List of Korg products
.jpg.webp)
Prototype No.1 (1970)
.jpg.webp)
KORGUE (1972)
.jpg.webp)
Donca-Matic DA-20 (1963)
.jpg.webp)
MAXI KORG 800DV (1974)
PE-1000 (1976)

Λ (Lambda), Polysix, and Trident
1960s
- 1963 – Donca-Matic DA-20: Rhythm machine, first product.[1]
- 1966 – Donca-Matic DE-20: Fully electronic rhythm machine.[1]
- 1967 – Korg Mini Pops: Fully electronic rhythm machine.[2]
1970s
- 1970 – Korg Prototype No.1: Synthesizer organ prototype, developed by Fumio Mieda [3]
- 1972 – Korg KORGUE: Synthesizer organ product [4]
- 1973 – Korg miniKORG 700: First Korg synthesizer [5]
- 1974 – Korg miniKORG 700S: 2VCO version of miniKORG 700 [5][6]
- 1974 – Korg MAXI KORG 800DV: Dual voice synthesizer [7]
- 1975 – Korg 900PS: Preset synthesizer [8]
- 1975 – Korg SB-100: Bass keyboard synthesizer [8]
- 1975 – Korg WT-10: World's first hand-held electronic tuner
- 1976 – Korg PE-2000/PE-1000: Full polyphonic preset synthesizers [9]
- 1977 – Korg 770: Successor of Korg 700S (2VCO + Ring modulator).[10]
- 1977 – Korg M-500 Micro Preset: Preset synthesizer
- 1977 – Korg PS-3100/PS-3200/PS-3300: World's first full polyphonic patchable synthesizers
 PS-3300 (1977)
PS-3300 (1977) - 1978 – MS-10/MS-20/MS-50/SQ-10: MS series semi-modular synthesizer system
- 1978 – Korg VC-10 Vocoder
- 1979~80 – Korg Σ (Sigma),[11] Λ (Lambda), Δ (Delta) [12]
1980s
.jpg.webp)
CX-3 classic (1980)
MS-20 (1978)

VC-10 (1978)
- 1980 – Korg CX-3: One of the first Hammond B-3 clonewheel organs. It earned especially high marks for its authentic simulation of the B-3's Leslie rotating speaker, a nearly inseparable part of the original instrument's sound. An updated model called the New CX-3 was released in 2000, and uses sample-based technology, as opposed to the original's analog emulation. Both incarnations of the instrument feature a double-manual version called the BX-3. The first-generation models also included an output for the instrument to hook up to a real Leslie speaker.
- 1980 – Korg Trident: At the time of its release, the Trident was the flagship of Korg's lineup. It was divided into three distinct sections – polysynth, brass and strings – and featured an on-board flanger, a rarity for any synth at the time. The Trident was capable of eight notes of polyphony, and featured a 16-program memory.[13] An upgraded version became available in 1982.[14]

Polysix (1981)

Mono/Poly (1981)

Poly-61 (1982)
- 1981 – The Korg Polysix is a 61-key, six-voice programmable synthesizer. It was released to compete with Roland's Juno-6 synth, and both keyboards shared similar features, such as a built-in chorus unit and an arpeggiator. However, the Polysix offered memory for patch storage, and its chorus unit was a fully-fledged analog delay unit capable of phaser and "ensemble" effects. The instrument was recreated in a virtual version, the PolysixEX for Korg's Legacy Collection, and is also available as an add-on for the OASYS synth. It is also one of the included synth engines with the Kronos line of synths.
- 1981 – Korg Mono/Poly
- 1982 – Korg KPR-77: Analog drum machine.[15]
- 1982 – Korg Poly-61: The successor of the Polysix with digitally controlled analog oscillators; Korg's first "knobless" synthesizer. Shortly before it was discontinued, a MIDI version known as the Poly-61M was released.
- 1983 – Korg Poly-800: The first fully programmable synthesizer that sold for less than $1000, notable for using digitally controlled analog oscillators and sharing a single filter for all eight voices. The second-generation Mk II model added a digital delay section. Was also released in a module version, the EX-800.
- 1983 – The Korg SAS-20 was Korg's first arranger keyboard. A built-in computer analyzed the melody played on the keyboard, and generated a complex accompaniment. This was the world's first auto-accompaniment function of this kind added to a keyboard. Also, a more traditional chord recognition system was included.
- 1984 – Korg RK-100: MIDI remote keyboard/keytar

DW-8000 (1985)
- 1985 – Korg MR-16: PCM-based digital drum machine, with dedicated outputs for each drum voice. It has been used by Aphex Twin[16]
- 1985 – Korg DW-6000: Eight-voice polyphonic, user selected two digital waveforms out of 8 total. Used an analog filter.
- 1985 – Korg DW-8000: Eight-voice polyphonic, user selected two digital waveforms out of 16 total. Used an analog filter. Was also released in a rack-mount version, the EX-8000.
- 1985 – Korg DDM-110 SuperDrums and Korg DDM-220 SuperPercussion: Low-cost digital drum machines[17]
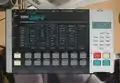
DDD-1 (1986)

