Hai'an, Guangdong 20°14′N 109°56′E
- West: Akto County, Xinjiang south-west of Ulugqat, on the China–Tajikistan border 39°22′48″N 73°30′00″E north of the Markansu River (瑪爾坎蘇河)
- East: Fuyuan County, Heilongjiang, on the west bank of the Ussuri River 47°44′09″N 134°46′08″E
Totality of the territory
- North: Mohe County, Heilongjiang 53°33′39″N 123°16′20″E
- South: Hainan's southernmost tip (18°09′33″N 109°34′27″E, south-east of Sanya) is the undisputed southernmost point. James Shoal (3°58′26″N 112°20′56″E) is the claimed southernmost point. Cuarteron Reef (8°51′50″N 112°49′40″E) is the Chinese southernmost point with effective control.
- West: Akto County, Xinjiang south-west of Ulugqat, on the China–Tajikistan border 39°22′48″N 73°30′00″E north of the Markansu River (瑪爾坎蘇河)
- East: Fuyuan County, Heilongjiang, on the west bank of the Ussuri River 47°44′09″N 134°46′08″E
Railway stations
- North: Mohe railway station, Heilongjiang 52°59′14″N 122°30′01″E
- South: Old Sanya railway station, Hainan (abandoned) 18°15′09″N 109°29′51″E
- West: Kashgar railway station, Xinjiang 39°29′31″N 76°02′47″E
- East: Fuyuan railway station On 19 December 2012, China extended rail service eastwards to Fuyuan, 17 hours northeast of Harbin.
See also
References
- "China opens world's highest civilian airport". Reuters. 16 September 2013. Retrieved 2013-09-16.
- "The Highest Lake in the World". Retrieved 2007-09-07.
- "The Mystery of World's highest river and largest Canyon". Archived from the original on September 21, 2007. Retrieved 2007-09-07.
- "Island Superlatives". Retrieved 2007-09-07.
- Xie Yuzhong 解玉忠 (2003). 地名中的新疆 (in Chinese). Ürümqi: 新疆人民出版社. p. 196. ISBN 7-228-08004-1.
斯木哈纳 Simhana 我国最西部村庄。
- Wen Hao 文昊, ed. (January 2007). 新疆地名与传说故事. 走进新疆丛书 (in Chinese). Ürümqi: 新疆美术摄影出版社, 新疆电子音像出版社. p. 46. ISBN 978-7-80744-012-3.
斯木哈纳 我国最西部村庄。
- 1997年乌恰县行政区划 [1997 Ulugqat County Administrative Divisions] (in Chinese). XZQH.org. 31 December 2010. Archived from the original on 15 October 2017. Retrieved 10 October 2020.
吉根乡 位于县城西94.5千米。是中国最西部的一个乡。
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.