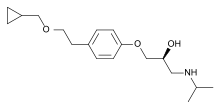
Levobetaxolol
Levobetaxolol is a drug used to lower the pressure in the eye in treating conditions such as glaucoma. It is marketed as a 0.25 or 0.5% ophthalmic solution of levobetaxolol hydrochloride under the trade name Betaxon. Levobetaxolol is a beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitor (beta blocker).
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | topical (ophthalmic) |
| ATC code |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 20 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H29NO3 |
| Molar mass | 307.434 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Indications
It is indicated for intraocular pressure reduction in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.[1]
Effect
Levobetaxolol inhibits the beta-1-adrenergic receptor. When applied topically, it reduces intra-ocular pressure (IOP) by 16-23% depending on time of day and the individual. It also has neuroprotective effects.[1] Levobetaxolol has fewer cardiovascular side effects than other beta blockers.
Contraindications and side effects
Levobetaxolol should not be used by people who have sinus bradycardia, atrioventricular block, cardiogenic shock, or overt cardiac failure. The drug has been associated with bradycardia and hypertension.
References
- Quaranta L, Turano R, Pizzolante T (June 2007). "Levobetaxolol hydrochloride: a review of its pharmacology and use in the treatment of chronic open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension". Clinical Ophthalmology. 1 (2): 93–7. PMC 2704505. PMID 19668496.
- "Betaxon New FDA Drug Approval | CenterWatch". www.centerwatch.com. Retrieved 11 April 2019.