DSS-1 (1986)
- 1986 – Korg DSS-1: Korg's first sampling keyboard with two oscillators per voice (eight voices) and superb filters. Offered additive synthesis, waveform drawing and effects, with superb analog filters.
- 1986 – Korg DDD-1: Sampling drum machine.[18]
- 1986 – Korg DVP-1: Vocoder, Pitch Shifter, Harmonizer, and Digital Synth Sound Module. Three-space rack unit.
- 1987 – Korg DS-8: Expandable FM synthesizer. This synthesizer were powered by Yamaha's second-generation 4-operator FM engine
- 1987 – Korg DSS-1 Sound Library: sound cards for Korg DSS-1
- 1987 – Korg DSM-1 is the rack module of DSS-1. Offered additive synthesis, waveform drawing and effects.
Total: 16 voices, single oscillator, doubled RAM from DSS-1, also superb analog filters. - 1987 – Korg 707: Expandable FM synthesizer. This synthesizer were powered by Yamaha's second-generation 4-operator FM engine[19]

M1 (1988)
- 1988 - DRM-1. 16 bits. Drums station with 8 triggers and 8 individual outputs and L-R. 2 bd, 2 snare, 1 rimshot, chs, plates and congas.
- 1988 – Korg M1: PCM sample based dual oscillator synth engine, with built-in effects, sequencer and drum machine, the M1 introduced many to the concept of a music workstation, a keyboard that could handle live performance, MIDI, sequencing, expandable sound banks, effects, and more in a single package. The best-selling synthesizer of all time (with 250,000 units sold worldwide, as a single model). Incredibly realistic sounds made possible by using rich samples of acoustic and electric instruments as initial sound source (vs.simple sine, saw and square waves used before) and applying full synthesizer processing chain (filters, modulators, effects, etc.).[20]
- 1989 – Korg T series (T1/T2/T3): Some improvements over the M1 with added features.
1990s

Wavestation (1990)
Wavestation A/D (1991)
Wavestation SR (1991)

01/W (1991)

X3 (1993)
- 1990 – Korg Wavestation: Vector synthesis and advanced Wave sequencing. Co-designed by Sequential Circuits founder Dave Smith. KORG hired Dave Smith and some of his engineers when Sequential went bankrupt in 1987.
- 1991 – Korg SoundLink SL-100C/M/S: Production quality DAW (digital audio workstation) system[21]
- 1991 – Korg 01/W: PCM rompler with more waveforms and effects than the M1. The 01-series was the first Korg workstation to employ their new Ai2 Synthesis engine. 01/w was produced in 4 model range: the 88-key 01/W ProX; the 61-key 01/W and its floppy disk-enabled cousin, 01/Wfd; 76-key 01/W-Pro and a rack-mount 01R/W. The series also started model naming system that lasted till the end of Triton line production, with standard model (61-key), Pro (76-key) and ProX (88-key with piano-style weighted keyboard).
- 1991 – Korg Wavestation EX Upgraded Wavestation with additional waves (samples) and effect programs.
- 1991 – Korg Wavestation A/D A rack version of the Wavestation EX with analog audio inputs that can be incorporated in wave sequences.
- 1991 – Korg S3 Rhythm Workstation: 8-pad sequencing drum machine.[22][23]
- 1992 – Korg Wavestation SR A 1 unit rack version of the Wavestation, emphasizing the preset sound library.
- 1993 – Korg X3 / Korg X2 / Korg X3R: Music Workstation
- 1993 – Korg i3 Interactive Music Workstation: Korg introduced its first professional arranger in 1993 with the i3 model, a more professional-level arranger that used the same AI2 sound engine as Korg's pro synthesizer line. The i3 also included a multitrack MIDI sequencer in addition to the auto-accompaniment styles and arrangements, large graphical display, improved chord recognition, and the new Backing Sequence feature, which facilitated creation of new songs based on styles.
- 1994 – Korg WAVEDRUM: DSP percussion instrument based on State Variable technology and multiple synthesis algorithms.[24]
- 1994 – Korg X5: 61-key, 32-voice AI2, 16-part multitimbral with General MIDI[25]
- 1994 – Korg 05R/W: 32-voice AI2 half-rack synth module with General Midi. Rack version of the X5.
- 1994 – Korg i2: Korg introduced the i2, an improved i3 with a 76-note keyboard and a new piano sound.
- 1995 – Korg i1: In 1995 a further improved version of i3 was introduced: the Korg i1, that included an 88-note weighted keyboard, a larger piano sample, and built-in speakers.
- 1995 – Korg i4S: The i4S (where "S" stays for "Speakers"). An i3-type keyboard with a slightly reduced feature set, but with built-in speakers.
- 1995 – Korg i5S: The i5S was a scaled-down version of the i4S, with a plastic chassis and a reduced set of features. Some new sounds and styles were added.
- 1995 – Korg i5M: An arranger module called i5M was also introduced, with specifications similar to the i5S, but with no keyboard, amplification, or joystick. Newly added traditional styles and sounds (shared with the i5S) particularly appealed to accordionists.
- 1995 – Korg ih: In 1995, the ih introduced the "ih Interactive Vocal Harmony" feature that allowed for creation of vocal harmonies based on the input from a microphone, starting from chords played live in Style mode, or recorded in a Song's track.
Prophecy (1995)

Trinity (1995)

Prophecy, Z1 (1997), and Triton
- 1995 – Korg Prophecy: One of the first physical modeling as well as virtual analog synthesizers. The Prophecy was monophonic and featured a unique cylindrical modulation wheel with integrated ribbon controller.
- 1995 – Korg Trinity: This very successful workstation was the first to feature a large touch-screen as part of the front panel user interface, a feature that continued on Korg's flagship pro synth and arranger lines, and even on some of their digital multitrack recorders.
- 1995 – Korg X5D/X5DR: X5DR is the half-rack version. It is similar to an 05R/W, but with 64-note polyphony[26] (instead of 32) and an additional set of patches.
- 1996 – Korg N364/264: Introduced RPPR (Realtime Phrase and Pattern Repeat)
- 1996/97 – Korg Soundlink Digital Recording System: consists of 168RC 8-bus digital console (1996),[27] 880 D/A & 880 A/D converter, 1212 I/O card (1997),[28] RM8 reference monitor (designed by Boston Acoustics), Trinity Pro X (HDR option), etc .[29]

880 D/A & 880 A/D ADAT↔analog 8ch audio I/F
⇐ 168RC 8-bus digital console with ADAT I/F
⇐ 168RC 8-bus digital console with ADAT I/F
- 1997 – Korg Z1: The Z1 carried concepts first heard on the Prophecy further, introducing Korg's Multi-Oscillator Synthesis System (MOSS), which produced sounds via dozens of different synthesis methods, including analog modeling and physical modeling.

D8 (1997)
- 1997 – Korg D8: The D8 was a Korg's first retail model of integrated digital recording studio package, with 16 bit @ 44.1 kHz, 8 track, and stereo digital effects. Following products were: D16 (1999), D12 (2000), D1600 (2000), D1200 (2002), D32XD/D16XD (2003), D3200 (2005), and compact D4 (2005), etc.[30]
- 1997 – Korg iX300: The iX300 Interactive Music Workstation was introduced with new sounds and more than 100 styles. This model did not have built-in speakers.
- 1997 – Korg NS5R: A half-rack AI2 module with 64-note polyphony and a large LCD display. Similar to the N364, but lacking RPPR or a sequencer.
- 1998 – Korg iS40: iS40 included new sounds (among them, a new stereo piano sample), new styles (128), and several new features. Keyboard Sets allowed for immediate recalling of keyboard track settings.
- 1998 – Korg iS50: iS50 was the low cost version of iS40, with a slightly reduced feature set.
- 1998 – Korg i30: The i30 Interactive Music Workstation was introduced, claiming to be the first arranger featuring a Touch Screen Display. This model was speakerless, had 64 notes of polyphony, and more sounds than the iS40.
 NS5R (1997) |
 Triton classic (1999) |
 Triton Pro (1999) |
- 1998 – Korg TR-Rack: The TR-Rack is a 1U rack module version of the Korg Trinity. It lacks any expansion slots, but has a larger internal sample ROM than the original Trinity.
- 1998 – Korg N5: The N5 was introduced as a keyboard version of the Korg NS5R sound module[31] without expansion slot.
- 1998 – Korg N1/N1R: The N1 is an 88-key (piano-action) synthesizer. It is the expanded version of the N5 with a larger sample ROM[32] for more AI2 voices and drum kits. In addition to the Korg voices, it provides full support for GM, GS and XG. It also has a very usable arpeggiator. It provides more output ports and effects than the N5 and the built-in voice (patch and combination) editor is easier to master. The N1R is the 1U rack[33] version.
- 1999 – Korg Triton: Successor to the Korg Trinity, Korg's first keyboard to offer sampling since the DSS-1 from 1986. As a series Triton (Classic, Studio, Le, Extreme, TR, Karma, X50 and MicroX, all sharing common synth engine and features) sold over 300,000 units.
- 1999 – Korg Kaoss Pad

Kaoss Pad (1999)

Kaoss Pad 2 (2004)

Kaoss Pad 3 (2006)
.jpg.webp)
Kaoss Pad Entrancer
- 1999 – Korg Electribe: Korg's groove machines consist of acid machine, rhythm machine, and sampler, etc.

Electribe A (1999)
.jpg.webp)
Electribe R (1999)
_-_lower_resolution.jpg.webp)
Electribe S (2000)

Electribe R mk2 (2003)
.jpg.webp)
Electribe MX (2003)
.jpg.webp)
Electribe SX (2003)
- 1999 – Korg i40M: Korg introduced a successor to the i5M: the i40M module. Specifications were similar to the iS40 (obviously, with no keyboard or joystick), but included the Vocal Harmony feature as standard. Furthermore, the module included 3 different pre-programmed MIDI setups, to make connection with various instruments even easier.
- 1999 – Korg iS35: iS35 was a new version of the iS40, featuring the same specifications, and adding the Vocal Harmony feature as standard.
- 1999 – Korg iS50B: iS50B boasted the same specs as the iS50, but in a Dark Blue chassis.
- 1999 – Korg NX5R – Successor to the NS5R half-rack model. Similar, but with an additional set of XG compatible sounds added through a daughterboard.
- 1999 – Korg OASYS PCI – a DSP card that offered powerful and flexible audio synthesis, effects and audio.
- 1999 – Korg SP-100: An 88 key velocity sensitive hammer-action simulation keyboard. Not much is known but manual can be found at Manualslib.com[34]
2000s
_left_angled_1.jpg.webp) New CX-3 (2000) |
 MS-20 controller for Legacy Collection |
 MS2000 (2000) | |
 microKORG (2002) | |
MS2000B (2003) |
microKONTROL (2003) |
- 2000 – Korg CX-3: Not to be confused with Korg's CX-3 from 1979. This digital modeling organ added MIDI and many new features.
- 2000 – Korg MS2000 Analog modeling synthesizer.
- 2000 – Korg Triton Rack 2U Rackmount version of the Triton.
- 2000 – Korg Pa80: A new range of arranger from Korg was introduced in year 2000: the Pa Series. Pa80 was the first model introduced in December 2000 with the same engine as Korg's Triton series, a wide selection of highly musical Styles, a Multitasking Operating System and a Dual Sequencer design.
 Triton Studio (2001) | |
 KARMA (2001) | |
 Triton LE (2002) |
- 2001 – Korg KARMA Kay Algorithmic Realtime Music Architecture, developed by Stephen Kay, a kind of arpeggiator that was more dynamic, organic, elastic and musical than previous forms.
- 2001 – Korg Triton Studio Featuring an onboard CD-R drive
- 2001 – Korg KM Mixers: The KM-2 (Kaoss Mixer) is a DJ Mixer, with a built-in update of the original Kaoss Pad, plus a sampler.[35]
- 2002 – Korg Pa60: Similar to the Pa80, but with a reduced feature set (lacking sampling and Harmony Board compatibility).
- 2002 – Korg MicroKorg: A compact analog modeling synthesizer with built-in vocoder.
- 2002 – Korg Triton LE
- 2003 – Korg Pa1X Pro: The flagship arranger of a new pro arranger line, which marked Korg's return to professional arrangers without built-in speakers. It also marked the beginning of a factive cooperation with the studio DSP manufacturer TC-Electronic.
- 2003 – Korg MS2000B: new version of the MS2000 synthesizer with updated sound set, black metallic color scheme and dedicated vocoder mic; Korg MS2000BR: rack-mount version
- 2003 – Korg microKONTROL: portable MIDI keyboard controller
- 2004 – Korg Legacy Collection: Includes software emulations of three famous Korg synthesizers: the MS-20,[36] Polysix,[37] and the Wavestation[38]
- 2004 – Korg Pa1X: A shorter-scale version of the Pa1X, but with built-in speakers.
- 2004 – Korg Pa50: An affordable professional arranger synth with most of the features of the more expensive Pa60.
- 2004 – Korg Kaoss Pad KP2, an improved re-release of the original Kaoss Pad.
- 2004 – Korg Kaoss Pad Entrancer, an audio & visual processor version of Kaoss Pad.[39]

Triton Extreme (2004)
.jpg.webp)
Korg OASYS (2005)
TR (2006)
- 2004 – Korg Triton Extreme: The successor to the Triton, which added "Valve Force" circuitry, a real vacuum tube circuit. Nicknamed "Russian Bullet," these tubes are rumored to last a minimum of 10 years. The Triton Extreme also featured a dramatically increased ROM size: 160 MB, featuring 32 MB of all new acoustic samples.
- 2005 – Korg OASYS (Open Architecture Synthesis Studio workstation)
- 2006 – Korg Legacy Digital Edition: Includes software emulations of the Korg M1 and Wavestation synthesizers[40]
- 2006 – Korg TR: enhanced Triton Le music workstation
- 2006 – Korg RADIAS
- 2006 – Korg PadKontrol drum-trigger style MIDI controller
- 2006 – Korg D888 8-track digital recorder
- 2006 – Korg Kaoss Pad 3[41]

Korg D888 digital recorder (2006)

Radias (2006)

X50 (2006)

M3 (2007)
- 2006 – Korg MicroX compact X50,[42] half sounds from the TR, half new, with the X50's software capability
- 2006 – Korg X50 A stripped-down Korg TR with no sequencer but a software-linking editor librarian
- 2006 – Korg Pa 800 Successor of the award-winning Pa 80, but boosted with features like in the Pa1X Pro
- 2007 – Korg M3 newest flagship workstation, diverging from the famous Korg Triton line, often called a "mini-Korg OASYS"
- 2007 – Korg R3 A portable version of the RADIAS synthesizer.[43]
- 2007 – Korg mini-KP – At 4.25" x 4.5", this smallest installment of the Kaoss series products packs all the punch of its larger brethren and offers both battery and AC power.
- 2007 – Korg ZERO Mixers – Console style (Zero8) and DJ style (Zero4) mixers. Each incorporate a multi-channel FireWire audio interface and full DSP with a customizable MIDI control surface. Interfacing and performing with all types of software become seamless. Both mixers had Traktor Scratch Certification.
- 2007 – Korg KM Mixers – KM202 and KM404 are Korg's 2 and 4 channel DJ Mixers. They featured the full Korg MiniKP interface and effects, which can be applied to selected channels. 8 different EQ models (including full cut isolator), selectable by a large dial on the panel, were another unique feature.
- 2007 – Korg Kaossilator – Compact, handheld dynamic phrase synthesizer that features 100 programs including acoustic, percussion, and electronic sounds, a gate arpeggiator, 31 scale types ranging from Chromatic and Blues to Egyptian and Gypsy, and an 8 layer 8-step sequencer for producing loop-based music. Following in the footsteps of Korg's KP technology, it features a touch pad where the horizontal axis varies in pitch and the vertical in tone. Released January 2008 in the US.
.jpg.webp)
Zero4 (2007)

padKontrol (2006)

mini KP (2007)

Kaossilator (2007)

Kaossilator Pro (2009)

Wavedrum WD-X (2009)
- 2007 – Korg Pa2X Pro – Successor to Korg's previous flagship professional arranger keyboard, the Pa2X Pro featured the Double MP3 Player/Recorder, the ability to slow down and transpose MP3 files, improved 76-key keybed, a tiltable touch screen, phantom power, balanced in/out, digital audio output, and internal clock.

ToneWorks AX3B

ToneWorks AX1000G

DS-10 (2008)

nano Kontrol, nano Pad, and nano Key (2008)
- Toneworks-Guitar Effects and processors
- AX10A – Modeling Signal Processor for Acoustic Guitar
- AX1000G – Modeling Signal Processor for Acoustic Guitar
- AX1500G – Modeling Signal Processor for Guitar
- AX3000B – Modeling Signal Processor for Bass
- AX3000G – Modeling Signal Processor for Guitar(The only model in AX series still being produced)
- AX3A – Modeling Signal Processor
- AX3B – Modeling Signal Processor
- AX3G – Modeling Signal Processor
- AX5B – Modeling Signal Processor for Bass
- AX5G – Modeling Signal Processor for Guitar
- PX4A – Pandora: Acoustic Personal Multi-Effect Processor
- PX4D – Pandora: Personal Multi-Effect Processor

M50 (2008)

SV-1 (2009)

microKORG XL (2009)

microSAMPLER (2009)
 |
|
| MR-2000S DSD 1bit Studio Recorder (2009) |
- 2008 – Korg DS-10 – Music program for the Nintendo DS.
- 2008 – Korg M50[44] – Music workstation
- 2008 – Korg Nano Series – Slim-line controllers (nanoPad, nanoKey and nanoKontrol) (Used by Distortion in the studio)
- 2008 – Korg Pa500 – After the success of Pa50, the Pa500 was introduced, with a completely redesigned user interface. considerably improving in the interface design.
- 2008 – Korg Pa588 – During year 2008, Korg introduced Pa588, a cross-over of an arranger (the acclaimed Pa500) and a digital stage piano, with the 88-note graded-weighted RH3 keyboard, built-in speakers, and a piano sample. It came with piano stand included, and featured Pa-Series compatibility.
- 2009 – Korg microKORG XL – An updated microKORG featuring the MMT (Multi Modeling Technology) sound engine as well as effects processors from their KAOSS line products.
- 2009 – Korg microSampler – A mini key dedicated sampler.[45]
- 2009 – Korg Pa50SD – The Pa50 lost the old floppy disk in favour of a SD Card media.
- 2009 – Korg SV-1 – Retro looking stage piano – available in 73 or 88 key versions.
2010s

monotron (2010)

monotribe (2011)

Sound on Sound (2010)
- 2010 – Korg Kaossilator Pro – An updated version of the KO-1, including external sampling, midi control, SD card and USB support contained in a bulkier, KP3-esque chassis.
- 2010 – Korg PS60 – Performance Synthesizer designed for the gigging musician.
- 2010 – Korg Microstation – Continuing with the "micro" series Korg releases a workstation with the traditional mini keys.[46]
- 2010 – Korg Monotron – A small analogue ribbon synthesizer that is capable of running audio through it using on board filters based on the Korg MS-20.[47]
- 2010 – Korg MP10Pro – Professional Media Player
- 2010 – Korg iElectribe – A touch screen version of the KORG Electribe made for Apple's iPad.
- 2010 – Korg microKEY – A compact midi controller[48] featuring the same keys used on the microKORG XL.
- 2010 – Korg AW2U – A dedicated clip on ukulele tuner.
- 2010 – Korg MR2 – High resolution mobile recorder.
- 2010 – Korg MicroMetro – A tiny compact metronome that doesn't compromise on quality.
- 2010 – Korg SP170 – cheapest and smallest piano to date
- 2010 – Korg SOS (Sound on Sound) – A completely self-contained unlimited track recorder.
- 2010 – Korg iMS-20 – Like the iElectribe, a digital touch screen version of the Korg MS-20 analog synth made for the Apple iPad.
.jpg.webp)
monotron (2010), DUO & DELAY (2011)

Kronos (2011)
- 2011 – Korg Kronos – New synthesizer-workstation, a successor of the Korg OASYS.
- 2011 – Korg Wavedrum Oriental – A middle-eastern, Arabian styled version of the Wavedrum.
- 2011 – Korg PA3X – Professional Arranger Workstation.
- 2011 – Korg KAOSS PAD Quad – A new version of the KAOSS PAD that allows the user to have four simultaneous effects being used at once.
- 2011 – Korg nanoSERIES 2 – New and improved versions of the nanoKEY, nanoPAD and nanoKONTROL were released providing exactly the same function as their predecessors.
- 2011 – Korg Monotribe – An advanced version of the Monotron[49] containing more features that are usually referenced to the Electribe series therefore dubbing its name.
- 2011 – Korg Wavedrum Mini – A more compact version of the popular Wavedrum, containing new features like a built in speaker for 'on-the-go' use.
- 2011 – Korg MMA130 – A powered mobile monitoring amp designed to be portable yet with no loss in quality.
- 2011 – Korg Pitch-clip – A clip on tuner.
- 2011 – Korg microARRANGER – A complete arranger keyboard with built in speakers and with KORG's signature miniature keys used on the microSTATION for example.
- 2011 – Korg Monotron Duo – A development on the Monotron Classic featuring two square wave VCOs, X-Mod and a VCF.[50]
- 2011 – Korg Monotron Delay – A development on the Monotron Classic featuring one saw tooth VCO an LFO with two wave shapes, a VCF and delay.[50]
- 2012 – Korg Kaossilator 2 – The successor to the Kaossilator and the Kaossilator Pro. Introduced at NAMM 2012, the Kaossilator 2 features a redesigned pocket sized body and a small OEL display.

Kronos X (2012)
- 2012 – Korg Kronos X – An expanded version of the already powerful Kronos workstation.
- 2012 – Korg microKEY 25 and 61[48] – Alternative sized options to the portable midi controller introduced after the original model.
- 2012 – Korg TM-50 – A tuner and metronome (hence 'TM') combi model.

Korg Krome (2012)
- 2012 – Korg Krome – A mid-price workstation with sounds derived from the Kronos.
- 2012 – Colour Options – Alternative colour versions were made available for some of Korg's existing products including the microKORG, microKORG XL and microKEY.
- 2012 – Korg microKORG XL+ - An updated version of the popular microKORG XL containing new and classic sounds from Korg's previous keyboards.
- 2012 – Korg PA600 and PA600QT – Mid-price arranger keyboards.PA600QT is quarter tone version with oriental program.
- 2012 – Korg TMR-50 – Portable tuner, metronome and recorder.

MS-20 mini (2013) on KingKORG (2013)
- 2013 – Korg MS-20 mini – A faithful analog recreation of the original MS-20 in a slightly smaller physical package.[51]
- 2013 – Korg KingKORG – A 61-key virtual analog synthesizer[52]
- 2013 – Korg SP-280 – Digital piano
- 2013 – Korg Wavedrum Global Edition – Improved usability, new soundsets and better sounding existing soundsets[53]
- 2013 – Korg KP3+ – Updated features and effects based on the original KP3
- 2013 – Korg Kaossilator Pro+ - Additional sounds including new drum kits as well as the original sets
.jpg.webp)
KR mini Korg Rhythm (2013)
- 2013 – KR mini Korg Rhythm – compact rhythm machine with a built-in speaker, battery powered
- 2013 – Korg TM-50C – Combo – Tuner Metronome plus a contact microphone
- 2013 – Korg pitchblack – Polyphonic tuner
- 2013 – Korg CM-200 – Contact microphone designed especially for tuners
- 2013 – Korg HeadTune – Clip on tuner for Guitar / Clip on tuner for Bass / Clip on tuner for Ukulele
- 2013 – Korg M01D – Music program for Nintendo 3DS[54]
- 2013 – Korg PA900 – Arranger.

volca beats, bass, keys (2013)
- 2013 – Korg Volca Series (Volca Keys, Volca Bass, Volca Beats) – True-analog synthesizers with built-in sequencers.[55][56]
.jpg.webp)
KROSS (2013)

RK-100S (2014)
- 2013 – Korg Kross – A mobile synthesizer keyboard / Music Workstation.
- 2013 – Korg Pandora Stomp[57] – A "stompbox" version of the Korg Pandora Mini multi-effects unit for guitar & bass, also incorporating a Korg pitchblack tuner.
- Korg MS-20 Kit - a full-size replica of the classic Korg MS-20, including selectable filter circuitry from both revisions of the original model. Assembly required.
- 2014 – Korg Pa300 – Entry Level Compact Sized Professional Arranger.
- 2014 – Korg Gadget – iPad DAW app.
- 2014 – Korg Pa3X Le – A professional arranger.
- 2014 – Korg Electribe (sampler) – A music production station.
- 2014 – Korg Mini Kaoss Pad 2S – A dynamic effects processor.
- 2014 – Korg Volca Sample – A digital sample sequencer.[58]
- 2014 – Korg RK-100S – MIDI remote keyboard (keytar)
- 2014 – Korg Kronos 2 – Update to the Korg Kronos/Kronos X.
- 2014 – Korg DSN-12 – music creation software for the Nintendo 3DS developed with Japanese developer Detune[59]

Korg ARP Odyssey (2015)

MS-20M Kit + SQ-1

SQ-1step sequencer

KAOSS DJ
- 2015 – ARP Odyssey duophonic synthesizer – reissue of ARP Odyssey at 86% of the original’s size.[60]
- 2015 – Korg SQ-1 step sequencer – compact 2x8 step sequencer.
- 2015 – Korg MS-20M Kit + SQ-1 step sequencer – monophonic synthesizer module kit[61] – desktop version of Korg MS-20 Kit, with new features including: oscillator sync, FM, PWM, early/later-type filter (switchable), and CV/Gate interface supporting various specs (Hz/V, V/Oct, S-Trig, V-Trig), etc. Also SQ-1 is bundled.
- 2015 – Korg Kaoss DJ – DJ controller.
- 2015 – Korg Kaossilator 2S – Dynamic phrase synthesizer.
- 2015 – Korg Havian 30 – Home piano with arranger.
- 2015 – Korg PA4X – KORG's flagship Professional Arranger Workstation.
- 2016 – Korg Pa600MY – KORG's official Malaysia localised version of PA600 with Malay, Chinese and Indian instrument sounds and musical styles

Korg Minilogue
- 2016 – Korg Minilogue – A programmable four-voice polyphonic analog synthesizer with a built in sequencer and delay effect.
- 2016 – Korg Volca FM – three-voice polyphonic digital FM synthesizer.
- 2016 – Korg PA4X ORIENTAL – KORG's flagship Professional Arranger Workstation, from Western to Oriental: Arabic, Persian, Turkish – the Oriental version delivers. The Oriental version comes with a bonus package that includes musical resources from Middle East libraries.
- 2016 – Korg Volca Kick – Analog kick generator.
- 2016 – Korg Kronos 2 Platinum music workstation.
- 2017 – Korg Kronos 2 Gold music workstation.
- 2017 – Korg Krome Platinum music workstation.
- 2017 – Korg Monologue – monophonic analog synthesizer.
- 2017 – Korg Grandstage – multiple engines stage piano.
- 2017 – Korg PA1000 – Arranger.
- 2017 – Korg PA700 – Arranger.
- 2018 – prologue - polyphonic analog synthesizer.
- 2018 - Korg EK 50 - Entertainer Keyboard
- 2018 - Korg Volca Drum.
- 2018 - Korg Volca Modular.
- 2018 - Korg Volca Mix.
- 2018 - Korg Minilogue XD.
- 2019 - Korg Kronos SE.
- 2019 - Korg Krome EX.
- 2019 - Korg Volca Nubass.
- 2019 - Korg Nu:Tekt.
2020s
- 2020 – Korg Wavestate – wave sequencing synthesizer, a tribute to the popular Korg Wavestation.
- 2020 – Korg i3 – entry-level arranger workstation.
- 2020 – Korg EK 50 Limitless - Entertainer Keyboard
- 2020 – Korg SV-2 – significant update to the stage piano (SV-1) which first appeared in 2009 – available in 73 or 88 key versions.
- 2020 – Korg opsix - FM-synthesizer with 5-octave keyboard.
- 2020 – Korg ARP 2600FS - semi-modular synthesizer, a reproduction of their ARP 2600 synthesizer from the 70s.
- 2020 – Korg RK-100S v2 - update to the new version from 2014 of the popular keytar from the 80s.
- 2020 – Korg Kronos 2 Titanium (Limited Edition) music workstation
- 2020 – Korg Nautilus (61, 73 and 88 key) music workstation - A lower cost version of the Kronos.
References
- "Donca-Matic (1963)". Korg Museum. Korg.
- "The 14 drum machines that shaped modern music". 22 September 2016.
- "Prototype No.1 (1970)". Korg Museum. Korg.
- "KORGUE (1972)". Korg Museum. Korg.
- "miniKORG700 (1973)". Korg Museum. Korg.
- "Korg Minikorg Family (Retro)". Sound On Sound. April 1998. Archived from the original on 10 December 2014.
- "MAXI KORG 800DV (1974)". Korg Museum. Korg.
- "900PS/SB-100 (1975)". Korg Museum. Korg.
- "PE-2000/PE-1000". Korg Museum. Korg.
- "770 (1977)". Korg Museum. Korg.
- "Sigma Enigma". Sound On Sound. June 2001. Archived from the original on 8 June 2015.
- "Σ - Performing Synthesizer / Λ - Polyphonic Ensemble / Δ - String Synthesizer (1979/80)". Korg Museum. Korg.
- "Trident – Performing Keyboard (1980)". Korg Museum. Korg.
- "Korg Trident". Sound On Sound. July 1995. Archived from the original on 6 June 2015.
- "Korg KPR77". One Two Testing. January 1983. p. 44. ISSN 0265-7139. OCLC 14985145.
- "Korg Trax+Tunings for falling asleep (2017)". Korg Trax+Tunings for falling asleep. Warp.
- "In Triplet Time". Electronic Soundmaker & Computer Music. January 1985. p. 21. ISSN 0268-5264. OCLC 498742683.
- "Dynamic Digital Drums". Sound On Sound. December 1986. pp. 14–16. ISSN 0951-6816. OCLC 925234032.
- "Korg 707 Performing Synthesizer". Sound On Sound. March 1988. pp. 8–12. ISSN 0951-6816. OCLC 925234032.
- "Korg M1 Digital Synth Workstation". Sound On Sound. SOS Publications Group. Archived from the original on 2013-10-20.
- "SoundLink SL-100C/M/S (1991)". Korg Museum. Korg.
- "Korg S3". Sound On Sound. March 1998. Archived from the original on 7 June 2015.
- "Korg S3". Music Technology. Vol. 5 no. 2. January 1991. p. 48. ISSN 0957-6606. OCLC 24835173.
- "WAVEDRUM (1994)". Korg Museum. Korg.
- "Korg X5". Sound On Sound. January 1995. Archived from the original on 7 June 2015.
- "Korg X5DR". Sound On Sound. May 1995. Archived from the original on 6 June 2015.
- "Korg Soundlink DRS 168RC – Automated Digital Recording Console". Sound on Sound (December 1996).
- "Korg Soundlink DRS 1212 – Multi-channel PCI Audio I/O Card". Sound on Sound (July 1997).
- Alex Kouznetsov (Autumn 1998). "Korg Soundlink Digital Recording System". Computer Music Journal. MIT Press. 22 (3): 69–72. doi:10.2307/3681164. JSTOR 3681164.
- "D8 Digital Recording Studio (1997)". Korg Museum. Korg.
- "Korg NS5R – Synth Module". Sound on Sound (February 1997).
- "Korg N5". Sound On Sound. March 1998. Archived from the original on 7 June 2015.
- "Korg N1R". Sound On Sound. December 1998. Archived from the original on 9 June 2015.
- "KORG SP-100 USER MANUAL Pdf Download". www.manualslib.com. Retrieved 2017-09-18.
- "Korg's KM2 KAOSS is in!". Sweetwater. August 2001.
- "Korg Legacy Collection (Part 2)". Sound On Sound. July 2004. Archived from the original on 6 June 2015.
- "Korg Legacy Collection (Part 3)". Sound On Sound. August 2004. Archived from the original on 7 June 2015.
- "Korg Legacy Collection (Part 1)". Sound On Sound. June 2004. Archived from the original on 7 June 2015.
- "Korg KPE1 Kaoss Pad Entrancer – Audio-visual Processor & X-Y Controller". Sound on Sound (June 2005).
- "Korg Legacy Digital Edition". Sound On Sound. February 2006. Archived from the original on 6 June 2015.
- "Korg Kaoss Pad 3". Sound On Sound. February 2007. Archived from the original on 15 September 2014.
- "Korg Micro X". Sound On Sound. December 2006. Archived from the original on 9 June 2015.
- "Korg R3 Synth/Vocoder". Sound On Sound. September 2007. Archived from the original on 9 April 2015.
- "Korg M50". Sound On Sound. October 2008. Archived from the original on 23 March 2015.
- "Korg Microsampler". Sound On Sound. December 2009. Archived from the original on 18 September 2015.
- "Korg Microstation". Sound On Sound. September 2010. Archived from the original on 23 March 2015.
- "Korg Monotron". Sound On Sound. August 2010. Archived from the original on 1 April 2015.
- "Korg MicroKey". Sound On Sound. March 2013. Archived from the original on 7 June 2015.
- "Korg Monotribe". Sound On Sound. July 2011. Archived from the original on 6 June 2015.
- "Korg Monotron Delay & Duo". Sound On Sound. February 2012. Archived from the original on 7 June 2015.
- "Korg MS20 Mini". Sound On Sound. May 2013. Archived from the original on 23 March 2015.
- "Korg KingKorg". Sound On Sound. April 2013. Archived from the original on 7 June 2015.
- "Korg Wavedrum Global Edition". Sound On Sound. December 2013. Archived from the original on 7 June 2015.
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ucViXskL0w0
- "Korg Volca Series". Future Music. No. 271. Future Publishing. pp. 78–80, 82. ISSN 0967-0378. OCLC 1032779031.
- "Korg Volca Beats, Bass & Keys". Sound On Sound. October 2013. Archived from the original on 9 June 2015.
- "Korg Pandora Stomp". Sound On Sound. August 2014. Archived from the original on 6 June 2015.
- "Korg Volca Sample". Sound On Sound. February 2015. Retrieved 26 June 2018.
- McMahon, Conor (October 8, 2014). "KORG DSN-12 Review (3DS eShop)". Nintendo Life. Retrieved October 14, 2018.
- "Korg ARP Odyssey". Sound On Sound. April 2015. Retrieved 26 June 2018.
- "Korg MS20M & SQ1". Sound On Sound. May 2015. Retrieved 26 June 2018.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Korg. |
- Korg official home page
- Korg Museum by Korg
- Korg Page at Synthmuseum.com
- Korg Page at Wikizic.org
- Korg Kornucopia – Korg analogue synthesizer information, manuals and resources
- Information on Korg's analogue vintage instruments
- Korg Monotron & Monotribe patches, sounds and videos
- Audio interview with Mitch Colby (EVP / CMO of Korg USA) (related topic on KorgForum.com)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.


